DOI:https://doi.org/10.34069/AI/2022.52.04.17
Innovative potential of the consumer sector of the economy: financial, economic and legal aspects
Інноваційний потенціал споживчого сектору економіки: фінансово-економічні та правові аспекти
Abstract
The authors of the article have analyzed the legal, financial and economic aspects of the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy of Ukraine. The problems that slow down the process of forming the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy have been identified. The results of theoretical and methodological research of the essence of the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy have been presented. It has been offered to consider the following the most influential financial and economic aspects for the formation of the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy: the dynamics of issuing security documents for industrial property facilities in Ukraine; volumes and sources of financing of innovation activity in Ukraine; motivation to intensify innovation activity. It has been concluded that Ukraine has created a regulatory legal base for regulating innovation activity, but it needs further improvement and adaptation to European legislation. It has been determined that the innovative capacity of education as a component of the consumer sector of the national economy is influenced by several factors, namely: the dynamics of budget funding of general secondary educational institutions and the dynamics of changing in the number of such institutions. The authors have suggested the list of resources, which are expedient to involve at acceleration of the process of the formation of innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy.
Keywords: innovative capacity, consumer sector, housing facilities stock, services sector, education, social safety, national economy, urban economics.
Анотація
У статті проаналізовано фінансово-економічні та правові аспекти інноваційного потенціалу споживчого сектору національної економіки України. Виявлено проблеми, які уповільнюють процес формування інноваційного потенціалу споживчого сектору національної економіки. Викладено результати теоретико-методологічного дослідження сутності інноваційного потенціалу споживчого сектора національної економіки. Запропоновано найбільш впливовими фінансово-економічними аспектами формування інноваційного потенціалу споживчого сектора національної економіки вважати такі: динаміка видачі охоронних документів на об’єкти промислової власності в Україні; обсяги та джерела фінансування інноваційної діяльності в Україні; мотивація активізації інноваційної діяльності. Зроблено висновок, що в Україні створена нормативно-правова база регулювання інноваційної діяльності, проте вона потребує подальшого вдосконалення та адаптації до європейського законодавства. Визначено, що на інноваційний потенціал освіти як складової частини споживчого сектору національної економіки впливають декілька чинників, а саме: динаміка обсягів бюджетного фінансування закладів загальної середньої освіти та динаміка темпів зміни кількості таких закладів. Запропоновано перелік ресурсів, які доцільно задіяти при прискоренні процесу формування інноваційного потенціалу споживчого сектору національної економіки.
Ключові слова: інноваційний потенціал, споживчий сектор, житловий фонд, сфера послуг, освіта, соціальна безпека, національна економіка, економіка міста.
Introduction
The transition to a circular model of world economic development, globalization challenges and the accelerated development of scientific and technological progress are causing changes that are taking place in all sectors of the economy, especially in the consumer sector. Innovation activity is recognized by modern economists as the driving force of economic development of all countries. The transition to a circular model of economic development requires the introduction of both technical and technological innovations and innovations in consumption, i.e. the formation of a different approach of consumers to the consumption of goods and services. Every year the consumption of goods and services by final consumers increases. Consumers in all countries of the world, and in particular in Ukraine, strive to consume quality goods and services. This requires constant improvement of technologies based on innovations. The potential of the consumer market both at the level of the world economy and at the level of the national economy is significant. Given the large annual consumption of goods and services by final consumers, the need for innovations in this segment of the economy is significant, which necessitates increased innovation activity. The concept of “innovation capacity” is generally interpreted as unused resources, in particular innovative, intellectual and human. The innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy is difficult to unambiguously measure, because it is formed by two different parts: production and consumer. On the one hand, the development of innovative capacity is facilitated by innovations introduced by industrial enterprises that produce goods and services for final consumers. On the other hand, the “prime engine” of innovation is consumer demand for increasing the comfort, convenience and safety of consumer goods and services. Thus, given the heterogeneous nature of the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy, it is advisable to study the legal, financial and economic aspects for the formation of the innovative capacity of the consumer sector on the example of the national economy of Ukraine.
