DOI:https://doi.org/10.34069/AI/2021.47.11.12
System of factors determining the pricing policy of machine-building enterprises in modern conditions
Система Факторов, Определяющих Ценовую Политику Машиностроительных предприятий в Современных Условиях
Abstract
The article considers modern economic categories of pricing policy and pricing strategy, which with some similarity have differences in practice. The definition of pricing policy and its importance in modern conditions is given. The basic elements of the pricing policy of enterprises are given. The aim of the study is to analyze the main factors that determine the pricing policy of an enterprise in modern conditions and the possibility of their competent use in practice. Methodologically, the study is aimed at an integrated approach to taking into account the most significant factors that determine an increase in the efficiency of an enterprise in post-crisis conditions, taking into account inflationary processes in the country's economy. As a result of the study, the factors under consideration are divided into the following groups: factors of the development of the market environment; factors of taking into account the strategic objectives of the enterprise development; factors of state control in the field of prices for goods and services; factors of characteristics of manufactured goods; factors of sustainable development of the enterprise; factors of influence of inflation on the pricing policy of the enterprise.
Keywords: pricing policy of the enterprise, pricing strategy, market conditions, marketing strategy, commodity policy.
Аннотация
В статье рассматриваются современные экономические категории ценовая политика и ценовая стратегия, которые при определенной схожести имеют некоторые различия на практике. Дается определение ценовой политики и ее значение в современных условиях. Приводятся основные элементы ценовой политики предприятий. Целью исследования является анализ основных факторов, определяющих ценовую политику предприятия в современных условиях и возможности их грамотного использования в практической деятельности. Методологически исследование направлено на комплексный подход к учету наиболее значимых факторов, определяющих повышение эффективности работы предприятия в посткризисных условиях с учетом инфляционных процессов в экономике страны. В результате исследования рассматриваемые факторы распределены на следующие группы: факторы развития рыночной конъюнктуры; факторы учета стратегических задач развития предприятия; факторы государственного контроля в области цен на товары и услуги; факторы характеристик выпускаемых товаров; факторы устойчивости развития предприятия; факторы влияния инфляции на ценовую политику предприятия.
Ключевые слова: ценовая политика предприятия, ценовая стратегия, рыночная конъюнктура, маркетинговая стратегия, товарная политика.
Introduction
The relevance and importance of pricing processes for goods and services, especially in post-crisis conditions, is beyond doubt, since it has the problems of economic sustainability of individual enterprises, on the one hand, at the microeconomic level and the issues of stabilizing inflationary expectations and taking them into account at the macroeconomic level. At the same time, the economic interests of individual business entities should take into account the need to ensure macroeconomic stability of the country's economy as a whole, which largely affects their activities in the future.
In the economic literature and in practice, two closely related concepts of pricing policy of the enterprise and pricing strategy are often used.
In general theoretical terms, pricing policy is a set of principles, methods and techniques of calculation and justification of prices for manufactured products. The concepts of pricing policy and pricing strategy in a certain sense are synonyms, but the strategic aspect of activity of the enterprise assumes forecasting of prices for a more distant perspective and in this sense it is logical to use the concept of pricing strategy, which to some extent defines the strategic objectives of development of the enterprise.
If the perspective of 1-2 years is considered, it is more logical to use the term pricing policy, although it should be noted that there is no clear distinction between these concepts in economics.
In the applied aspect, pricing policy of the enterprise is understood as a management of prices for the main types of goods and services depending on strategic objectives of its development and external economic conditions.
The implementation of the pricing policy of an enterprise provides for:
- Calculation and justification of prices for manufactured goods;
- Timely change of prices depending on the market situation;
- Varying prices depending on sales markets (segments);
- Solving operational tasks related to the sale of goods in accordance with its life cycle stage (LCG);
- Responding to the pricing policy of competitors.
