DOI: https://doi.org/10.34069/AI/2025.86.02.8
Volume 14 - Issue 86: 90-102 / February-december, 2025
How to Cite:
Savchenko, Y., Savchenko, R., & Sokhan, M. (2025). Development of creativity in future teachers of musical disciplines. Amazonia Investiga, 14(86), 90-102. https://doi.org/10.34069/AI/2025.86.02.8
Development of creativity in future teachers of musical disciplines
Розвиток креативності майбутнього викладача музичних дисциплін
Received: December 20, 2024 Accepted: April 20, 2025
Written by:
Yuliia Savchenko
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1217-3190
Associate Professor of the Department of pop singing, Kyiv Municipal Academy of Performing and Circus Arts, Kyiv, Ukraine. WoS Researcher ID: MDT-7008-2025 - Email: yulia_sa@ukr.net
Rehina Savchenko
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4380-8777
Professor of the Department of Choral Conducting and Theory and Methodology of Music Education of Ukrainian State University named after Mykhailo Drahomanov, Kyiv, Ukraine. WoS Researcher ID: AEA-9389-2022 - Email: sarina_30@ukr.net
Maksym Sokhan
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3743-8060
Тeacher of the Department of academic and pop vocals of Borys Grinchenko Kyiv Metropolitan University, Kyiv, Ukraine. WoS Researcher ID: MDT-9161-2025 - Email: tigraalfa007@gmail.com
Abstract
The article highlights methodological innovations in the ascertaining and formative stages of research The purpose of the study is to evaluate the outcomes of an experimental study future music teachers. A specially designed choice situation serves as a pedagogical. The pedagogical tool for developing creativity in future music teachers of artistic disciplines used in this study is a specially designed choice situation. The means of achieving the desired results included diagnostics of students’ initial creativity levels, conducting an experimental test based on a system of creative tasks developed from the choice situation classifier. Statistical analysis confirmed the effectiveness of the proposed methodology. The criteria for monitoring the development of creativity in future educators were established, and the effectiveness of the methodological innovations was evaluated through tests comparing results at the initial and formative stages of the study. Received positive changes in the levels of creativity formation of future teachers of musical disciplines according to all established criteria. The system of students' creative personal qualities that contribute to the formation of their readiness for professional activity was identified and expanded.
Keywords: creativity, creative abilities, development methods, criteria and levels of development, music teacher.
Анотація
У статті висвітлено методичні інновації констатувального та формувального етапів дослідження. Мета статті – оцінити результати експериментального дослідження щодо розвитку креативності майбутніх викладачів музичних дисциплін. Педагогічним засобом розвитку креативності майбутніх фахівців у дослідженні виступає спеціально спроєктована ситуація вибору. Засобами досягнення результату з’явилися діагностика вихідного рівня креативності студентів, проведення експериментальної перевірки на базі створеної системи творчих завдань, заснованої на класифікаторі ситуації вибору. Ефективність запропонованої методики підтверджена результатами статистичної обробки експериментальних даних. Одержано позитивні зміни у рівнях сформованості креативності майбутніх викладачів музичних дисциплін за всіма встановленими критеріями. Доповнено систему креативних особистісних якостей студентів, що сприяють формуванню їх готовності до професійної діяльності.
Ключові слова: креативність, творчі здібності, умови та методика формування, критерії та рівні сформованості, викладач музичних дисциплін.
Introduction
Theoretical basis or literature review
The problem of the development of individual creativity at the present stage has been studied by Ukrainian and foreign researchers: Ivanchenko, 2017; Voitsekhivska et al., 2013;
Gorban, 2018; Grinenko, 2008; Derevyana, 2009; Drozdova, 2008; Dunaeva, 2008;
Ilyakhova, 2018; Epstein, 2003; Karpenko, 2016; Molyako, 2013; Pavlenko, 2016;
Pavlyuk, 2007; Poznyak, 2013; Renzulli, 2012; Posluszna, 2017;
Rebriy, 2012; Sahlberg, 2009; Simonton, 2017; Sysoeva, 2015; Tkachenko, 2014;
Frytsiuk, 2018; Furman & Shandruk, 2013; Hamm, 2012; Yaochen, 2013;
Shevchenko & Brodsky, 2013, etc.
The analysis of scholars' interpretations allows us to conclude that creativity is a personal quality based on the potential capabilities of each individual, the actualization of an unconscious need to be a unique personality – free, yet connected to the collective through the products of their creativity – harmoniously combining individual and socially significant interests. The works of scientists focus on exploring ways to develop individual creativity and methods for organizing creative activity, as well as addressing the development of creative abilities in educational activities. It is emphasized that creativity, as the optimal development of all available individual potentials and a general universal ability, is manifested and realized in the creative process. In the studies of scientists who reveal the features of the creative process of a teacher-musician (Aksinina, 2011; Frytsiuk, 2018; Shevchenko & Brodsky, 2013, etc.), the importance of thinking outside the box, responding quickly and flexibly to situations that are constantly changing in the process of musical activity is emphasized – making adequate decisions in a choice situation, finding unconventional ways to solve creative tasks, and unconventional approaches to the embodiment of artistic images. The issue of using the potential potential of choice in the musical educational activity of adolescent students was considered by Pan Qianyi, Regina Savchenko & Yuliia Savchenko-Shlapak, (2021). However, the problem of purposeful use of choice in musical educational activity as an active development of creativity of future specialists was not the subject of independent research. In higher education institutions, as practice shows, the development of creativity of a future teacher of musical disciplines occurs spontaneously, without systematic organization, as evidenced by Savchenko, Savchenko, Sokhan (2024).
The scientific novelty of the study lies in an attempt to fill the gap in research between the need for high-quality training of a teacher of music disciplines with a high level of creativity development and the lack of methodological developments for its formation in the system of higher music and pedagogical education. Also, the insufficient study of the possibilities of music disciplines and pedagogical conditions for their implementation in the formation of the creativity of a future specialist. The potential of the choice situation has been identified and a model for the formation of creativity of future teachers of music disciplines has been developed based on their use in educational and musical activities; criteria and indicators of the formation of creativity have been determined; pedagogical conditions for the productive use of the choice situation as a means of forming creativity of future specialists have been substantiated and experimentally confirmed.