Literature Review
A limited number of research papers is focused on the current financial, economic and legal aspects of the innovation capacity of the consumer sector of the economy. It is a bright confirmation that the topic of the innovation capacity of the consumer sector is still poorly researched and relevant for research. Different methodological approaches to assessing the present state of innovative capacity were suggested in the works of contemporary Ukrainian scholars and the use of different methodological tools in forecasting the level of innovative capacity was offered for the future (Loiko, 2018; Vikhlyaieva, 2018; Volodin and Chekamova, 2017; Glushenkova, 2016; Huk, Deineka and Lieksin, 2016). The authors of scientific works that conducted research on the essence of the concept of “innovative capacity” believe that the economic essence of innovative capacity constitutes the presence or combination of different resources (Volodin and Chekamova, 2017; Glushenkova, 2016; Hurochkina, 2015; Yepifanova and Hladka, 2018; Khmyzova and Sysan, 2016; Shylova and Chermoshentseva, 2012; Yankovets, 2010). A structural approach to defining the essence of the concept of “innovative capacity” has been offered in the scientific work (Vikhlyaieva, 2018). The essence of innovative capacity is defined in other scientific works as the readiness of the entity to implement a program of innovative changes (Fedulova and Kolosh, 2007). Some scholars argue that the innovative capacity is the ability of the organization to generate a high level of innovation activity (Huk, Deineka, and Lieksina, 2016). Other scholars consider the ability of the organization to implement innovations as innovative capacity (Cherby and Kryshy, 2018). A.Ya. Paulik understands innovative capacity as a resource opportunity and economic readiness to conduct research and implement innovations in the real economy sector (Paulik, 2015). The innovative capacity in quantitative terms is more often assessed by the resource approach, which is offered by scholars in their scientific works (Glushenkova, 2016; Hurochkina, 2015). Given the fact that scientific research, the results of which are already published in the scientific literature, were mostly about has focused more on methodological approaches and selected issues of assessing the state of innovation potential in the economy of the country, then it is advisable to pay attention to a more narrow area of the research, namely the financial, economic and legal aspects of innovation the potential of the consumer sector of the economy.
Methodology
Scientific articles by Ukrainian and foreign scholars, which are focused on studying the problems of innovative capacity of the national economy constitute theoretical basis of the research. The empirical basis of the article is represented by the provisions of Ukrainian legislation regulating innovation activity in Ukraine, statistics of the State Enterprise “Ukrainian Institute of Intellectual Property”, the State Statistical Service of Ukraine, the Main Department of Statistics of Kyiv and the Department of Economy and Investment of the city council.
Analysis of the problem of legal, financial and economic aspects of ensuring the process of forming the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy involves the use of several leading methodological approaches. One of the approaches is synergetic one, which allows us to combine the results of research in the legal, financial and economic spheres in order to determine the priority areas for the formation of innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy. Economic and mathematical models and methods, as well as methods of forecasting were also used in the research. The method of complex statistical analysis was used to identify tendencies in the dynamics of issuance of security documents for industrial property facilities in Ukraine for the period 2016-2020. Methods of analysis and synthesis were used in the analysis of the essence of the current regulatory base regulating innovation activity in Ukraine. The method of trend statistical analysis was used to identify tendencies in the dynamics of the distribution of budget expenditures for the organization of the educational process in general secondary educational institutions of Kyiv City. The logical method and the method of generalization were used for the analysis of scientific achievements, regulatory legal acts of Ukraine and formation of own conclusions.
