DOI:https://doi.org/10.34069/AI/2021.44.08.13
The Cult of Health Philosophy in Traditional Culture of the Inhabitants of the Ukrainian Carpathians’ Mountainous Regions*
Культ філософії здоров’я у традиційній культурі жителів гірських регіонів Українських Карпат
Abstract
The article highlights the theoretical and applied aspects of health philosophy phenomenon in the traditional culture of the mountainous regions of the Ukrainian Carpathians. Based on the elaboration of philosophical, psychologico-pedagogical literature, study of archival materials, ethnographic research, students’ questionnaire, the authors reveal the phenomenon of cultivating healthy lifestyles through the prism of ethno-cultural traditions, types of activities and ways of the population’s life support in the mountainous regions. It is indicated that the phenomenology of human health philosophy in ethno-cultural traditions of the inhabitants of this region is extremely multifaceted, since it contributes to overcoming the boundaries between bodily and spiritual, biological and social, individual and global, and includes the integrity of the human personality, the harmony of psychophysical strength, the way of a person’s life, the main parameters of which are work, everyday life, educational and cultural activities, a variety of customs, traditions, human behavior. The methodological bases of the research comprise the results of achievements of modern psychologico-pedagogical schools in studying the uniqueness of the process of interaction of a person with a mountain environment and authentic culture. The research aims at determining the optimal psychological and pedagogical conditions for the effective use of the achievements of ethnocultural traditions of different peoples and ethnic groups living in remote mountainous areas.
Keywords: philosophy of health, region Ukrainian Carpathians, ethnocultural traditions, healthy lifestyle.
Анотація
В статті розглядаються теоретичні і прикладні аспекти феномену філософії здоров’я зростаючої особистості у традиційній культурі жителів гірських регіонів Українських Карпат. На підставі опрацювання філософської, психолого-педагогіч-ної та етнографічної літератури, вивчення архівних матеріалів, власних польових етнографічних досліджень, анкетування студентів, автори розкривають феномен процесу культивування здорового способу життя людини крізь призму етнокультурних традицій, видів діяльності та способів життєзабезпечення населення гірських регіонів. Вказується на те, що феноменологія філософії здоров’я молодої людини, яка увиразнюється в етнокультурних традиціях, побуті та звичаях жителів цього регіону є надзвичайно багатогранною, оскільки сприяє подоланню меж між тілесним та духовним, біологічним та соціальним, індивідуальним та глобальним, і включає цілісність людської особистості, гармонію психофізичних сил, спосіб життя людини, основними параметрами якого є праця, побут, освітня, суспільно-корисна та соціокультурна діяльність та поведінка. Методологічні основи дослідження складають досягнення сучасних психолого-педагогічних наукових шкіл з вивчення унікальності процесу взаємодії людини з гірським середовищем та автентичною культурою жителів гір. Мета дослідження полягає у визначенні оптимальних психолого-педагогічних умов для ефективного використання надбань етнокультурних традицій різних народів та етнічних груп, що проживають у віддалених гірських районах у процесі формування здорового способу життя сучасної людини. Зазначене дає підстави стверджувати, що філософія здоров’я зростаючої особистості змінюється не лише у часі, але й в просторі, і у його формуванні беруть безпосередню участь люди.
Ключові слова: філософія здоров’я, регіон Українські Карпати, етнокультурні традиції, здоровий спосіб життя.
Introduction
A nation’s health indicator is a peculiar characteristic of the level of any civilized country that reflects its socio-economic, moral and spiritual development and is the criterion of appropriate management and a leading factor of the effectiveness of its people’s cohabitation and activities. Consequently, the problem of national health, its preservation and improvement was one of the major at all times and historical stages of the society’s development.
The traditional cult of health philosophy, which has been formed for centuries in the culture of the native minorities and ethnic groups, that inhabit the Ukrainian Carpathians, is a certain phenomenon of the modern science. It constitutes a considerable educational potential for further scientific researches and discoveries. The problem of human interaction with geographical environment caused certain challenges in the contemporary world. Such challenges include: socio-economic, ecological, moral-spiritual, cultural, educational, health-caring. According to the priorities, there appeared an urgent need to create an innovative methodology for highlighting the process of health preservation and adherence to a healthy lifestyle, which would include the rich experience of mankind and new challenges and realities of modern human existence, taking into account its key needs, interests and wishes. In connection with this, the study of the phenomenon of human health philosophy, which is seen by us through the prism of traditional ethno-culture of the Ukrainian Carpathians’ mountainous regions, has become particularly important.
