DOI:https://doi.org/10.34069/AI/2022.51.03.13
Тhe nature and characteristics of the evolution of the phenomenon of geopolitics
Природа та характеристики еволюції феномену геополітики
Abstract
The article has revealed the nature of the phenomenon of geopolitics as being the basis of the international relations and serving both as a scientific methodology to explain the behavior and relationships of a state with other countries in accordance with the geographical location and the interests. The concept of modern geopolitics is multifaceted, and scientists disagree regarding the definition of geopolitics as an independent science. Geopolitics is a methodology of international relations and foreign policy. Ultimately, the key to modern understanding of geopolitics is the policy and the image of a state within its geographical location, which can impact other subjects / objects of international life to ensure their national interests and national security. A number of conceptual approaches have been formed in the scientific discourse aiming to ensure the geopolitical advantage of a state. New processes and conflicts have been associated with the expansion of the Internet space and information technology. Recently, geopolitical theories have taken into account the latest tools and capabilities to influence used by leading states, including use of information, "hybrid" and "semantic" warfares. One of most urgent problems of the modern world is information warfare targeting creation of favorable conditions to gain geopolitical and geo-economic priority.
Keywords: Geopolitics, geopolitical theories, geopolitical influence, geopolitical space, international relationships.
Анотація
У статті розкрито природу феномену геополітики як основи міжнародних відносин і одночасно слугує науковою методологією для пояснення поведінки та взаємовідносин держави з іншими країнами відповідно до географічного положення та інтересів. Поняття сучасної геополітики багатогранне, і вчені розходяться щодо визначення геополітики як самостійної науки. Геополітика — це методологія міжнародних відносин і зовнішньої політики. Зрештою, ключем до сучасного розуміння геополітики є політика та імідж держави в межах її географічного положення, які можуть впливати на інших суб’єктів/об’єктів міжнародного життя для забезпечення своїх національних інтересів та національної безпеки. У науковому дискурсі сформувався ряд концептуальних підходів, спрямованих на забезпечення геополітичної переваги держави. З розширенням простору Інтернету та інформаційних технологій пов’язані нові процеси та конфлікти. Останнім часом геополітичні теорії врахували новітні інструменти та можливості впливу, які використовуються провідними державами, включаючи використання інформаційних, “гібридних” та “семантичних” війн. Однією з найактуальніших проблем сучасного світу є інформаційна війна, спрямована на створення сприятливих умов для отримання геополітичного та геоекономічного пріоритету.
Ключові слова: геополітика, геополітичні теорії, геополітичний вплив, геополітичний простір, міжнародні відносини.
Introduction
The modern world is an arena of global transformations in all spheres of human existence. It intertwines the trends of globalization, regionalization, fragmentation, integration, democratization of international relations, information technology development, rapid population growth, intensification of global terrorism, etc. Objectively, the contradictions of these phenomena impact the behavior of the international relations participants, determine the transformation of the international system, make it difficult to apprehend and forecast the development of events.
The era of globalization and, at the same time, regionalism is an example of the world development paradoxes. This era creates new challenges for the world players: the world order transformation, the interaction of states and other international actors in a multipolar world, the world leading states’ ranking decline, significant claims to the world leadership of regional centers of influence, confrontation between western and eastern civilizations, intensification of global terrorism, targeted steps of many political forces to reach imbalance of the modern world, threats to the information sphere and cyberspace, etc.
All these geopolitical challenges lead to the geopolitical balance disruption – transformational shifts, deformations and emergence of new threats to the national security. Under these circumstances, each state in the world should assess its own development risks clearly and, if necessary, adjust its actions at the international level, in accordance with its geopolitical and international status.
Returning to the logic of the global geopolitical transformation stages, it is obvious that the fundamental clarifications should be made to their dynamics. The analysis of modern geopolitical changes requires the apprehension that in the process of its evolution, moving from one stage to another, the geopolitical world order changes not only its external characteristics, but also its nature. Accordingly, the theoretical-methodological apprehension of geopolitics changes with the initial (basic) matrix of geopolitical patterns acquiring specific features.