Results and Discussion
The concept of “innovative capacity” has been recently used in the scientific literature (approximately in the 80s of the XXth century). Therefore, the issues of the essence and methodology for the formation and implementation of innovative capacity, methods of assessing the level of innovative capacity in quantitative and qualitative terms, methods of forecasting the level of innovative capacity are still discussed in the scientific community. Each scholar, conducting research on innovative capacity in different areas, adds new knowledge to the knowledge base on the phenomenon of innovative capacity. It should be agreed that it is impossible to develop or implement innovations without a resource base, so the availability of a resource base for the formation of innovative capacity is important. One can agree with the author (Vikhlyaieva, 2018) on the expediency of dividing the innovative capacity into separate structural components, in particular, production, financial, personnel, marketing, information, scientific, organizational and managerial. According to the specified components, it is convenient to calculate the quantitative value of each individual component of innovative capacity and, as a result, to obtain the quantitative value of the integrated indicator of innovative Capacity. In order to plan the achievement of a sufficient level of innovative capacity, it is advisable to allocate resources in accordance with functional components. N.V. Tkalenko singled out typical blocks for studying the essence of innovative capacity: block of research organizations, block of design and engineering organizations, block of production enterprises, block of service organizations and enterprises, block of information support, block of staffing (Tkalenko, 2011). This approach made it possible to choose the optimal model for the development of innovative capacity. We agree with scholars (Maslak, Bezruchko, & Maslak, 2014) who argue that the mere availability of a resource base for the formation and implementation of innovative capacity is not enough, because we still need to be able to implement and realize innovative changes. However, it’s a difficult task to calculate the quantitative indicator of such a capacity in methodological terms, to implement and realize innovative changes. We must agree with these two positions of scholars (Huk, Deineka, and Lieksina, 2016; Cherby and Kryshy, 2018), because the innovative capacity is not only the set of necessary resources, but also the ability of the organization or country to move these resources to increase innovation activity, to develop and implement innovations, to encourage scholars and employees of enterprises to create intelligent products. The author (Paulik, 2015) emphasizes that regions that maintain a sufficient level of scientific and production potential have a higher level of innovative capacity. Combining the positive aspects of the above definitions of the concept of “innovative capacity”, we suggest the following formulation. Innovative capacity is a combination of resources of the national economy or economic entities to intensify innovation activity and the development and implementation of innovations in order to achieve competitive advantages.
Thus, some scholars (Glushenkova, 2016; Hurochkina, 2015) in order to make the quantitative assessment of innovative capacity offer to apply special-purpose programme to the organization of research and innovation process, which involves the formation and implementation of innovation projects depending on set goals, but not on available resources (Volodina and Chekamova, 2017). When implementing special-purpose programme to the organization of research and innovation process, special attention should be paid to assessing the suitability of research results for commercialization. To form the innovative capacity at any hierarchical level of the national economy, the first stage is to find sources of available resources for their purposeful further use to increase the level of innovation activity. The formation of innovative capacity to the resources that form the innovative capacity at the micro level (at the level of enterprises, organizations, companies), may include the following: financial capacity of the enterprise, quality personnel, willingness and ability to be engaged in innovation activity. The formation of innovative capacity to the resources of innovative capacity at the meso level (at the level of the region or type of activity) may include the following: the presence of research potential (research institutions), the availability of production potential (industrial enterprises), the level of innovation activity, dynamics of applications and issuance of patents for industrial property facilities. The formation of innovative capacity to the resource base for the formation of innovative capacity at the macro level (at the level of national economy) depends on the totality of scientific knowledge and technologies accumulated in the country, funding for research and innovation (volume of financial investments in the national economy of Ukraine into intellectual property products in 2020 amounted to only 3.3% of the gross accumulation of fixed capital (State Statistical Service of Ukraine, 2020), the availability of specialists who carry out research and development, the compliance of the regulatory legal base with modern conditions of economic development.