Methodology
As a means of developing the creativity of future specialists, a choice situation in educational and musical activities was chosen. On its basis, the entire complex of the implementation system is built, where the choice situation is the core of the system, its central link. The methods and techniques of implementation are didactic games, theater technologies, role modeling, compiling repertoire lists, psychological and pedagogical training on the development of creative qualities, musical works, etc. The forms of implementation of the process of developing students' creativity based on the use of the choice situation in educational and musical activities were individual, pair, group classes. The individual form of solving tasks by students to choose from without the participation of other subjects – classmates, etc. In the pair form, there is a compromise choice of participants in the situation; at the same time, everyone who participates in the pair creative process makes their contribution, and the chosen solution is defended together. The group form is characterized by a collective solution to the problem, discussion of different options for the task, development of the ability to negotiate, the ability to communicate.
Methodological innovations included an author's lecture course on the topic of "Modern Trends in the Development of Music Education"; psychological and pedagogical training on the development of creative qualities of the individual; a competition of self-studied works "Music for Children"; diagnostic materials; a classifier of choice situations; recommendations for the teacher and the student; means of checking and assessing the level of creativity development.
The methodology for forming the creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines consists of three stages; each of which solves its own tasks for the development of students' creativity, which is reflected in the steps – situations of choice. The first stage is the initial one. The tasks of the stage include preparing students for action in the conditions of a situation of choosing an educational task and developing such creative qualities: interest, the ability to see and identify problems, imagination and fantasy, a positive attitude towards creative activity, the desire to make an independent choice. Steps-situations of choosing an educational task: information, musical material, form of its presentation, partner, style of communication with the audience, performing means, interpretation. The teacher's action at this stage is pedagogical support for the student. The second stage is the main one. The task of this stage was to actualize the students' independent actions in a situation of choice and develop such creative qualities as: purposefulness, susceptibility to new ideas, independence, having one's own opinion (argumentation of choice), readiness to choose. Steps-situations of choosing: educational task, volume of work, level of complexity, form of performance, partner, method of presenting results. The choice of material, form of presentation, style of communication, performing means and interpretation remain among the previous tasks, but their implementation requires students to make some independent decisions. At this stage, the teacher acts as a consultant, and students begin to independently manifest themselves in a situation of choice. The third stage is the final one. The tasks of the stage were the independent actions of students in a situation of choice and the development of such creative qualities as: initiative, focus on the result of educational and musical activity – the creation of a personal creative product, the presence of one's own opinion, the absence of categorical judgments, readiness and ability to choose, responsibility for making a decision. Steps-situations of choice: partner (partners), goals of the activity, topic, form of performance, the content of the activity, methods, the volume of work and method of presenting results, level of complexity, nature of activity and its types, duration of performance, form of presentation of material, style of communication, means of performance, interpretation, value choice. The teacher acts at this stage as an observer. The peculiarity of this stage is to provide students with complete freedom of action in a situation of choice and to identify their manifestations of responsibility for making a decision.
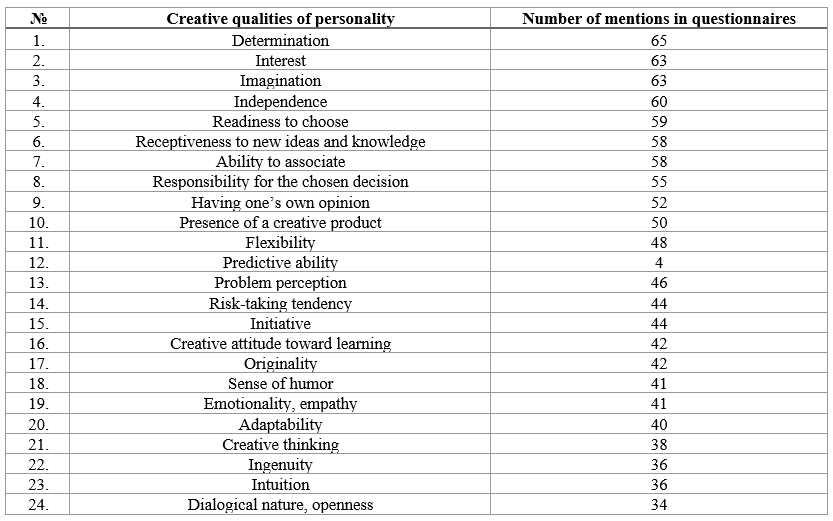
The assessment of students' creative qualities was conducted using the expert evaluation method by teachers of music disciplines, utilizing a table listing 24 creative qualities (Table 1).
Table 1.
Creative qualities of future teachers of music disciplines

In addition to the qualities listed in the table, expert teachers also noted the following traits in students: curiosity – 33, emotional openness – 32, imagination – 30, a sense of novelty and uniqueness – 29, the ability to overcome stereotypes – 28, inspiration – 25, daydreaming – 22, originality – 17, independence – 16, the ability to apply knowledge and skills in new situations – 16, a tendency toward creative doubt – 15, modesty – 10, contemplation – 7, and insight – 3.
Experimental testing of the proposed methodology lasted from 2022-2024. The results of the study were implemented in the educational process of the Faculty of Arts of the Mykhailo Dragomanov Ukrainian State University, Kryvyi Rih State Pedagogical University and Melitopol State University. The total number of participants in the experiment at all stages (confirmatory, formative, final) was 207 students.
The method of ascertaining tests was used to verify the results of the implementation of the developed methodology for the formation of creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines (Pavlenko, 2016).
