DOI:https://doi.org/10.34069/AI/2021.47.11.30
Readiness of future teachers for sociocultural education of children in modern conditions of society development
Готовность будущих педагогов к социокультурному воспитанию детей в современных условиях развития общества
Abstract
The modern sociocultural situation of the development of society involves taking into account all aspects of human life in the educational process. Are our students - future preschool teachers - ready to build their activities taking into account socio-cultural aspects. The authors consider the characteristic of readiness, highlighting motivational and value-based component (awareness of the importance of their process, readiness for continuous improvement and professional development, highlighting the values of professional activity), activity-technological component (knowledge of the ways of interaction with the subjects of the pedagogical process, design of the educational and educational process, the use of modern teaching tools (IT), information and knowledge component (knowledge of the specifics of preschool childhood, modern trends in the development of society and education, learning technologies). The study shows the insufficient level of development of the 2nd and the 3rd components of the readiness of future teachers. The proposed methods of professional training of future teachers of preschool education are associated with the use of business games, conducting master classes, studying the technological component of the educational process.
Keywords: sociocultural aspects, future teachers, preschool children, readiness for pedagogical activity.
Аннотация
Современная социокультурная ситуация развития общества предполагает учет в образовательном процессе всех аспектов жизнедеятельности человека. Готовы ли наши студенты – будущие педагоги детских садов к построению своей деятельности с учетом социокультурных аспектов. Авторы рассматривают характеристику готовности, выделяя мотивационно-ценностный (осознание значимости своей процесс, готовность к непрерывному совершенствованию и профессиональному развитию, выделение ценностей профессиональной деятельности), деятельностно- технологический (владение способами взаимодействия с субъектами педагогического процесса, проектирования учебного и воспитательного процесса, применение современных средств обучения (ИКТ), информационно- знаниевый ( знание специфики дошкольного детства, современных тенденций развития общества и образования, технологий обучения) компоненты. Проведенное исследование позволяет констатировать недостаточный уровень развития 2 и 3 компонента готовности будущих педагогов. Предлагаемые методы профессионального обучения будущих педагогов дошкольного образования связаны с использованием деловых игр, проведением мастер классов, изучением технологической составляющей учебного процесса.
Ключевые слова: социокультурные аспекты, будущие учителя, дошкольники, готовность к педагогической деятельности.
Introduction
The relevance of this study is justified by the new sociocultural conditions of growing up of children, which are closely intertwined with the traditional values of our society. Educational institutions of different levels are faced with the tasks related to the development of various aspects of education and upbringing in the conditions of new realities related to the actualization of the problem of multiculturalism of society, its digitalization, the expansion of the educational environment by means of social interaction, the creation of conditions for children with disabilities, etc. According to the Standard for Preschool Education, one of the basic principles of preschool education is the inclusion of children in sociocultural norms, the traditions of the family, society and the state, as well as taking into account the ethnocultural situation of children's development. The relevance of the problem under consideration is also related to the need to strengthen the educational aspect within the framework of the humanistic paradigm of education.
A number of authors consider the sociocultural aspects of modern reality, distinguishing them by the scale of influence (Mudrik, 2016, Petrusevich, 2008), by the nature of the influence on systemic changes in the field of education.
We define sociocultural challenges to the educational system not only as factors that stimulate the development of concepts, theories of education and learning, the search for new approaches to the transformation of the educational system, but also as incentives that motivate subjects of the educational process to constantly develop and improve skills in the field of professional activity, on other approaches to the training of future teachers of preschool education.
The purpose of this article is to identify the level of readiness of teachers of preschool education and students, future educators to implement the aims of socio-cultural education in modern conditions.
Literature Review
In the recent decade, the problem of sociocultural development of children has been studied by researchers in a multidimensional manner, not only mechanisms, technologies that contribute to the assimilation of sociocultural patterns and norms, traditions are determined; but it also determines the content of growing up in conditions of specially organized activities of children. Today, a child from preschool age is placed in a different system of interaction with society at micro and macro levels.
How do the features of the development of society affect the educational process in preschool organizations, the upbringing of a developing personality today?
Today, the child is in a "huge expanded social" space of interaction, this space is multifaceted:
- This is also related to the openness of borders, the possibility of movement both within and outside the country, the possibility of communication with people of different ethnicity and nationality, the availability of cultural information. Which allows the interaction of the child in the interpersonal communication system (person).