To form the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy, it is advisable to use the following resources: a set of scientific knowledge and technologies accumulated both in Ukraine and in other countries related to the consumer sector of the economy; availability of specialists who carry out research and development in the field of consumer goods and services; research of the dynamics of consumer demand for consumer goods and services in order to identify perspective areas for the development and implementation of innovations. The innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the economy is a complex dynamic complementary socio-economic system. Therefore, the process of the formation and implementation of innovative capacity will be influenced by a significant number of different factors (Grigashkina and et., 2019). Due to globalization, the achievements of the world economy in terms of developed and implemented innovations in the consumer sector can be very quickly implemented in other countries. Undoubtedly, many factors influence the speed of the process of introducing innovations into the consumer sector of the national economy of Ukraine. However, the population of Ukraine due to modern means of information and communication can very quickly get information about innovations in the consumer sector of the economy. The speed of dissemination of such innovations in Ukraine will primarily depend on how relevant these innovations are today, how accessible they are to consumers and what benefits they can bring to consumers. According to the conducted research of methodological approaches to defining the economic essence of the concept of “innovative capacity” it was concluded in the works of various authors on the existence of the following areas: the availability of resources, functional components, the ability to generate high innovation activity as a basis for innovation activity, as the ability to innovate. The most negative factors influencing the process of forming the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy of Ukraine are: a significant reduction in the number of employees involved in research and development activities (for the period 2016-2020 was reduced by 35.29%), reducing the share of enterprises engaged in innovations (for the period 2016-2020 – by 1.5%, but the share of innovative enterprises in 2020 amounted to only 15.8% of the total number of enterprises in Ukraine), reducing the total expenses for innovations and research and developments (for the period 2016-2020 – by 43.12%) (State Statistical Service of Ukraine, 2020). Among the positive factors influencing the process of forming the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy of Ukraine are the following: growth of invention activity indicators of Ukrainian innovators (for the period 2016-2020 the number of registered security documents for industrial property facilities increased by 8.15 %); increase in the share of registered applications for industrial property facilities to the total volume of submitted applications (for the period 2016-2020 – by 11.47%). Taking into account the analysis of the impact of negative and positive factors on the process of innovative capacity formation and data on Ukraine’s rating according to the Global Innovation Index, a conclusion has been made on the gradual decline of innovative capacity of Ukraine’s national economy. To increase the level of innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy of Ukraine, it is advisable to focus the efforts of scholars and practitioners on maintaining and creating an innovative type of national economy that will allow Ukraine to have perspectives at the world market. To form a more capacious essence of the concept of “innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the economy”, it is advisable, in addition to resource base and scientific knowledge, to add a counter vector – it is consumer expectations and consumer needs in consumer goods and services through innovations. The offered authors’ definition of the essence of the concept of “innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the economy” looks like this. The innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the economy is a combination of modern scientific knowledge, resources of the consumer sector and identification of consumer needs to intensify innovation activity to develop and implement innovations into the consumer sector in order to achieve competitive advantages at the world market.
Despite the fact that decentralization reform has been underway in Ukraine since 2014, local budgets are not directed to innovations. Thus, little attention is paid to the intensification of innovation activity by local authorities, which is reflected in the level of funding for this area of activity (Teremetskyi and et., 2021a). Innovation activity in developed countries is financed by venture funds, which are not developed in our country. Insufficient level of financing of innovations by foreign investors can be explained by the fact that Ukraine is perceived as a country with significant risk, which according to European experts is up to 80% (Teremetskyi and et., 2021b). Ukraine’s chosen path of integration into the European Union requires the introduction of a European model of innovative development. This requires the adaptation of the legal base of Ukraine in the field of innovation activity to European legislation and its further improvement.
Modern regulatory legal provision of Ukraine in the sphere of scientific and technical, innovation activity has about 200 regulatory legal acts. The Constitution of Ukraine (Law No. 254к/96-VR, 1996), the Commercial Code of Ukraine (Law No. 436-IV, 2003), the Laws of Ukraine “On Innovation Activity” (Law No. 40-IV, 2002), “On Investment Activity”(Law No. 1560-XII, 1991), “On Priority Areas for Innovation Activity in Ukraine” (Law No. 3715-VI, 2011), "On Scientific and Scientific-Technical Activity” (Law No. 848-VIII, 2015), “On the Special Regime of Innovation Activity of Technology Parks” (Law No. 991-XIV, 1999), and other regulatory legal acts constitute the national legal base for the development of innovation activity. The listed documents establish the types of state support for innovation activity, forms of state regulation for the formation of innovative capacity of the national economy and the consumer sector in particular. The formation of the innovative capacity of the national economy in general and the consumer sector in particular is based on the protection of intellectual property rights. We agree with those scholars who argue that the legal base existing in Ukraine, which regulates legal relations in the field of intellectual property protection, mostly meets international norms and standards. Analysis of the content of regulatory documents relating to innovation activity and innovation capacity of the national economy, made it possible to draw the following conclusions (Table 1).