Pricing policy of the enterprise in modern conditions is a complex concept that has a multifunctional purpose (Figure 1). It is at the same time an element of marketing strategy, since it allows promoting goods on the market and ensures their effective implementation and element of planning and accounting activities of the enterprise, since all the main planning indicators (revenue, profit, profitability, etc.) are based on a certain level of prices of products. If the prices changes, relative to planned ones, it is always possible to assess the degree of benefit or damage from planning pricing policy and element of participation in competition, because by reasonably manipulating prices, the enterprise can achieve certain advantages in certain markets.
Literature Review
In order to consider the peculiarities of the formation of prices for the products of mechanical engineering enterprises, it is necessary to carry out a comparative analysis of the approaches to the definition of the categories "price" and "pricing", formulated by various scientists-economists. By "pricing" we mean a rather complex and contradictory process. It is during this process that a specific price is established for a specific type of product at a given moment in time. Often, pricing is associated with various compromises, taking into account the interests of the enterprise, with certain actions of competitors, with the prevailing market conditions, with the psychology of buyers, etc.
Under the pricing of A.S. Yakoreva understands the process by which prices for a product/service are set (Yakoreva, 2008). That is, pricing is determined through the process of calculating and setting prices.
I.K. Salimzhanov gives a similar definition, in which he also says that pricing is a complex, multi-stage process of setting the price of good or service (Salimzhanov, 2001). O.V. Vasyukhin (Vasyukhin, 2010) gives the following definition: “Pricing is the process of price formation for goods and services” (Salimzhanov, 2001). At the same time, he distinguishes market and centralized (state) pricing. V.V. Buzyrev agrees with the previous authors and points out that “pricing is the process of price formation for goods, works and services” (Buzyrev et al., 2008). That is, he adds the price of work to goods and services. Having analyzed the existing approaches to the definition of the term "pricing", we come to the conclusion that, in general, the given interpretations of this concept are identical.Purpose of the Study
Prices for the products manufactured by the enterprise are decisive in its economy. Demand for goods, market advantage in relation to major competitors, efficiency of the enterprise, quality of management of economic resources and efficiency of their use, quality of enterprise cost management and the cost of goods, etc. depend on them (Daly, 2004).
The purpose of the study is to analyze the main factors determining the pricing policy of the enterprise in modern conditions and the possibility of their competent use in practical activities.
It seems expedient to divide the study of the influence of individual factors on the pricing policy of enterprises into the following most significant groups:
- factors of the development of market conditions, which allow assessing capacity of each market and its possible change over time, number and status of competitors, average market prices for analogue goods, as well as predicting the possibility and prospects of an enterprise's participation in the competition;
- factors of taking into account the strategic objectives of enterprise development, which may pursue various goals, for example: profit growth due to a rational pricing system, achieving stable market positions and consistent growth of its share using justified modern marketing techniques;
- factors of state control in the field of prices for goods and services, which may impose certain restrictions on a number of prices for enterprises, especially in post-crisis situations when effective demand for goods does not correspond to the prices declared by the manufacturer;
- factors of characteristics of manufactured goods, which must be constantly improved in the process of increasing the competitiveness of products against the background of the need for an objective development of equipment and technology and production;
- factors influencing inflation, which significantly affect prices and pricing policy of manufacturers, on the one hand, and the change in the level of purchasing power of buyers and customers, on the other hand.
When analyzing the effectiveness of the pricing policy it is necessary to determine:
- to what extent changes in prices for certain types of products give an increase in revenues and profits of the enterprise;
- what opportunities the enterprise has to adjust the pricing policy;
- exactly what factors in the pricing policy contribute most to the efficiency of the enterprise;
- what strategic objectives the enterprise sets for itself and what changes in pricing policy can contribute to the achievement of these objectives, etc.
Practice proves that it is not possible to develop uniform methodological rules for the development of pricing policy for all enterprises. Since, for example, the market situation of each product of the enterprise has certain features, based on the interests and opportunities of different markets or customers. The dynamics of its development is difficult to predict and requires an individual approach, as well as the specifics of a particular product (Labzunov, 2013).