Taking into account the above, the purpose of the article is to analyze the state and prospects of modern geopolitical trends in the context of modern transformations of a cross-border nature.
Materials and methods
In the modern world the geopolitical evolution studies are based on three groups of methods: general scientific – systemic, socio-psychological, comparative, historical, functional, institutional and others; logical – analysis and synthesis, induction and deduction, modeling; empirical – document analysis, polling, direct observation, political games theory, etc.
The systemic method used in the research of Parsons (1950) enables us to consider any sphere of public life, including geopolitics, as an integral organism being inextricably linked with the environment. The scientist stated that geopolitics reveals the interdependence between its constituent parts, elements and processes in such a way that it becomes possible to establish patterns of relations between its components. Any political system seeks self-preservation and it performs its own characteristic functions, with the most important of which being the distribution of values and resources. Thus, in the article the systematic method was used in identifying the theoretical foundations and doctrines of geopolitics as a science.
The socio-psychological method focuses on studying the dependence of individuals’ or social groups’ behavior on their place and role in the system of more global communities. This method also studies the psychological characteristics of nations, classes, small groups, etc. In the article the socio-psychological method is covered in the process of comparing the factors of geopolitical transformations in modern realities.
The comparative method involves comparing similar (the same type) life phenomena to define their common features and specificity. Owing to this method, it becomes possible to thoroughly study the experience of other nations and states. Thanks to the comparative method, the results of comparative studies of the phenomenon of geopolitics in different countries were taken into account.
The historical method requires the study of all social life phenomena in a consistent historical development, following the scheme "past - present - future". The historical method was tested in the context of highlighting the gradual formation of modern understanding of geopolitics through the prism of the genesis of state-building processes and socio-cultural changes.
The normative-value method (a moral and legal method) adds a human dimension to geopolitics, introducing a certain moral principle into it. It is thanks to the normative-value method that the moral and ethical context of modern geopolitical transformations has been revealed.
The functional method requires a detailed study of the relationships between various public life spheres, states at the global and regional levels. The functional method provided an opportunity to identify gaps in modern scientific approaches to the evolution of geopolitics.
The method of structural and functional analysis involves considering a society, a state and a union of states as a complex structure, each element of which performs specific functions. Thus, the method of structural and functional analysis allowed to substantiate methodological approaches to models of geopolitical transformation in the era of digitalization, the realities of society, integration processes of national and regional innovation development.
The institutional method is aimed at studying the institutions activities through which a political activity is carried out. The institutional method made it possible to trace the fragmentary influence of institutional transformations in different jurisdictions on the phenomenon of geopolitics.
The anthropological method determines, first of all, not social factors, but the nature of an individual and his / her social needs. The anthropological method allowed to group the factors of direct influence of human nature on the geopolitical vectors of development of modern society and states.
In theoretical terms, empirical methods are crucially important for geopolitical researches, with the method of a political play prevailing. By using only overt information this method enables to assess political sustainability of the governmental establishments. It allows to consider the state mechanisms development through two factors – informational (more transparent) and economic, the consequences of which could be more serious than they seem at the beginning of the geo-economic study. The method of political game allowed, taking into account the complex results of comparative research, to reveal the transformational challenges of the dominant understanding of geopolitics through the prism of modern realities.
Literature Review
The problematic of geopolitics gained crucial importance already with the emergence of ideas on spatial and geographical substantiation of the behavior of states in the international arena. These studies were carried out by specialists representing different scientific fields: political scientists, sociologists, economists, military analysts, demographers and others. Works on geopolitics were being done even when it did not yet exist as a separate scientific branch and was not regarded as a science. The first studies of a predominantly ideological nature were conducted by the founders of various geopolitical trends trying to methodologically substantiate the foreign policy of states based on their geographical location. These studies include the works of Criekemans (2021), Dalby (1996), Devetak et al. (2012), Dittmer and Dodds (2008), Snyder (2017), Spang (2013), Umland and Yurchuck (2020) and others.