Table 1.
Content of motivational aspects for the formation innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the economy in regulatory legal acts of Ukraine.

Source: compiled by the authors of this article according to the Constitution of Ukraine (Law No. 254к/96-VR, 1996), the Commercial Code of Ukraine (Law No. 436-IV, 2003), the Laws of Ukraine “On Innovation Activity” (Law No. 40-IV, 2002), “On Priority Areas for Innovation Activity in Ukraine” (Law No. 3715-VI, 2011), "On Scientific and Scientific-Technical Activity” (Law No. 848-VIII, 2015) Law of Ukraine “On Protecting Consumer Rights” (Law of Ukraine, 1999).
Based on the results of the conducted analysis of the content of regulatory legal acts of Ukraine, it can be concluded that there is no clear motivational mechanism for the formation of innovative capacity of the national economy and the consumer sector in particular in the current legislation of Ukraine concerning innovation activity. A more detailed analysis of the content of regulatory legal acts of Ukraine allowed us to conclude that these documents declare the following tools to motivate the formation of innovative capacity: the property right for the results of their intellectual and creative activities is enshrined; freedom of entrepreneurial activity within the limits set by law is guaranteed; strategic priorities for the development of the national economy on innovative principles are defined; the state guarantees the integration of the national research space into the European research area; the state provides consumer rights protection. Thus, Ukraine has created a regulatory legal base for regulating innovation activity. However, it needs further improvement and adaptation to European legislation.
Education belongs to the sphere of services of the consumer sector of the national economy. Education is a driving force for further scientific achievements and innovations. The dynamic pace of modern life requires a person to receive education throughout the whole life. The first level of education, which lays the foundations of the educational and intellectual level of a human being, his creative and innovative abilities, is the level of general secondary education. Free secondary education in Ukraine is guaranteed by the Constitution of Ukraine for every child. The organization of the educational process in general secondary educational institutions is financed from the state and local budgets. General secondary educational institutions in the cities of Ukraine and the Kyiv City also receive funding from local budgets. The distribution of local budgets for the organization of the educational process in general secondary educational institutions is performed in accordance with the approved standards. Standards for the distribution of budget funds take into account the optimal amount of funds to ensure all the functions of the educational process in each individual institution of general secondary education. The organization of the educational process includes: obtaining a sufficient level of knowledge by pupils and their stay during the educational process in heated and household premises during full-time education, providing opportunities to conduct physical education classes, creative areas in specially equipped premises. In the context of distance learning, which arose in connection with the COVID-19 pandemic, general secondary educational institutions must ensure that the educational process is conducted in a new distance format. Conducting the educational process in terms of distance learning requires additional equipment for general secondary educational institutions, advanced training for teachers. There is an imbalance between the amount of tasks that the state sets for general secondary educational institutions and the amount of budgetary financial support for these tasks in terms of normative distribution of budget funds to ensure the educational process in general secondary educational institutions. In terms of distance learning, the workload of teachers has increased significantly due to the need to prepare materials that can be offered to pupils online and, of course, the expenses of general secondary educational institutions to purchase equipment for online lessons increased. The dynamics of financing general secondary educational institutions in the Kyiv City shows the annual increase in funding (Table 2).
Table 2.
Dynamics of the distribution of state expendetures for the organization of reaching and learning activities in general secondary educational institutions of the Kyiv City.