Results and discussion
The ascertaining stage of the experiment determined the initial state of the development of students' creativity in educational and musical activities. Diagnostic materials in the study are presented in the form of the following methods: pedagogical observation, questionnaires (four author's questionnaires), testing, expert assessment method, competent assessment method, project method, etc. Based on the analysis of a significant number of choice situations (250 cases) and the personal pedagogical experience of Savchenko R., a classifier for educational activity choice situations was developed. This classifier is presented as a table containing components that reveal the content of the choice situation in the educational activity of future teachers of music disciplines. (see Table 2).
Table 2.
Classifier of choice situations
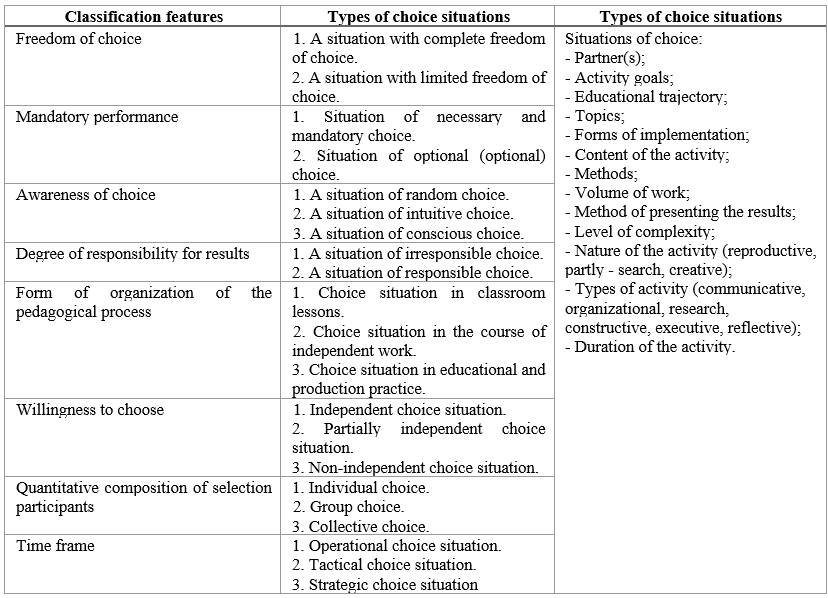
The classifier is the central link of the methodological complex, which allows to consistently build the process of developing creative personal qualities of students through situations of choice in educational activities. Diagnostic tools aimed at diagnosing the existing levels of formation of creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines included methods of observation, questionnaires, testing, a method of creating creative products including situations of real choice; situations of choosing educational tasks of different levels; situations of choosing according to certain criteria; situations of choosing an educational goal by the degree of orientation; situations of choosing according to the motivation for achieving the goal. The connection between the development of creative qualities of the personality and the situation of choice in educational and musical activities was traced.
The results of the ascertaining stage of diagnostics showed that the general level of development of creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines does not meet the requirements established by regulatory documents. This is manifested, in particular, in the passive attitude of students to choosing a non-standard situation; weak expressiveness of goals and interest in educational activities; the undeveloped sphere of cognitive personal qualities; indifferent attitude to the choice of the educational task; creation of low-quality creative product; weakly expressed ability to analyze the result of one's activity; episodic manifestations of flexibility in assessing the results of joint activity; weakly expressed ability to predict the result of choice; reluctance to take responsibility for decision-making and lack of need to transform the situation (Sahlberg, 2009; Sysoeva, 2015; Simonton, 2017). The listed factors complicate the possibility of developing creativity in educational activities. This circumstance allowed us to determine the conditions for the development of the creativity of future specialists through situations of choice in academic activities. Students with different basic training participated in the study: graduates of colleges and art schools. The results of the comparative analysis of the first diagnostic test showed that the difference in the levels of creativity of students with different basic training is insignificant, so we did not further differentiate students on this basis and evenly distributed them into 2 groups; experimental (EG) – 32 people and control (CG) – 35 people.
Discussion
The musical and pedagogical process, which is associated with the constant creative search of a teacher of musical disciplines, operates in various pedagogical situations. A special place in considering the creative nature of the activity of a future specialist is occupied by performing instrumental activity. The specifics of the development of creativity of students of the faculties of arts are directly related to the creative nature of the musical pedagogical activity: purposeful, constructive, exploratory (the content of musical education), communicative, organizational (a process of musical education), and performing (Aksinina, 2011).
The structure of students' creativity is made up of personal qualities. Artistic activity is inextricably linked with creative activity, which is clearly manifested in the performing training of students. The creativity of the personality of a teacher of musical disciplines is a condition for original pedagogical activity since it transfers it from the skill of a teacher to the field of art.
The search and use of effective techniques and methods of problem-based learning in the process of studying musical instrumental disciplines will contribute to the activation of creative potential, the development of creative personal qualities, which will ultimately affect the quality of future professional activity. One of the main achievements of this activity will be a qualitatively unique result, distinguished by novelty and originality.
The essence of the concept of "choice situation in educational activity as a means of developing students' creativity" is analyzed, which is associated with the characteristics of the content of the choice situation, its potential, which ensures the development of creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines. The classifier of the situation is presented, its types. Types, forms and means are determined. The choice situation is a multivariate and multifunctional problem situation, the solution of which requires students to have a developed ability to make an independent decision, a desire and readiness to make a choice in a non-standard situation, the manifestation of strong-willed qualities in the process of solving the situation, possession of illogical heuristic procedures – intuition, insight, the ability to go to another plane to solve the problem.
A model, criteria and indicators of the process of developing creativity of future teachers of music disciplines based on the use of the choice situation in educational activities have been developed. The model includes a description of the functions and conditions for developing the creativity of future music teachers based on the use of the choice situation in educational activities: a classifier of the choice situation in educational activities – types, forms and means of its implementation; its phased use in the process of developing creativity; levels, criteria and indicators of the development of students' creativity.