The methodology of geopolitics was used by well-known western political scientists and experts: Ankerl (2000, p. 51-56), Brzezinski (2004), Dalby (2008), Dittmer and Dodds (2008), Huntington (2016), O’Tuathail (1996), Owens (1999), Purchla (1996).
The problems and features of regional geopolitics were studied by Criekemans (2021), Devetak et al. (2012), Haas (2008), Mazgaj (2020), Rothkopf (2009) and others.
Many scientists study the fundamental laws of geopolitics and the principles of their implementation into the public life: Rohkraèmer (1999), Brandom (2016), etc.
Results
The need to explain a number of processes ongoing in the modern developing world has brought about the trend for geopolitics to turn into a fully independent science. It is the geopolitical studies that enhance apprehension of the status of a particular state in the modern world, making it possible to more clearly apprehend the motives of the national interests, as well as to apprehend the development of multi-level relations between various international actors in the context of upholding and asserting the national interests.
The methodological apprehension of all components of geopolitical issues allows us to determine new accents and the newest approaches in the transformation of geopolitical relations, as well as to reveal more deeply the multidimensionality and specificity of the global development asymmetry, taking into account the ideological background, the initial principles and laws, theories and concepts on which the modern geopolitics is based.
Taking into consideration the aforementioned, the aim of the study is to carry out a systemic analysis of main geopolitical ideas having made an important impact on the modern methodological base, comprising studies of international systems and peculiarities of international relations implementation by the world countries at a regional and global level.
Discussion
The concept of "geopolitics" is quite multifaceted and diverse. The world scientific community has developed different approaches to define the phenomenon of geopolitics. Frequently, geopolitics is interpreted as a political doctrine stating that superpowers (powerful large states), pursuing their foreign policy, seek to create spheres of influence, to change and establish a new world order. Such an interpretation of the term primarily characterizes the ideological substance of geopolitics, which in a certain way and to a certain extent justifies the political struggle for the revision of the world as a natural phenomenon of human civilization.
At the same time, geopolitics as a science involves an analytical assessment of "balances" and "counterbalances" ensuring stability and interaction between states. Simultaneously, the term "geopolitics" can act as a kind of methodology for understanding and explaining the havior of states in the international arena, depending on their geographical location and national peculiarities. Geopolitics is a field of knowledge about the place and functioning of a state in the international community, depending on objective, primarily geographical factors.
Geopolitics is based on the concept of a national power as the main system-forming factor that determines the behavior of states in the international arena. The power indication of the geopolitical stature of the postmodern system of the world lies in the fact that it is determined primarily by the great powers, politically and economically powerful states. To a lesser extent, geopolitical changes are influenced by middle-income states, frequently upholding their national interests at the expense of small countries, economically underdeveloped, which are assigned the role of objects (observers) of the modern world.
In the last century, geopolitics was regarded as a component of international relations and a methodological basis for the analysis of these relations. However, for a long time, there have been discussions between social scientists and political scientists about what geopolitics really is: a science or an ideology.
Today geopolitics takes into account not only the interdependence of all subjects of international relations, but also the contradictions ongoing between them. Numerous scientific studies provide a semantic substantiation of the phenomenon of geopolitics as a science. This branch of knowledge focuses on a specific object – assessment of world and regional policies as interrelated processes with certain characteristics and dynamics of development.
Thus, we confirm the opinion that geopolitics is not identical to the concept of the "international relations" or the "foreign policy", although it is related to the foreign policy activity of a state or a system of states. The difference between geopolitics and public studies of the foreign policy and international relations lies in the enhanced attention to a geographical location of a state, its environment, its natural resources availability, its population and density size, ethno psychological characteristics of the population, the configuration and the state of the borders, its environmental indicators, etc.