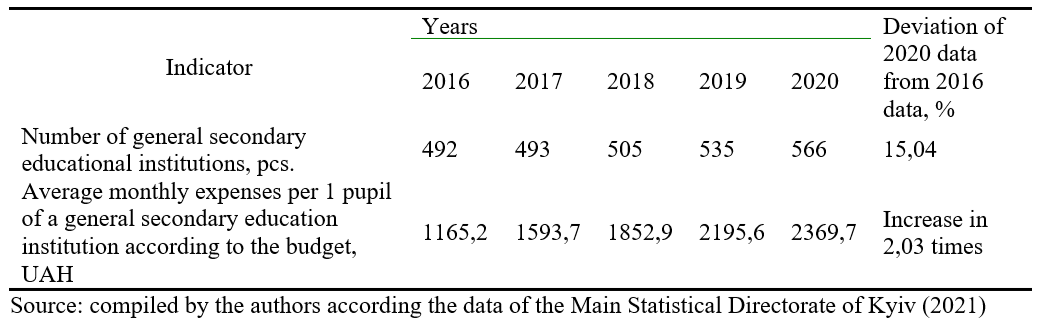
Source: compiled by the authors according the data of the Main Statistical Directorate of Kyiv (2021)
The number of general secondary educational institutions in the Kyiv City increased by 15.04% during the studied period 2016-2020. Expenditures from the budget of the Kyiv City for the period 2016-2020 increased in 3.54 times. The average monthly expenses on January 1 of a general secondary educational institution of the Kyiv City from the budget for the period from 2016 to 2020 increased by 2.03 times. If the budget expenditures in ordinary general secondary educational institutions in 2020 per 1 pupil averaged UAH 2,369 per month, the costs of financing the provision of educational services in specialized educational institutions of Kyiv are much higher and amounted UAH 10,882.44 on January 1, 2020 (Department of Economics and Investments of the executive agency of the City Council (KMDA), 2020).
Budget financial support for the organization of the educational process in general secondary educational institutions of the Kyiv City is spent to cover the basic expenditure items of general secondary educational institutions, namely: wages, single social contribution, energy fees. The annual deficit of funds needed to fully finance the organization of the educational process in various general secondary educational institutions in the Kyiv City ranges from 10% to 50%. Additional amount of UAH 70 184.4 was allocated to secondary schools in Kyiv in 2020To from the State budget in order to improve the organization of distance learning for pupils to prevent the spread of infectious diseases caused by coronavirus SARS-CoV – 2. Those funds are intended for the purchase of equipment, including laptops for teachers, other equipment to enable the implementation of the learning process in a distance format. Due to the allocation of additional funds from the State Budget In 2020, 7.93% more funds than in 2019 were spent from the city budget for each pupil of general secondary educational institutions in Kyiv. Innovations that are introduced into the educational process in educational institutions, in particular in general secondary educational institutions of Ukraine in general and the Kyiv City in particular need additional funding. Pandemic challenges require additional funds to improve the educational process in general secondary educational institutions. According to the practice, the sources of these funds can be not only budgetary.
Conclusion
Many of the economic problems that modern Ukrainian society faces are caused by the state of social ambiguity, which can be considered as a model of organization of modern Ukrainian society (Yereskova and et., 2021). Given the state of social ambiguity in society and a number of external problems, the modern development of the national economy through the development and implementation of innovations is very slow. The pace of the development and implementation of innovations into the consumer sector of the national economy is also slow, which hampers the process of forming the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the national economy.
The change in consumer preferences of the population has been happening at a faster pace in recent decades. People want to improve their living conditions and increase the level of its comfort, so there is an increase in consumption of goods and services by the population in the global and national economy. The development of the consumer sector of the national economy is dynamic due to the mutual influence of the processes of emergence and implementation of a large number of innovations. The consumer sector of the national economy is both a producer and a consumer of various types of innovations. The consumer sector can be considered as an indicator of socio-economic efficiency of innovation activity of enterprises that produce products and provide services to final customers. The innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the economy is a combination of resources of the production sector of the consumer sector, the current level of scientific knowledge and identification of consumer needs to intensify innovation and develop, implement innovations in order to achieve competitive advantages. The first stage in the process of the formation of innovative capacity at all structural and hierarchical levels of the economy is the search for sources of available resources, which in the future must be purposefully used. To form the innovative capacity of the consumer sector of the economy, it is advisable to use the following resources: a set of scientific knowledge and technologies accumulated in Ukraine and other countries related to the consumer sector of the economy; availability of specialists who carry out research and development in the field of consumer goods and services; study of the dynamics of consumer demand for consumer goods and services in order to identify perspective areas for the development and implementation of innovations.