The following criteria have been identified: motivational-targeted, cognitive, activity, and reflective. Among the indicators of creativity development are the manifestation of interest in choosing an educational task (interest), the need to independently choose the goal of academic activity (purposefulness), the desire to make a choice in a non-standard situation (risk-taking); the ability to choose the necessary information (vision of the problem), the ability to navigate in styles and genres, to promptly respond to changes in the interpretation of musical material (perception of new ideas and knowledge), the ability to produce a variety of associations (development of imagination); readiness to choose an educational task (readiness to choose), independence in implementing the selected task (independence), creating an original creative product taking into account the free choice of means (availability of an innovative product); the ability to independently analyze the result of one's activity (availability of one's own opinion), the manifestation of variability in assessing the results of joint activity (flexibility), the ability to predict the consequences of choice, transform the situation (responsibility for one's choice).
The pedagogical conditions for the development of creativity of future teachers of music disciplines through situations of choice in educational activities have been substantiated and experimentally verified: 1) stimulation of a meaningful choice by the student of an active personal position in educational activities, actualization of the internal need to independently solve the assigned educational tasks and the desire for personal development in professional situations (actualized motivation affects the probability of a positive result); 2) creation of a creative environment in the educational environment of an educational institution allows the future teacher of music disciplines to act creatively, to apply the acquired knowledge in a non-standard way in the educational process; 3) implementation of a differentiated and individual approach to learning provides stimulation of the development of creativity of future specialists through situations of choice, which is built on the basis of differences in general and special abilities, interests, and psychophysiological characteristics; 4) use of the program-methodical complex for the development of creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines (course program for choice, diagnostic materials, classifier of choice situations, recommendations to the teacher and student, means of checking and assessing the level of creativity development). The listed conditions form the basis for implementing the process of developing the creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines through choice situations in educational activities.
The formative stage of experimental and research work was aimed at increasing the initial level of creativity of the future teacher of musical disciplines. Achieving the set goal was determined by solving the following tasks: testing and experimental verification of the pedagogical conditions for the process of developing students' creativity based on the use of a choice situation in educational and musical activities; implementing a program of psychological and pedagogical training for the development of creativity; carrying out analysis, systematization, generalization and testing of the results obtained. The implementation of the set tasks in the educational process took place in three stages: initial, main, and final. At each stage, local tasks were solved to develop students' creativity, which was reflected in the steps – situations of choice. The tasks of the initial stage include preparing students for action in the conditions of a situation of choosing an educational task and developing creative qualities: interest, the ability to see and identify problems, imagination and fantasy, a positive attitude towards creative activity, the desire to make an independent choice. Steps-situations of choosing an educational task: information, musical material, form of its presentation, partner, style of communication with the audience, performing means, interpretation. The teacher's actions at this stage are pedagogical support for the student. The task of the main stage was to actualize students' independent actions in a situation of choice with the development of such creative qualities as purposefulness, perception of new ideas, independence, having one's own opinion (argumentation of choice), readiness to choose. Steps-situations of choice: educational task, volume of work, level of complexity, forms of execution, partner, way of presenting results. The choice of material, presentation forms, communication style, performance means and interpretation remain among the previous tasks, but their implementation requires students to make some independent decisions. At the main stage, the teacher acts as a consultant, students begin to express themselves in a choice situation independently. The final stage's tasks are students' independent actions in a choice situation. Creative qualities such as initiative, focus on the result of educational and musical activity - the creation of a personal creative product, the presence of one's own opinion, the absence of categorical judgments, readiness and ability to choose, responsibility for making a decision are developed. Steps-situations of choice: partner (partners), goals of the activity, topic, a form of performance, the content of the activity, methods, the volume of work and method of presenting results, level of complexity, nature of the activity and its types, duration of the performance, a form of presentation of material, communication style, performance means, interpretation, value choice are developed. At the final stage, the teacher plays the role of an observer, students are given complete freedom of action in a situation of choice and revealing their manifestations of responsibility for making a decision.
The peculiarity of the formative methodology is the use of a choice situation to develop students' creativity in educational and musical activities. The choice situation is the central link on the basis of which the process of forming creativity is built. The methods and techniques for implementing the conditions for the formation of creativity are: didactic games, theater technologies, role modeling, compiling repertoire lists, psychological and pedagogical trainings on developing creative qualities, musical works, etc. The forms of implementing the process of developing students' creativity based on the use of a choice situation in educational and musical activities are individual, pair, and group classes. The individual form of solving tasks by students to choose from without the participation of other subjects – classmates, etc. In the pair form, there is a compromise choice of participants in the situation; at the same time, everyone who participates in the pair creative process contributes, and the chosen solution is defended together. The group form is characterized by a collective solution to the problem, discussion of different options for the task, development of the ability to negotiate, and the ability to communicate.
During the formative stage, the pedagogical conditions were checked. The implementation of the first condition is aimed at actualizing the motivation of students to make independent and free choices in educational and musical activities. Motivation is a set of stable motives, incentives that determine the content, direction and nature of the individual's activity, their behavior, which contributes to the disclosure of creative potential. The list of identified motives includes: interest in the problem, obtaining knowledge, the desire to independently choose a creative task, satisfaction from creative activity, the significance of one's own personality, competitiveness, interest in creating a personal original creative product (Gorban, 2018). The algorithm consists of four steps, where the first step is the choice of the type of musical activity. The second step involves the choice of educational tasks of different levels – reproductive, productive, and creative. The third step is to choose among tasks of varying complexity – those that are liked. The fourth step is the student's independent choice of a task from the three proposed (Gorban, 2018).
The creative task aimed at concentrating the motivation for choice was the compilation of individual repertoire lists by students. Students of the experimental group were asked to compile a list of 10-15 works that they would like to master, indicating the motives for their choice (musical and figurative content, originality of musical language, the opportunity to expand the musical worldview; the desire to get acquainted with this music, etc.). The identification of the hidden position of the experimental group students (the use of projection techniques) made it possible to obtain information about the motives for choice and the level of readiness of the student to choose an educational task.