Therefore, the article aims to summarize the main factors that determine the pricing policy of enterprises, taking into account the peculiarities of their use in specific conditions.Materials and Methods
It should be noted that the pricing policy is subordinate to the commodity policy of the enterprise. First, the enterprise determines the object of pricing (nomenclature and assortment of goods and services), as well as their markets, and then develops a pricing policy (Okladnikov & Tsvirkun, 2013).
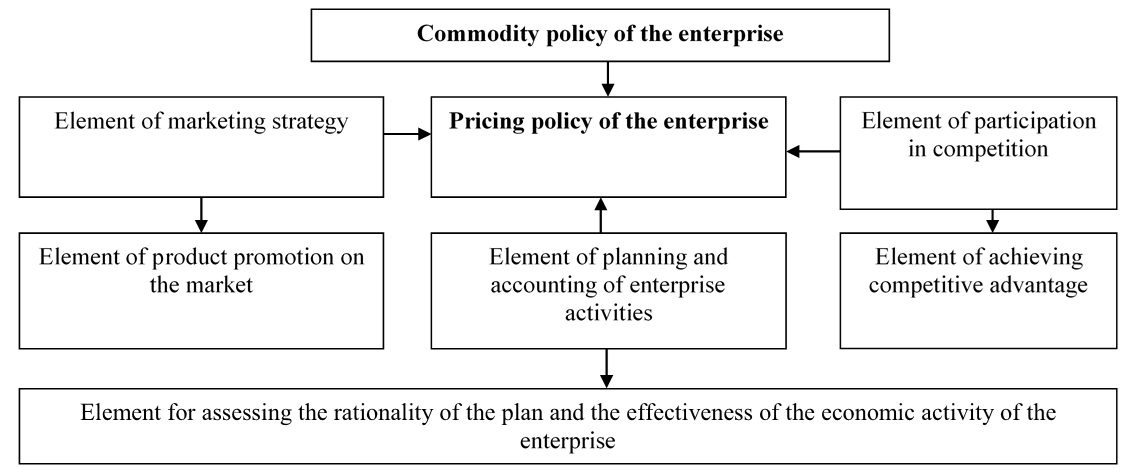
Figure 1. The main functions of the pricing policy of the enterprise (source: authors)
Factor analysis of the development of producers' price policy in post-crisis conditions can be attributed to the problems of finding a certain compromise between the interests of individual producers and the country's economy as a whole, with the latter being the priority.
The pricing policy of the enterprise depends on many factors, the main ones are:
- Factors of development of market conditions
- Strategic objectives of the development of the enterprise and its pricing policy
- goal of the strategic development of the enterprise;
- strategic period during which the goal is to be achieved;
- projected growth of key economic indicators obtained in the process of implementing the strategy;
- main directions of the pricing policy.
- Achievement of stable market positions of the enterprise in the market space due to: consistent reduction of prices to ensure growth in demand for goods, price constancy against the background of an increase in product quality and price increase with a significant increase in the competitiveness of goods;
- Preservation or increase of the enterprise's liquidity occurs by means of priority of customers with a high level of solvency, use of new forms of payments, application of a system of discounts to regular customers, etc;
- Increase in profit occurs due to a rational pricing system, focused on changes of the market situation, improvement of the quality of goods, taking into account new developments and their modernization and decrease in the cost price, in particular on the basis of the use of the scale effect and other activities;
- Strengthening of the enterprise's market position based on consistent growth of its share using justified modern marketing techniques (advertising campaigns, briefings, demonstration of product advantages and use of discount system).
- State control of prices for goods and services
- Commodity and its characteristics play an important role in the pricing policy. The set of basic characteristics of goods largely depends on its purpose and may include: technical indicators of goods in accordance with their application, reliability indicators, ergonomic and economic characteristics, etc., quality level in accordance with modern standards, level of competitiveness in relation to the most representative goods analogues in a particular market or in relation to the best world samples and number of years of goods production at the enterprise, taking into account its stage of life cycle.