The discussion on the need to substantiate geopolitics as an independent science and to determine the peculiarities of its development and functions in the modern world was conducted by many political scientists over the past century and it has been continuing until nowadays. This discussion began in the work of Dittmer and Dodds (2008), who upheld the classical principles of the political science. The theory was based on the concepts of a living space and it defined geopolitics as a political geography, as a scientific and methodological basis for analyzing the behavior of states in the international arena. While there were discussions in scientific circles about the distinction between "geopolitics" and "political geography", many scientists expressed an opinion about the contiguity of these concepts, about the possibility to consider them as a relationship between the fundamental and applied science.
In these discussions, the geopoliticians mainly focuses on individual political subspaces (separate regions), on possible changes in the geopolitical boundaries between the regions. The interest of geopolitical studies is also focused on issues of political influence and political ownership of certain territories, that is, on a spatially oriented foreign policy. The issue of the genesis and origins of the geopolitics of greater powers has become crucial nowadays, which is evidenced by the active discourse in the political science literature.
It is generally accepted that the geopolitical thought emerged as a theory of active external actions taken by states in accordance with their geographical location. The authors of this theory believe that the classical geopolitical thought is tied to a geographical map, it thinks by its components, and in fact, it itself is the most simplified geographical map in a political sense.
At the same time, geopolitical theorists compared geography with the trends of political processes, created the concept of a holistic, panoramic overview of the world political space. Criekemans (2019), who coined the term "geopolitics", substantiated that geopolitics was an element related to economy, demography and social policy. He viewed geopolitics as the science of a state, which acts as a life-form developing in space. One of the most important achievements of Criekemans (2019) is the conceptualization of the subject of political research and the substantiation of the structure of political science (politology), where the leading place belongs to geopolitics. The scientist developed a theory of the problem of the geographical foundations of a strong state. Of course, the idea of the power of the state in its ability to expand its territories through conquest and colonization has undergone significant changes in the modern world. However, the growing trends of interdependence of planetary political and economic processes have so far been transformed into new challenges and relate to a variety of global problems. One example of the existence of such theories is the study of a military-strategic nature, in particular, that scientific research that was carried out in the era of the bipolar world system.
Modern geopolitics deviates from the principles of traditional geopolitics inherent in the last century. It provides for the consideration of global problems and processes of globalization through the prism of foreign policy activity and the balance of state and national interests. Modern geopolitics studies the basic structures of subjects, global or strategic directions, external laws and principles of life, the functioning and evolution of the modern world society. It mainly studies the spatial aspect of international relations.
Rethinking of the methodological and conceptual apparatus of geopolitics has changed the meaning of two key categories: "space" and "borders" in the context of globalization, as well as economic and informational progress. Interpretation of geopolitics as a set of physical and social, material and moral resources of a state enables us to determine the potential which allows the state to achieve its goals in the international arena (Rohkraèmer, 1999).
The modern view of geopolitics is determined by the conflicting reality of global processes. The further development of geopolitics as a science is based on the recognition that the main object of study is the relationship between all actors in international relations, i.e. – between various elements of the system and the system as a whole.
Dittmer and Dodds (2008) focused on economic potential as an integral characteristic of geopolitics. He emphasized the balance of foreign trade, the dynamics of migration processes, cultural and social factors.
The central subject of geopolitics is a state, which is a life-form in a geographical space with its natural laws of growth and development (Devetak et al., 2012). According to the concept given above, the state passes through the essential cycles of its existence: birth – development – old age – decline. Large/powerful states, according to the geopolitician, always fight for their living space, often contrary to and at the expense of the interests (territories) of small states.
The civilizational approach to geopolitical research is the basis of a humanitarian methodology. The authors of this approach are Devetak et al. (2012), Mazgaj (2020), Rothkopf (2009) and other scientists. The debatable theory is the principle of a "clash of civilizations" done by Huntington (2016). This theory stems from geopolitical thinking about the struggle of a civilization as the meaning of existence of world civilizations and cultures.