Choice situations were simulated by the teacher and offered to students in the form of a didactic game, because it is in the game that the possibility of free choice is of paramount importance. The feeling of free choice constitutes its psychological basis, based on the positions of the students themselves, on their experience of the feeling of free choice in this process (Qianyi et al., 2021, p. 53). Choice situations must meet several requirements, namely: to be in the zone of proximal development of a young person and affect the sphere of his current needs and interests; to be included in the system of students' life activities. The basis for expanding freedom of choice should be the activity's success, which requires a well-thought-out mechanism for protecting the student from his mistakes.
The list of educational tasks of the project "Music in Our Life" includes the search for musical material (musical work); theoretical information (about the composer, style and genre of the work); choosing the form of written presentation of a musical work (written annotation), choosing the form of oral presentation of music (oral annotation), choosing a partner in the ensemble, emotional and expressive means, interpretation, etc. During the experimental work, it was found that students are not ready for independent choice, there is an irresponsible choice that is random in nature. Thus, out of 18 students, only 22% (4 people) consciously made their choice. Among them, Nikita P., who presented an interpretation of B. Filts. "Sad song" (Shestopalova, 2019) stood out in particular. Usually, in a situation of free choice of a musical work at the first stage, situations with limited freedom of choice were mainly used: with a small list of musical works. However, during the independent work of students, a conscious and responsible choice begins to manifest itself in the search for new, interesting musical material. Thus, student Oksana S., choosing the plays by V. Kosenko "Rain" and "Polka" (Shestopalova, 2019), pointed out the simplicity of the musical language of the work, the brightness and accessibility of musical images, which made her oral presentation interesting.
The next task – choosing a method of presenting music – also included options for a written annotation (reference and informative – "classical", "artistic" – essay, essay, poetic form) and oral (mini-lecture, story, riddle, staging of a musical fairy tale, etc.). Three options for writing a "classical" oral annotation included different levels of tasks. The first option involved listing a number of patterns, facts, phenomena, and features of choosing a given work. The second option was based on the principle of comparison, which includes determining the similarities and differences in the features of the work. The third option is search, which contains an analysis of the style of a musical work and a performance solution, which are associated with the search for material from musicological and fictio literature. The students' choice of the oral, more complex version of the annotation is associated with a developed ability to creative activity. Students of the experimental group in the oral annotation preferred a fairy tale and a riddle, which is due to the appeal to music used in pedagogical practice classes with schoolchildren.
A specific feature of the creative nature of the educational and musical activity was performing an activity, which was modeled in the "Music in our life" project. Students learned to set the goal of their activity independently, mastered search, research activities, constructed, organized and implemented the form of presentation and transmission of material using interpretation. This became possible due to the free choice from various alternatives, which stimulates the development of independence, susceptibility to new ideas, and a creative attitude to educational and musical activity. An attempt has been made to systematize creative tasks to develop students' personal creative qualities based on a choice situation. Steps – situations of choice that arise in the process of educational and musical activity have a different nature, imply a sequential solution of tasks. These are the search and selection of new musical material, new forms of its presentation, the choice of the form of written and oral annotation, the choice of performing means, interpretation, the choice of partners from the ensemble, the value choice. Tasks for the development of creativity based on the use of the choice situation are distributed over stages, at each of which the corresponding tasks are set, in turn, each task contains step-situations.
The choice situation in the educational and musical activity of the future specialist is presented in terms of its nature: in the purposeful – the choice of the goal; in the constructive – the choice of the form of presentation of musical material; in the research – the search and selection of new musical material, repertoire, information about the authors, written annotation; in the communicative – the choice of the style of communication, oral annotation; in organizational – the ability to make the right choice in non-standard situations; in musical and performing – the choice of performing means, the choice of interpretation, the choice of ensemble partners.
The idea of a "creative room" was used to create a creative environment in a higher education institution, saturated with situations of choice. The project "Music in Our Life" acted as a kind of "creative room", a creative environment created in the educational space, where students can choose for themselves what is closer and more interesting to them. Since the creative environment is the personal space of each student, which flexibly responds to his requests, aspirations, needs, we are talking about the functioning of a set of situations of choice precisely in the creative environment. In this context, we considered the project "Music in Our Life" as a pedagogical workshop, where everyone is given the opportunity to show their creative individuality, which allowed us to imagine the implementation of a differentiated and individual approach to learning as the third pedagogical condition, which provided targeted and gradual stimulation of the development of creativity of future teachers of music disciplines through situations of choice in educational reflection. The condition involves the student's transition from a no-alternative position to independent actions in a situation of choice and is one of the stimulating factors that influence the development of creative qualities and is reflected in the student's creation of a personal creative product.
A significant factor that ensures the development of the student's creativity is educational reflection, which in scientific research is understood as the individual's awareness of the limits of his knowledge and ignorance, goals, methods, results of activity, possible and current difficulties, their causes and ways to overcome them. Educational reflection participates in self-regulation mechanisms that allow students to be subjects of activity (Epstein, 2003; Karpenko, 2016). Reflective processes include: highlighting the conditions of subject activity that contradict existing knowledge and skills; fixing the boundary of knowledge and ignorance, translating ignorance into the form of an educational task; modeling the method of action, using existing ones in the arsenal and attracting new means in the course of action; establishing the correspondence of the result to the goal of activity; highlighting real and possible difficulties in the process of activity, analyzing their causes and ways to overcome them (Ivanchenko, 2017).
To ensure the process of developing students' creativity, the following methods of educational reflection were included: stopping, remembering the course of activity where difficulties arose; isolating units, methods of activity, creating a structure of activity, identifying internal contradictions and ways to achieve the best results; analyzing the results of activity, comparing the results obtained with the goals set; clarifying the personal meaning of activity, one's own educational gains; looking at one's own educational activity and its results from the outside (presenting oneself as another, external subject); comparing the obtained "real self" with the "ideal self"; correcting educational goals and the course of further activity (Rebriy, 2012). Addressing similar musical phenomena and facts creates conditions for their active comprehension and synthesis, which contributes to developing creative competence as one of the creative personal qualities. This applies to both understanding the genres of classical and contemporary music and mastering the stylistics of different musical directions. For example, observing the reaction of students in the experimental group made it possible to reveal their genuine interest in the following proposed topics: "Journey to the Country of Baroque", "Movie Music", "Jazz Plus... ", "Invitation to Dance: Variety of Genres". The study of joint creative products of activity on these topics made it possible to draw a conclusion about the possibilities of ensemble music making, which gives students a deeper understanding of music.