- Sustainability factors of the enterprise should also be taken into account in the development and justification of pricing policy. For this purpose the following is evaluated:
- Production capacities of the enterprise for manufacturing of the considered goods and the prospect of their change (increase, decrease);
- Level of mobility of production facilities, i.e. the enterprise's ability to quickly rearrange production capacities for the production of technologically-similar goods when the market conditions change;
- Level of development of the material and technical base of production, which primarily provides a high quality of products and affects the structure and cost of goods produced;
- Level of qualification of workers and management staff, which provides the whole complex of production and marketing activities and allows the enterprise to obtain economic results of all production and commercial activity (sales revenue, profit, labor remuneration at the proper level, etc.);
- Level of marketing research that contributes to the most effective sales of goods and profit growth;
- Level of provision of pre-sale and after-sales service of goods, which promotes the image of goods and their producer and allows increasing prices on this basis;
- Financial position of an enterprise which can change considerably in case of unreasonably high and unreasonably low prices for some kinds of goods;
- Innovative activity of enterprises, i.e. its ability to quickly master new goods and their modifications, new modern technologies, etc.;
- Production costs, which due to the reserves of cost reduction create opportunities for the enterprise to reduce the selling price of the goods without loss, etc.
- Inflation change factor in the country's economy
These factors are crucial when a manufacturer justifies a pricing strategy, because each market has a certain composition of competitors and, accordingly, the level of competitiveness of their counterparts. Each competitor is constantly improving its products and strives to gain additional market share or market segment by means of a properly structured pricing policy. In connection with this, enterprises regularly monitor changes in market conditions over time in order to forecast their opportunities for favorable positioning in the market (Cram, 2010).
Particularly important indicator of the commodity market is its capacity. The capacity of any market is understood as the volume of goods sold in it during a calendar year. The capacity of any market (![]() ), especially the capacity of the Russian market of the country (industry), is calculated on the basis of industrial and trade statistics in physical units according to the following formula:
), especially the capacity of the Russian market of the country (industry), is calculated on the basis of industrial and trade statistics in physical units according to the following formula:
![]() , (1)
, (1)
NpS is the total annual (national) production of a given product (by all enterprises producing);
![]() are the inventory balances at manufacturers (in warehouses);
are the inventory balances at manufacturers (in warehouses);
![]() are the inventory balances of retailers;
are the inventory balances of retailers;
![]() is the merchandise export;
is the merchandise export;
![]() is the import of goods;
is the import of goods;
![]() is the indirect export;
is the indirect export;
![]() is the indirect import.
is the indirect import.
Indirect export of a commodity exists when an item is used in another commodity and is the subject of export. Indirect import is used in the case when the product is imported into the country as part of another product. The purpose of comprehensive market analysis is to assess the market situation (conjuncture) and forecast its development.
In working out the price policy of the enterprise the level of competition in the market of the goods produced which is characterized by an extensive list of indicators from their quantity, occupied share, price advantages to the level of costs and prospects of their reduction has a special importance.
In economic practice of the USA for these purposes Herfindahl–Hirschman Index (HHI) is successfully used, which is determined by:
![]() , (2)
, (2)
![]() is themarket share of the i-th enterprise (%).
is themarket share of the i-th enterprise (%).
![]() , (3)
, (3)
If HHI < 1000 (and more than 10 producers are present), it is competitive enough.
If HHI >1800, the market is considered monopolized.
If the enterprise has decided on a product policy, i.e. it knows the nomenclature and range of products and services provided, it develops a pricing policy for each product for each market, which contributes to the implementation of the strategic plan (Van der Rest et al., 2018; Arsenieva & Putyatina, 2021).
In developing a strategic plan, it is customary to define the following:
Such goals may include:
When striving for leadership in the market, the following conditions must be met: offered goods have a high level of quality, enterprise has a high level of market stability and authority and enterprise uses the pricing policy in full compliance with the existing market conditions. The list of strategic tasks is practically unlimited and necessarily concerns price aspects of competition to a greater or lesser degree.