Individual geopolitical theories and scientific directions are being actively developed by the leading scientific and analytical centers of the European Union and the United States. In particular, Hyndman (2008) pointed to the formation of a new analytical theory of geopolitics.
Nowadays, the information revolution has brought a number of new categories of geopolitical analysis, the central of which are: "information warfare", "hybrid warfare", "semantic warfare", "information weapons". One of the tasks of the modern information warfare is to create a favorable environment for any geopolitical and geo-economic operations (Huntington, 2016).
The use of the potential of geopolitics by leading world figures to increase its influence on the progress of international development is becoming increasingly active. Given the peculiarities of modern political evolution at the international level, this fact is quite justified. The rapid growth of the role of globalization, the expansion of political and cultural borders, the renewal of the range of strategic threats direct the efforts of analysts and political elites to solve complex international problems, where the main component is politics in its various manifestations: economic, informational, security, environmental, etc.
Active power players in the international arena demonstrate a high degree of applied use of geopolitical tools to achieve their national interests. Powerful actors are able to directly influence the world development through opportunities to intervene in the geopolitical order of the international relations. The national-state geopolitical potentials determine the features and dimensions of the international life. The most important aspect of success on the world stage is the ability to make competent strategic choices that guarantee productive economic and political development. Thus, the vital historical necessity and desire to maintain strategic positions serve as an incentive for foreign policy managers to understand the achievements of geopolitics, their development and use.
Given the global foreign policy of the leading actors of the international community, geopolitics is becoming one of the ways in which political leaders view the world reality. Geopolitics is becoming kind of a method to navigate in the global space from the standpoint of ensuring the national security. In this context, the geopolitical basis for the formation of external strategies is one of the fundamental levers of influence on the global system of the world development. This basis is an important element of the international security.
Strategic analysts are increasingly distinguishing in the actions of international actors a simultaneous game within several spaces. They note that unipolarity is being replaced by a world in which many different strategic interactions coexist.
Many regional poles spring up, each with its own leading and influential actors, with whom it is necessary to maintain cooperation in order to address urgent international issues.
Geo-economics also occupies a prominent place in the subject of discussions within the framework of the new paradigm of geopolitics. In the new reality economic conflicts are among top potential international contradictions. Geo-economic analysis proponents state that many traditional geopolitical concepts and theoretical constructs have become obsolete due to the globalization deployment. The border protection and the struggle for control of the geopolitical space in its classical form are meaningless. The search for a new adaptive strategy, based on economic policy, is beginning to play a major role.
Of course, geo-economic competition is a positive phenomenon that should improve the environment for continuous and fairly dynamic economic growth, and geo-economic strategy is associated with attempts to conquer the economic territory of the future. A number of experts predict the onset of the era of "real economy" – a new stage of the world development, which will be characterized by tough economic actions done by the international actors to attain their political goals. Thus, geo-economics is to play a significant role in analysing the international developments and processes.
Proponents of this conceptual choice stem from the fact that the geo-economic vision itself focuses on those forms of conflict that are dominant in the age of globalization. Global economists believe that geo-economic conflicts determine the content of political processes in the international arena. The United States of America, alongside the leading countries of Europe, is already actively experimenting with new directions of geopolitics and political approaches. In addition to geopolitical studies of new economic and strategic spaces, there exists, for example, "cosmopolitism" (Dussouy, 2010).
There are programs involving functioning of innovative technologies focused on structural changes in the production and consumption. Serious importance is also attached to finding practical solutions to the problems of ecological safety, searching for mechanisms to stimulate development of a new ecological culture. In our opinion, benefits should be expected from long-term programs providing specific economic and political gains.