- The digital transformation of society increases the possibilities of obtaining information with the help of numerous gadgets, IT- technologies, which increases the interaction of the child in the technology- the child system. At the same time, people do not have enough time to understand everything that is happening, they are included in the frantic rhythm of modern civilization. The nature of communication between children is changing, they do not know how to build productive interaction; Trends in the physical health of children are noted.
- Another aspect of the changing socio-cultural situation of the child's development is related to the changes in the system of moral values, the nature of people's relations to intercultural differences (Barrett, 2012), to ideals (Aryabkina, Bogomolova, Shcheglova, Subbotina, Dormidontova & Vasilyeva, 2019). Against a fairly positive background of intercultural interaction, sometimes there is a lack of desire for dialogue and mutual understanding; national intolerance at the State and inter-State levels. (Zakharova, & Chibisova, 2021). All this, ultimately, determines the nature of the influence on the emerging personality; on the development of its value orientations and attitudes, on the situation of its socio-cultural formation.
In connection with the identified features of the socialization of the modern child in new socio-cultural conditions, the task of developing the person is performed not only according to the cultural and historical values and traditions of their people, the multinational fatherland; but also with the help of the individuals who know how to build their activities and communication in a different socio-cultural environment. A sociocultural context is a social and cultural environment in which a person grows and lives, which affects thoughts and behavior (Zydney et al, 2012).
Sociocultural specifics reflect not only global and all-Russian trends, but also ethnocultural, confessional and regional features.
The implementation of the socio-cultural context is based on the construction of a social partnership of an educational organization.
The study of psychological and pedagogical literature (Abitova, 2015, Kalinina, T., 2020, Zakharova, & Purskalova, 2013, Rubinstein, S. L., 2000, Sokolova, 2012; Fedoskin, 2004) allows us to consider sociocultural education as a process of pedagogical support for a child during their socialization, entry into society, understanding and assigning to them the rules of human interaction, the culture of society, and the development of their own model of behavior.
The question arises - are our students - future teachers of preschool organizations - ready to take into account modern trends in the development of our society in their professional activities, to implement the tasks of pedagogical support for the child's entry into the world of adult life?
The characteristics of the concept of the teacher’s readiness in modern research is considered from the position of a functional approach, when readiness for activity is determined by the manifestation of personal qualities and mental processes, the second position connects readiness for professional activity with psychological setting of personality, the third approach reveals readiness through a set of qualities, properties and conditions necessary for successful professional activity. (Vadurina, 2012, Sladkova, 2017)
In the structure of the teacher's readiness are distinguished motivational and value-based component (awareness of the importance of his process, readiness for continuous improvement and professional development, highlighting the values of professional activity), activity-technological component (knowledge of the ways of interaction with the subjects of the pedagogical process, the design of the educational and educational process, the use of modern teaching tools (IT), information and knowledge component (knowledge of the specifics of preschool childhood, modern trends in the development of society and education, learning technologies).
Methodology
In order to identify the main components of the teacher's (student’s) readiness for socio-cultural education of preschool children, a pilot study was conducted, which determined the level of development of the readiness of teachers (students and educators) to carry out socio-cultural education of preschool children in modern conditions at the intermediate stage of the study.
The sample was 50 students of the 4th (second last) year.
The main methods of study were questionnaire, design task - the development of a technological map, the methodology "Motivation of professional activity" by K. Zamfir in the modification of A. Rean (Mironova, 2006) and the methodology "Motives of the pedagogical profession" (Silchenkova, 2005).
The developed questionnaire included a number of questions that related to understanding the nature of the influence of the socio-cultural situation on the development of the individual, awareness of the transformations that require adjustments in the content and technology of the educational process, the desire to develop themselves in personal and professional terms. The design technique allows you to identify the ability to design an educational process using modern methods and means of training, designing didactic objects, the ability to translate socio-cultural substantive aspects into an instrumental component.Results and Discussion
The analysis of students' choice of professional motivations showed that students are more oriented on the results rather than the process of professional training. The methodology "Motives of the pedagogical profession" (Silchenkova, 2005) involves ranking in a scale of 0-5 and counting the average score of each of the motives for choosing a profession. The results are as follows:
Table 1.
Prevailing motivations for choosing a teacher's profession.

Despite the leading motive for getting education and a profession, interest in pedagogy as a science, in the educational process occupies a significant place in the ranking of answers, which indicates the desire for self-development, the acquisition of professional competencies that ensure success in the profession. This confirms the level of self-esteem of their abilities.