Literature Review
The scientific reflection of the research is aimed at comprehension of how authentic valuable heritage of the regional culture determines the real state and dynamics of the development of health-preserving space of this unique in all aspects and characteristics territory of the Ukrainian Carpathians. The whole galaxy of scientists R. Kaindl “Hutsuls: Their Lives, Customs and Folk Legends” (2000), M. Lavruk “Hutsuls of the Ukrainian Carpathians (Ethnographic Research)” (2005) sought to learn it more deeply and reveal the phenomenon of its uniqueness in the past century. The analysis of the scientific literature on the defined topic O. Vozniuk (2014), E. Prystupa & V. Pilat (1991) enables us to distinguish the scientists’ views on health and healthy lifestyle, to define their dynamics and sustainability, to correlate various viewpoints, to analyse historical sources and field researches of ethnographers. Some of the Ukrainian national scientists of the Carpathian region such as I. Chervinska & A. Chervinskyi (2020), V. Klapchuk (2009), B. Savchuk (2004) consider the culture of health philosophy of the people who live in the mountains (further – the Goriany) not only from the temporal viewpoint but also from the spatial approaches to its formation and development. Scientists Yu. Boichuk (2017), O. Vakulenko (2015), O. Blynova & I. Chervinska et al (2020) analyses the phenomenon of “health” in its social and philosophical reconstruction and social and psychological manifestations of professional identity.
Methods and Materials
The objective of the study is to reveal the phenomenon of cultivating the philosophy of human lifestyles through the prism of ethno-cultural traditions, types of activities and ways of life support of the population of mountainous regions on the basis of philosophical, psychological, pedagogical, ethnographic literature, and the study of archival materials and field ethnographic research in the Ukrainian Carpathian region. During the research the following methods were used: the study and analysis of pedagogical, ethnographic and philosophical literature (summarizing and systematization of information from different sources); elaboration of records from field researches of life and household, traditions and customs of inhabitants of mountainous regions of the Ukrainian Carpathians by scientists, ethnographers, local lore, antiquities collectors, art critics; statistical methods for generalization and systematization of materials, the questionnaire and surveys of different categories of population.
Reference to ethno-cultural traditions of the residents of mountainous areas in order to determine the key principles of the phenomenon of cult health philosophy, according to the specifics of the research object will help to highlight the specified parameters, based on the declared ethno-pedagogical M. Stelmakhovych (1997), ethnocultural B. Savchuk (2004), and environmental approach Yu. Manuilov (2008) in more detail.
Results and Discussion
Mountains are the area of coexistence of human beings and wild nature and the harsh conditions are expressed in the Highlanders’ vitality, temperament, their ways of life and in their traditional outer world perceptions. Being the carriers of traditional folk culture even in conditions of economic and social crisis, they manifest high vitality and have been distinguished in the last decade because of the notable enlivening of cultural life and spiritual resurgence. However, in conditions of globalization of social-economic processes experienced by the whole civilized world and thus affected by modern technologies, ethnic culture tends to decay (Kibych, 2010: 38). Human health is a complex phenomenon of global significance, which by the definition of O. Vozniuk (2014) can be considered “as philosophical, psychological-pedagogical, socio-economic, biological, medical category, as an object of consumption, capital investments, as individual and public value, a phenomenon of systematic character, which dynamically and constantly interacts with the environment” (Vozniuk, 2014: 119). However, the problem is, that not always the latest methods of health improvement can be implemented in the way of human life and activity, as they need a drastic change of the “style” of life, reevaluation of already formed values and patterns of behaviour, etc. This causes some difficulties for the successful implementation of the suggested idea. “The metabolic value of recreational activities has been considered in recent years as one of the most prominent factors that affect their effectiveness” (Kozhokar & Vaskan et al., 2019). After all, along with its positive achievements, modern civilization has a negative impact on human health, it changes the nature of its physical activity, causes sedentary lifestyle, deprives the body of life balance, which leads to many problems with the health conditions of the population.