Despite the market freedom in the field of pricing, the state constantly monitors the level of prices for various goods, imposes certain restrictions on a number of prices for enterprises, especially in post-crisis situations, when the solvent demand for consumer goods is falling and the output of industrial goods is also reduced. This may manifest itself in the following cases: use of fixed prices for a list of goods approved by the state, provision of benefits and subsidies to enterprises in the production of socially important goods, restriction of exports and imports, regulation of customs duties upward and downward, etc.
The principle of using LCG is determined by the limited period of its market sustainability in connection with the development and implementation of new products with improved quality characteristics (Lipsits, 2014; Milenković et al., 2019).
LCG usually has the following stages: introduction (I), growth (G), maturity (M) and decline (D). When analyzing these stages, indicators such as revenue and profit of the enterprise are used. Therefore, businesses often identify groups of products in the same stage in order to plan and timely update their product range to consistently improve their financial results.
A sound pricing strategy requires a certain adjustment for each stage of LCG, since marketing costs are involved in this chain, which must be justified from the perspective of the enterprise development (Popov et al., 2016; Zamkovoi et al., 2019). Practice shows that it is the pricing policy that allows providing an additional saturation stage and bring additional profit to the enterprise.
The price policy of the enterprise in modern conditions should have a sufficiently reliable substantiation taking into account the assessment of inflation expectations, which is based on a reasonable forecast of changes in prices for manufactured goods and purchased resources.
Change of inflation is important to take into account when planning production in the short and in the long term.
The factor of changes in inflation is important to consider when determining:
- pricing policy while taking into account the specifics of each market;
- producer's status in the main markets;
- financial and economic possibilities of the producer;
- most promising structure of manufactured goods;
- possibility of changing the level of staff salaries;
- level of financial stability and independence of the producer, etc.
Determination of predicted inflation is carried out on the basis of research of specialists of the enterprise and macroeconomic calculations carried out by external structures (Van Kranenburg, 2004; Plaskova & Prodanova, 2021).
In Russian and foreign practice, inflation-adjusted commodity price forecasting is carried out taking into account the indexation of the cost of all resources used in its production according to the formula:
![]() , (4)
, (4)
Ppred is the predicted price of goods in the planning period;
Pb is the price of goods in the basic period;
Sm i is the specific weight of i-th material in the basic price of the goods;
Im i is the price index of i-th material;
Scom j is the specific weight of the j-th component in the basic price of the product;
Ij is the price index of the j-th component;
Sam is the specific weight of amortization in the basic price of the goods;
![]() is the average price index for fixed assets of an enterprise;
is the average price index for fixed assets of an enterprise;
Ssal is the specific weight of salary in the basic price of goods;
Isal is the index of salary planned at the enterprise;
Sother is the specific weight of other expenses, inflation of which can be ignored.
When forecasting commodity prices, the following condition must be met:
![]() . (5)
. (5)
If the "consumer basket" index (inflation index) is much less than the average wage index, then at the first stage there is an increase in welfare and the emergence of free money, there is an active accumulation of funds and the development of investment processes. With the accumulation of certain disproportions in prices, crisis situations and higher inflation are possible.
The basis for the development of a rational pricing policy of the enterprise in conditions of inflation is:
- determination and analysis of the main imbalances in the prices of raw materials, materials, semi-finished products, component parts and final products of the enterprise;
- determination of economic opportunities of the enterprise to eliminate the arisen disproportions;
- increasing the reliability of price forecasting (price indices) for all types of used material and labor resources;
- increasing the reliability of forecasting the development of competitive environment and other factors.
Development and implementation of a rational pricing policy, taking into account all influencing factors, provides enterprises with commercial success, economic growth, as well as competitive advantages, allowing solving the main strategic tasks of development.
Results and Discussion
The influence of prices and pricing policy of the enterprise on the products is extremely important, directly affecting the results of its financial and economic activity and ensuring planned economic growth (Nagle & Holden, 2001; Rashid, 2019).
The analysis showed that the pricing policy of the enterprise in modern conditions is influenced by a huge number of factors that must be taken into account in its development and justification. The most important of them are: market conditions of goods, which depend on a particular market with its own features and prospects. Changes in market capacity over time determine not only the product policy of the enterprise, but also its price features. In case the producer has a sufficiently high market share, it seeks to increase it or at least to maintain it. An important competitive advantage of enterprises in the struggle for market share is the ability to effectively manage costs in order to maneuver prices (Gort, 1962; Allen, 2007).