In the process of preparing and conducting the project "Music in Our Life", the creative abilities of students were actualized, which was expressed in the creation of new, original forms of presentation of musical and textual material, storylines in musical stagings, in work on musical images – characteristics, improvisation. For example, students of the experimental group were offered the topic "Jazz plus..." within the framework of which they independently chose a work. The degree of independence – 3 options - students left.
In order to determine the motives of students' choices, we added a questionnaire to traditional tasks. Analysis of the responses to the questionnaire "All this jazz" allowed us to identify the predominance of cognitive motives in students, which was expressed in interest in the topic of the project, and indicated the activation of cognitive components of creativity: interest in the problem, new ideas, reduction in the manifestation of inertial thinking.
There was a manifestation of interest in new, unusual forms of presentation of musical material. This was reflected in the oral annotation, for example: in the form of a riddle, mini-quiz, fairy tale, skit. The number of students who chose the first version of the annotation significantly decreased, which is associated, in our opinion, with the actualization of interest in the project topic and the possibilities of independent search.
Management of any process, in particular the development of creativity, is only possible with taking into account the changes occurring within the process itself (Molyako, 2013). Taking into account intermediate changes in the creative qualities of the personality of future specialists during the formative stage of the experiment involved constant monitoring of these changes, as well as the selection of methods and methods for correcting the process by diagnosing the development of the studied student's personality trait. The diagnostic methodology in our study was based on pedagogical observation, questionnaires (four author's questionnaires), testing (J. Kincher, N. Vishnyakova) (Pavlenko, 2016), the method of expert assessment, the method of competent assessment.
The means of checking and assessing the level of creativity development of future teachers of music disciplines through situations of choice in educational activities include analysis, comparison, systematization, generalization, questionnaires, the method of competent assessments, the method of collective expert assessment, and methods of mathematical statistics. The Mann-Whitney U criterion was used to prove the significance of the differences in the indicators of the level of creativity in the EG and CG after conducting the formative methodology (Zhluktenko et al., 2001). We put forward the following hypothesis: H0 – the level of creativity in the CG exceeds the level of creativity in the EG. Hj – the level of creativity in the CG does not exceed the level of creativity in the EG. The results of the mathematical and statistical verification of the reliability of the differences between the classes of respondents are presented by Yuliia Savchenko in Table 3.
Table 3.
Statistical test of the reliability of differences in creativity parameters between EG and CG after the formative stage of the experiment.
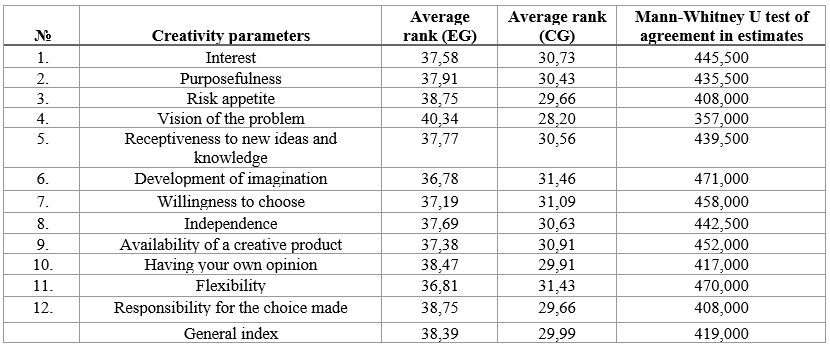
Note. Significant differences are found between the EG and the CG in the parameter "vision of the problem" (U3Mn = 357 **), "propensity to risk" (U3Mn = 408 *), "presence of one's own opinion" (U3Mn = 417 *), "responsibility for one's own choice" (U3Mn = 408 *), as well as in the parameter "general index" (U3Mn = 419.5 *). After the experimental exposure in the EG, these indicators increased significantly. Interpreting the results of the statistical test, we can assume the following: as a result of the experimental work, the most significant differences are observed in the EG respondents in the parameter "presence of one's own opinion", which in our study corresponds to the indicator "ability to analyze the result of one's activities independently". This is due to the actualization of the respondents' reflective skills as a result of the implementation of a differentiated and individual approach to learning, during which purposeful and gradual stimulation of the development of creativity of adolescent students through situations of choice in educational reflection is provided. Next are the parameters "propensity to risk" and "responsibility for one's choice", which indicate the reasonableness of the risks of future specialists in uncertain situations and the adequacy of their ability to predict the consequences of choice, and is associated with the actualization of the motivational-goal and reflective sphere of schoolchildren in the process of research and experimental work. The parameter "vision of the problem" indicates the developed ability of the student to select the necessary information during educational activities, and is a particularly significant personal quality for a teacher of musical disciplines in the modern world. It is possible to establish a certain connection in the significant differences between these indicators of the development of creativity and the situation of choice, because the ability to independently analyze the result of one's activity, the desire to make a choice in a non-standard situation, the ability to predict the consequences of choice, transform the situation, the ability to select the necessary information indicate not a set of disparate personal qualities, but a manifestation of systematicity in the development of a complex of creative qualities precisely in the process of the experiment.