In addition to external influences and threats, the factors of domestic geopolitics of states also impact on the global future significantly. Destabilization of the way of life within a country leads to such dangerous consequences as violation of law and sovereignty and changes in the socio-political organization of societies. The most important issue of the dialogue between the leaders of the most developed countries of the world with other actors in the international system is the development of the energy market and access to energy resources. All tools of external influence, such as economic, political, military, cultural and civilizational, are made use of in solving these problems. The United States of America is leading in this process, implementing a program of comprehensive systemic transformation of the world policy actors located in geographical areas of the energy resources concentration or within the supply routes. At the same time, serious geostrategic tasks are being solved – through energy cooperation and development of energy transit relations, the basis for adequate political evolution in all directions of the global geopolitical space is being formed (O’Tuathail, 1996).
There are other trends: regional cooperation acceleration, entry of new partners into global markets, joining alternative energy supply routes and ensuring security of export routes. Activities of the US multinational corporations contribute to the development of the commercial sphere and the intensification of investment flows. The coverage of official events, social trends and the practical implementation of political strategies are the information sources of modern geopolitical realities (Figure 1).
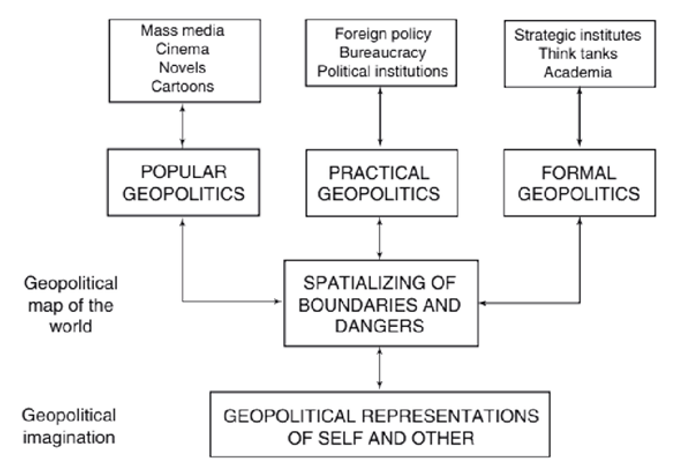
Figure 1. Formal, Practical and Popular Geopolitics. Source: Authors
Peculiarities of modern geopolitics are changes in historical traditions, transition from spatial to resource imperative, involvement of international players of different levels in geopolitical governance.
The dynamics of globalization has a significant impact on the global space of international cooperation. It requires states and state institutions to develop (create) a new spatial logic and new strategies. Today, geopolitics is aimed at the indispensable appropriation of resources of all kind; it is involved in the formation of new global forces. Geopolitics changes the methods of space control and forms new types of spaces. The structural factors of the world politics (presence and number of centers of power, global political processes), the impact of globalization and informatization processes transform the geopolicy and the realities of a society regarding security and new threats.
Conclusions
Today, in the context of globalization, the pursuit of expanding the territory of a state has lost its relevance, as the main condition for all international participants is equal participation in the competition for innovative technologies and intellectual capital. Therefore, the leading actors of the world politics in the post-imperial era have to solve completely different tasks, in particular to join the processes of gradual formation of a single global economic space and look for ways to deal with contradictions to raise the competitiveness of national economies.
The concept of geopolitics is multifaceted, and the experts working in this field still do not have a unanimous opinion regarding the definition of geopolitics as an independent science. Geopolitics is interpreted as a separate branch of knowledge and methodology of apprehending the international relations and foreign policy of statesin conformity with their status. Ultimately, the key to the modern understanding of geopolitics is the behavior and relations of a state within its geographical location that can be used to influence other subjects/objects of international life in order to assert its national interests. To date, a number of conceptual approaches ensuring the geopolitical advantages of states have been formed in the scientific discourse. The current geopolitical theories take into account the latest means and capabilities of influence used by leading (large) states, which are associated with the conduct of information, "hybrid" and "semantic" warfares.