The goals and objectives of the manufacturer in the strategic aspect, realized through pricing policy, which depend primarily on the strategic alternatives to achieve the set priorities for the future: consistent (rapid) revenue and profit growth, systematic increase in market share, effective use of factors of production and system scale of loyal discounts, etc. (Marne et al., 2015; Novikov, 2018).
State control and regulation of prices for certain types of products are also factors affecting the pricing policy of producers, because they lead to the need to take into account: fixed state prices for certain types of goods, changes in customs rules for exports and imports of goods, use of certain benefits for socially important goods, etc. and level of competitiveness of goods, which is also used in the development of pricing policy. To ensure it, enterprises use an active innovation policy, which allows introducing: new goods and modernize already produced, technology, means of communication with customers and clients, improvement of the material and technical base of production to improve the efficiency of production and sales of products, including a high level of mobility and the most complete use of production capacity, etc.
Modern researchers in the field of pricing policy of enterprises agree on the fact that with a huge variety of influencing factors it is almost impossible to develop a unified methodology and even methods of its justification and implementation (Bazdnikin, 2012; Putyatina & Arsenyeva, 2020).
The complexity of justification of pricing policy in modern conditions is that it is developed by enterprises differentiated for each product, market, region, time period, etc., taking into account the actions of major competitors, which introduce a certain element of uncertainty.Conclusion
Modern research uses two closely related concepts enterprise pricing policy and pricing strategy.
Pricing policy is a set of principles, methods and techniques of calculation and justification of prices for manufactured products. In spite of the fact that these concepts are almost synonymous, the strategic aspect of the enterprise involves the prediction of prices for the longer term and in this sense it is logical to use the concept of pricing strategy, which determines the strategic objectives of the enterprise.
Pricing policy is always very important in relation to product policy of the enterprise, since the enterprise firstly forms the nomenclature and assortment of manufactured goods and services, considers specific markets or customers and only then works out pricing policy for them.
Pricing policy of the enterprise depends on many factors, the main of which are the following: factors of market development, taking into account peculiarities of each market (composition of competitors, level of competitiveness of their goods in relation to present analogues, market capacity and its possible change).
Strategic objectives of development of the enterprise and its pricing policy: as such objectives we may consider the following:
- achievement of stable market positions of the enterprise in the market space;
- increase in profits, including through a rational pricing policy;
- consistent reduction of the cost of goods;
- consistent growth of its share with the use of justified modern marketing techniques, etc.
Factors of state control in the field of prices for goods and services. This manifests itself in:
- use of fixed prices for a list of goods approved by the state;
- provision of benefits and subsidies to enterprises in the production of socially important goods;
- regulation of customs duties upward and downward, etc.
This is especially acute when prices are limited in post-crisis conditions with a significant decrease in income and demand for goods and services.
The product and its characteristics play an important role in the pricing policy. The set of main characteristics of goods largely depends on its purpose and is determined by the manufacturer for the growth of its competitiveness in the market.
Factors of sustainability of enterprise development in the analysis of which the following is evaluated:
- production capacity of the enterprise;
- level of their mobility;
- level of qualification of workers and management staff;
- level of marketing research;
- financial position;
- innovation activity of enterprises, etc.
Factors of change in the level of inflation: the basis for the development of a rational pricing policy of the enterprise in an inflationary environment is:
- determination and analysis of the main imbalances in the prices of raw materials, materials, semi-finished products, component parts and final products of the enterprise;
- determination of economic opportunities of the enterprise to eliminate the arisen disproportions;
- increasing the reliability of price forecasting (price indices) for all types of used material and labor resources;
- increasing the reliability of forecasting the development of competitive environment and other factors.
Development of effective pricing policy taking into account all influencing factors is able to provide the enterprise with commercial success, economic growth and to realize the main strategic objectives of development.