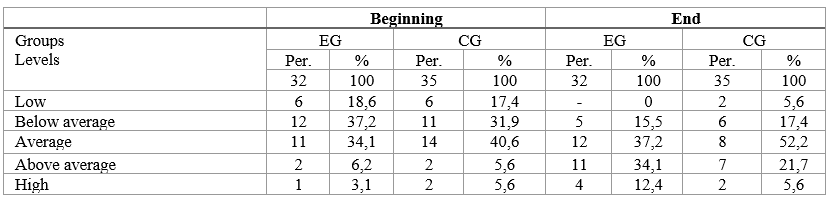
According to the study results, positive dynamics are observed not only in the EG, but also in the CG. This is due to several factors: the influence of the creative environment formed in the educational space of the educational institution; the specifics of the creative nature of educational and musical activity; a differentiated and individual approach to students. Comparing the results of the control diagnostics in the EG with the results of the CG, in which the experimental work was carried out fragmentarily, we found significant differences in the severity of changes, which is a confirmation of the feasibility of the model we proposed and the effectiveness of the conditions of the educational and methodological complex developed on its basis for the development of creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines through situations of choice in educational and musical activities. The information presented in Table 4 shows that the number of students with a level of creativity "low" and "below average" decreased, due to this there was a significant increase in the "average level" in both groups.
Table 4.
Dynamics of the development of students' creativity based on the use of a situation of choice in educational and musical activities.
As a result of modeling the process of developing the creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines based on the use of the choice situation in educational activities, the conditions were determined and methods of its implementation were identified, and the programmatic and methodological support of the studied process was developed. The process model received a specific embodiment in the step-by-step system of using the choice situation in educational activities developed by us, which includes: a lecture course on the choice of "Modern trends in the development of musical education", a psychological and pedagogical workshop on the development of creativity, compiling repertoire lists, creation, ensemble music making, a competition of a self-studied work "Music for children", a student group "Music for children" within the framework of students' research work, individual lessons in instrumental training disciplines, organization of extracurricular activities of students – festivals, creative competitions, role-playing games, theatrical events.
Conclusions
The conducted research and experimental work proved the validity of the development of creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines through the situation of choice in educational activities and confirmed the effectiveness of the developed pedagogical conditions, which was manifested in the dynamics of students' creativity levels by the end of the experimental work. The issues of creativity of future specialists and the specifics of its development in educational activities were clarified using the example of students studying at the faculties of arts. It was proved that the problem of creativity of a future teacher of musical disciplines is a manifestation of the creative nature of his work, due to the specifics of pedagogical activity, which is public in nature, is carried out in front of a certain audience and requires the ability to manage one's feelings and moods. Thus, the author's methodology for the formation of creativity of future teachers of musical disciplines was substantiated and experimentally tested. The criteria and levels of formation of this phenomenon in students in the process of musical educational activities are presented. The results of the formative experiment are analyzed and their reliability is proven.
We see the prospect of further scientific exploration in developing the structural and functional components of models for creativity formation in various types of musical activities, as well as in shaping individual strategies for independent creative activity among future teachers of musical disciplines.
Bibliographic References
Aksinina, N.M. (2011). Creative approach to training future music teachers. Bulletin of Taras Shevchenko National University of Luhansk. Pedagogical Sciences Series, 7(218), 13–18. http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/OD_2012_5_21
Bodak, V., Pantiuk, T., Pantiuk, M., & Hamerska, I. (2021). Globalization and integration of Ukrainian education as indicators of its optimization and development. Youth & market, (11-12), 6-11. https://doi.org/10.24919/2308-4634.2021.252820
Derevyana, L. (2009). Creativity as a component of professional training of future social educators. Visnyk Lviv University. Series Pedagogy, 25(4), 168–174. http://liber.onu.edu.ua/opacunicode/index.php?url=/notices/index/IdNotice:354319/Source:default
Drozdova, I. P. (2008). Development of creativity as a necessary quality of a professional's personality in the process of teaching students of the VTNZ by means of Ukrainian speech. Collection of scientific works "Pedagogical Sciences", 2(50), 108-113. https://ps.journal.kspu.edu/index.php/ps/article/view/2555
Dunaeva, O. M. (2008). Formation of pedagogical creativity of future teachers in the process of professional training (author's abstract of the dissertation ... candidate of pedagogy. sciences: 13.00.04), Vinnytsk State Pedagogical University named after Mykhayl Kotsiubynsky. Vinnytsia. https://irbis-nbuv.gov.ua/cgi-bin/irbis64r_81/cgiirbis_64.exe?Z21ID=&I21DBN=ARD&P21DBN=ARD&S21STN=1&S21REF=10&S21FMT=fullwebr&C21COM=S&S21CNR=20&S21P01=0&S21P02=0&S21P03=A=&S21COLORTERMS=1&S21STR=Дунаєва%20О.М.$
Epstein, R. (2003). Generativity theory and creativity. In M. Runco & R. S. Albert (Eds.), Theories of creativity (Rev. ed., pp. 116–140). Cresskill, NJ: Hampton Press.