Table 2.
Results of ranking of professional motives.
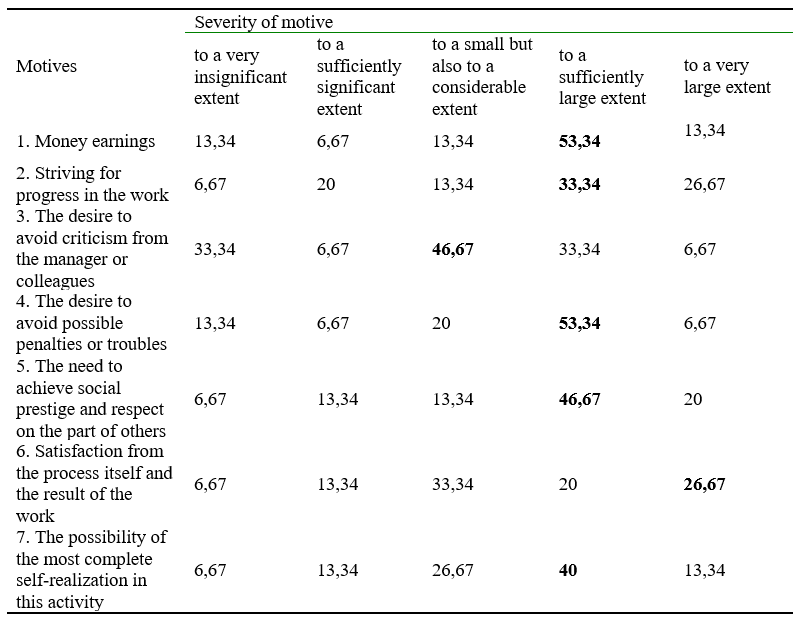
This methodology assumes the identification of ratios of groups of motifs: internal (opportunities for self-realization and satisfaction from the process) (IM), external positive (related to monetary and career achievements) (EPM) and external negative (avoidance of criticism and troubles) (ENM). Obviously, the result of the predominance of internal and external positive motivations is preferable. As a result of the survey, we found that in respondents, IM = 3.2 < IPM = 3.6 > INM = 3.1. This group of students is characterized by a predominance of external positive motives, which actually confirms the results of diagnostics according to the method of T.N. Silchenko. But for interpretation, it is also important that the difference between the 3 groups is insignificant, which proves a certain uncertainty of future teachers in their professional competencies and chosen activities. An assessment of the motives for the activities of bachelors of the 4th year shows that external motives (career, profession, earnings) belong to the category of leading ones, which is correlated with the general trends in the monetization of any activity in modern society. Social motives are slightly inferior, which indicates not fully formed ideas about the teacher's activities in modern socio-cultural conditions.
The information and knowledge component was examined through a questionnaire. All respondents noted that the socio-cultural development of preschoolers was associated with the "entry of the child into society," the development of cultural norms. Analysis of the answers showed that both students and practitioners determined the decisive aspect in the characterization of sociocultural education of children.
Content linked to ethical notions of good and evil, moral values and norms (42 per cent), of which 8 per cent stressed the importance of the values that parents broadcast; with the ability to build relationships with people of different nationalities and disabilities;
- with means of education - books, children's games, films and performances - 32%;
- with the formation of communication skills -18%;
- 8% of respondents could not decide on the characteristics of this process and could not give an answer.
In general, students managed to characterize the main components of the process of socio-cultural education, highlighting the substantive and procedural aspect. Noteworthy are the answers in which children's games are called a significant form of acquiring a child's socio-cultural experience. It is them, according to the Russian teacher of the past W.D. Ushinsky, who are a reflective projection of the socio-cultural environment of the child; what the child sees around, what they observe, arouses interest, then is reproduced in their games. On the other hand, it is the playing activity of children that is a unique means of establishing the subject socio-cultural experience of the child.
All 100% of respondents noted that changes taking place in the world and our society undoubtedly affect the nature and content of modern preschool education, but in choosing the priority areas that are characteristic of modern socio-cultural reality, a preference was given to computerization (56%) and environmental problems (16%); 28% of respondents could not identify the most significant changes in the modern world that affect the nature of human life and accordingly contribute to making adjustments to the content of preschool education. At the same time, only 25% of students identified the need to create a digital environment in a preschool organization. The remaining respondents could not characterize the socio-cultural context of education and formulate their attitude to proposals for its renewal. There is some inconsistency in the answers of students: the inability of students to see the essence of socio-cultural problems and the misunderstanding of which they should be taken into account in their work.