Frytsiuk, V.M. (2018). Development of creativity of future teachers of musical art in the process of studying "Methods of teaching professional disciplines". Scientific notes of Vinnytsia State Pedagogical University named after Mykhailo Kotsiubynsky. Series: Pedagogy and Psychology: Collection of scientific works. Issue. Vinnytsia: Nilan LTD. P. 146-15 Scientific Notes of Vinnytsia State Pedagogical University named after Mykhailo Kotsiubynsky. Series: Pedagogy and Psychology, issue unknown, 30(1-2021), 146–150. https://acortar.link/mwPDUO
Furman, A. V., & Shandruk, S. K. (2013). Psychological features of the development of professional creativity of future specialists of the socio-humanitarian profile. In Scientific and methodological approaches to teaching management disciplines in the context of labor market requirements (pp. 32–36). Dnipropetrovsk. https://acortar.link/pu71qe
Gorban, S. I. (2018). Formation of professional competence of future artists of sacred painting using innovative technologies (dissertation ... candidate of pedagogical sciences: 13.00.04). Kremenchug National University named after Mykhailo Ostrogradskyi, Ukraine. https://uacademic.info/ua/document/0418U000296
Grinenko, I. V. (2008). Pedagogical conditions for the development of creativity of future teachers of the humanitarian profile in the process of professional training (author's abstract of dissertation ... candidate of pedagogical sciences: 13.00.04). Ternopil National pedagogical university named after V. Hnatyuk, Ukraine. https://uacademic.info/ua/document/0408U000935
Hamm, O. (2012). Theoretical foundations of the formation of creative thinking of a future teacher. Scientific Works of the IAUP, 33(2), 255–259. Access mode: https://journals.maup.com.ua/index.php/psychology/article/view/1527
Ilyakhova, M. V. (2018). Creative competence of a scientific and pedagogical worker: theoretical and methodological analysis. Pedagogy of the Formation of a Creative Personality in Higher and General Education Schools, 61(1), 70–75. http://www.pedagogy-journal.kpu.zp.ua/archive/2018/61/part_1/61-1_2018.pdf#page=70
Ivanchenko, A. (2017). Psychology of personal creativity: theoretical, methodological and applied aspects (author's abstract of the dissertation ... candidate of pedagogy. sciences 19.00.01) National Academy of Pedagogical Sciences of Ukraine H. S. Kostyuk Institute of Psychology, Kyiv, Ukraine. https://ekhnuir.karazin.ua/server/api/core/bitstreams/7f16d64c-25c1-45b7-9be0-ea78ef1656f5/content
Karpenko, N.A. (2016). Psychology of creativity. Lviv: Lviv State University of Social and Cultural Development. https://dspace.lvduvs.edu.ua/bitstream/1234567890/347/1/Карпенко%20психолог%20творчості.pdf
Molyako, V.O. (2013). Problems of functioning of creative perception in conditions of excess of information of different modality and significance. Current problems of psychology: Collection of scientific works of the G. S. Kostyuk Institute of Psychology of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, 12(16), 7-19. http://eprints.zu.edu.ua/24955/
Pavlenko, V.V. (2016). Personality creativity tests: essential characteristics and features of application. Androgogic Bulletin, (7), 219–232. http://eprints.zu.edu.ua/30379/1/%D0%9F%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BA%D0%BE.pdf
Pavlyuk, R. O. (2007). Creativity as a component of the professional training of future teachers. Rusnauka. http://www.rusnauka.com/16_NPM_2007/Pedagogica/22154.doc.htm
Posluszna, J. (2017). Psychology of art and creativity. Vol. 2. Contents & Introduction. Krakow. [in Ukrainian].
Poznyak, T.M. (2013). Development of creative abilities of the individual. Bulletin of Chernihiv National Pedagogical University. Series: Psychological Sciences, 114, 161-166. https://acortar.link/BKzQzi
Qianyi, P., Savchenko, R., & Savchenko-Shlapak, Y. (2021). Evelopment of the creativity of adolescents in learning musical activities. Innovative Solutions In Modern Science, 5(49), 52-66. DOI: 10.26886/2414-634X.5(49)2021.4
Rebriy, O.V. (2012). Modern concepts of creativity in translation. Kharkiv: V.N. Karazin KhNU. https://foreign-languages.karazin.ua/resources/a28dc3bfe2522ad80245ccdf2ad02789.pdf
Renzulli, J. S. (2012). Reexamining the role of gifted education and talent development for the 21st century: A four-part theoretical approach. Gifted Child Quarterly, 56(3), 150–159.
Sahlberg, P. (2009). The Role of Education in Promoting Creativity: Potential Barriers and Enabling Factors. Measuring Creativity, 22, 337-344.
Savchenko, R.A., Savchenko, Y.O. & Sokhan, M.O. (2024). Formation of creative competence of future teachers of music disciplines: psychological and pedagogical aspect. Successes and achievements in science, (3), 280-292. https://doi.org/10.52058/3041-1254-2024-3(3)-280-292
Shestopalova, E. (2019). Pearls of Ukrainian piano music 3rd - 4th grade. Muzichna Ukraina. [in Ukrainian]. http://nlib.org.ua/_download/0.530746001740473415/kosenko24-14.pdf
Shevchenko, I., & Brodskyi, G. (2013). Formation of the creative personality of the future teacher-musician. Scientific notes [Kirovograd State Pedagogical University named after Volodymyr Vynnychenko]. Series: Pedagogical Sciences, (123(2)), 380-384. [in Ukrainian].
Simonton, D. (2017). Big-C versus little-c creativity: Definitions, implications, and inherent educational contradictions. In R. A. Beghetto (Ed.), Creative contradictions in education (pp. 3–19). Springer. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-21924-0_1
Sysoeva, S.O. (2015). Social, psychological and pedagogical approaches to defining a creative personality. In Pedagogical creativity, mastery, professionalism in the system of training educational personnel: Achievements, searches, prospects (pp. 23–56). Kyiv: Publishing House of the National Pedagogical University named after M. P. Dragomanov. https://lib.iitta.gov.ua/id/eprint/711902/1/Guz-Sys-mon.pdf-pages-23-56.pdf
Tkachenko, L.I. (2014). Creativity and creativity: modern content. Education and Development of a Gifted Individual, (9–10), 32–35. [in Ukrainian]
Voitsekhivska, I. S., Il'eva, O. P., & Budyak, T. A. (2013). Formation of creativity of future specialists. Scientific Notes of Vinnytsia National Agrarian University. Social and Human Sciences Series, 2, 45–50. [in Ukrainian]
Yaochen, J. (2013). Development of the creative potential of future graphic design specialists in professional training. (Unpublished candidate dissertation), National Pedagogical University named after M. P. Dragomanov, Ukraine. https://npu.edu.ua/images/file/vidil_aspirant/dicer/D_26.053.01/dis_Jia_Yaochen.pdf
Zhluktenko, V. I., Nakonechny, S. I., & Savina, S. S. (2001). Probability theory and mathematical statistics: Part II. Mathematical statistics. Kyiv: KNEU. https://acortar.link/tGXX90
https://amazoniainvestiga.info/ ISSN 2322- 6307

This article presents no conflicts of interest. This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). Reproduction, distribution, and public communication of the work, as well as the creation of derivative works, are permitted provided that the original source is cited.