Studying the answers and results of the project task made it possible to evaluate the methodological aspect of the readiness of future educators, the formation of skills for choosing technological tools in the field of socio-cultural development of children. Among the priority working methods are games (28%), conversations (28%), cultural and leisure activities (20%), and creative activities of children (4%). 3% of respondents emphasized the role and participation of the older generation in sharing social experience with the children in the process of their communication and joint activities. Also, 8% of students could not clearly articulate and present their position on the technological aspect, which undoubtedly requires special attention in their future professional training.
The analysis of technological maps of sociocultural education by means of children's activities showed the presence of all the main components of the map, the proposed content corresponds to the age characteristics of children, but the selection of the content, the proposed methods do not clearly represent the ideas of the active approach, verbal methods prevail in which the child becomes a passive participant in cognition. Among the socio-cultural aspects of reality, the substantive component highlights the ideas of the peaceful existence of people, moral norms, and family traditions.
The activity-technological component was determined by the formula K = K fact/K max. The low 53% and 47% sufficient level of development of this component prevailed.
The results obtained during the pilot study allowed us to focus in the professional and personal development of students on the practical training of students, focusing their attention on the implementation of a personal and activity approach in organizing the life of a child. In practice, students were led to the understanding that the sociocultural context of the upbringing of preschool children is determined in close cooperation with the families of pupils, the study of the value foundations of their vital activities characteristic of a particular family, and the inclusion of adults in socially significant actions.
In expanding the theoretical and methodological position of students in the field of sociocultural education of children, there played a great role the courses on the design of the subject environment in a preschool organization, on the socio-cultural development of children by cultural means, on the history of education. The views of classics of pedagogy made it possible to develop the analytical skills of students in characterizing the cultural and historical era, pedagogical ideas and concepts of that time, educational practice.Conclusions
The analysis of the results of the development of the main components of the professional readiness of students-future teachers of preschool education showed an unequal degree of their representation among students of the 4th year. With a sufficient level of theoretical knowledge, most students have insufficient planning skills. There is uncertainty among students about the level of mastery of technologies for working with children, including their socio-cultural development.
The motivational component is characterized by students understanding the significance of the chosen profession and the need for constant striving for success (both morally and materially) in future professional activities.
In general, the prevailing level of readiness of 4-year students for sociocultural education of children in modern conditions turned out to be sufficient (68%) and insufficient (32%), which is quite permissible at the intermediate stage of vocational education. The identification of the dynamics of the development of the main components of student readiness during the training process allows adjusting the content and nature of student education in the next stages.
The results obtained during the pilot study allowed us to focus on the last, fifth year of study students on their practical training, focusing on the implementation of a personal-activity approach in organizing the life of a child during the students' courses and workshops.
During practice, students were led to the understanding that the sociocultural context of the upbringing of preschool children is determined in close cooperation with the families of pupils, the study of the value foundations of their vital activities characteristic of a particular family, and the inclusion of adults in socially significant actions.
In expanding the theoretical and methodological position of students in the field of sociocultural education of children, there played a great role the courses on the design of the subject environment in a preschool organization, on the socio-cultural development of children by cultural means, on the history of education. Special attention was paid to modeling practical situations in classes.
The views of classics of pedagogy made it possible to develop the analytical skills of students in characterizing the cultural and historical era, pedagogical ideas and concepts of that time, educational practice.
The pilot research conducted to study the level of readiness of future teachers of preschool education in the intermediate stage made it possible to identify general patterns. These categories of respondents are aware of the influence of sociocultural aspects of the modern development of society on the content of preschool education, noting the need to take them into account in modern educational practice. At the same time, there is no clear understanding of the mechanisms of this process. In the process of professional training, the primary methods of training are practical-oriented: project and creative activities, participation in joint events with the parents of pupils, master classes held by university teachers, business games.
Professional readiness in the field of socio-cultural development of children is an integral part of the general readiness of teachers to implement the tasks of social and personal development of children of preschool age. Its formation is provided in the process of theoretical-practical training using a practical-oriented instrumentation of variations in the spectrum of methodological work taking into account the socio-cultural context of the educational situation.