It should be emphasized that the concept of “health” is a widely-spread category, as it is used in various fields of science, where the problems of human existence and activity, functioning and development of its body are explored (philosophy, biology, medicine, sociology, psychology, pedagogy, etc.).
In particular, the study of human health dependence on different factors and generalization of the results obtained through a questionnaire confirm that the main factors which affect human health, according to the object of our research, should include:
- lifestyle and living conditions (environmental conditions, social settings and natural indicators that collectively determine a certain type of personal behaviour, the possibility of feedback) (50 %);
- environment (geographical location, natural landscape, socio-economic indicators) (20 %);
- heredity (genetic similarity, body structure, predisposition to certain diseases) (20 %);
- general condition of health care system (availability of medical institutions, effective medicines, qualitative staff support) (10 %).
The analysis of the study of the situation in the region and the elaboration of the results of the questionnaire (60 respondents living in the mountainous and lowland areas) made it possible to define the risk indicators for the health of a person who resides in the mountain environment. These include:
- contamination of the mountain environment (unauthorized deforestation, dumping domestic waste into mountain rivers, pollution of land);
- a sedentary lifestyle of young people (hypodynamia, unmanaged digitalization);
- unbalanced nutrition (lack of healthy diet, GM products);
- psycho-emotional state (constant stress, overstrain, loneliness, aggression);
- harmful habits (tobacco smoking, drugs consumption, alcoholism).
The philosophical discourse of the scientific knowledge reveals the ambiguity and versatility of the interpretation of the phenomenon “health of the Goriany” and is considered in the philosophical, axiological and socio-cultural context. In recent years, the world's community is trying to attract researchers’ attention to the problems of ethnic identity, preservation and protection of national cultures of native minorities. The traditional cult of philosophy of a healthy person, formed in the culture of native minorities living in hard-to-reach, remote natural environments, is of certain interest for modern science, as it reveals considerable educational potential for new scientific researches. One of the solutions to the outlined problem is to draw researchers’ attention to the ethno-cultural traditions of the formation of a healthy person’s cult philosophy by the inhabitants of the Ukrainian Carpathian region, “a kind and basis of which is a healthy lifestyle, based on the traditional principles and philosophy of the Ukrainian people” (Boichuk, 2017). After all, realizing the importance of cultural and historical heritage and the ability of a young person to orient well in the modern socio-cultural space, contributes to the preservation and conscious application (under new conditions and realities of the society) of the mountain population’s life experience for the organization of a healthy lifestyle. Because it is the cultural and historical heritage that reflects the whole life experience of the people, preserved in traditions and customs.
“A meaningful organization of leisure can serve as a significant stimulus for harmonious forming (in particular, morphological and functional, psychological and social) a young generation. Individual forms of physical, social or intellectual activity effectively influence an educational process. At the same time, dynamic changes in the modern world determine both positive and negative phenomena in the lives of children and young people. Purposeless and irresponsible spending of time brings forth phenomena of anti-culture, alcohol abuse, hooliganism, drug addiction, gambling, deviant behavior, etc.” (Budnyk et al., 2020: 495).
In recent years, the tendency to worsen the general condition and indicators of public health prevails in Ukraine. In some way it is caused by complications of ecological situation (harmful atmospheric emissions, deforestation, annihilation of animals, violation of ecological balance of territories), widely-spread popularization of health destructive stereotypes of behaviour (drug consumption, tobacco smoking, sedentary lifestyle), reduction of quality and professional medical services availability for socio-unprotected groups of population.
It should be mentioned, that a young person’s residing in urban space of a large city, significantly reduces his/her motor activity, and on the contrary, living in a mountain environment makes a person work physically more, move, cover considerable distances (the average walking distance of a student going to a mountain school is 7-10 km daily), climb high mountains, steep slopes and so on.
The results of our survey, which are presented in Table 1 and in Comparative Figures 1 and 2, show that motor activity indicators in urban areas of a big city and in the mountainous regions are different. Most of the time (from 5 up to 10 hours and from 10 up to 15 hours) allotted to motor activity falls on the mountainous regions – 50,9 % and 7 % respectively, which together makes up – 57,9 %. Conversely, the amount of time spent on motor activity from 1 to 5 hours is 61 % in urban space in Table 1.
Table 1.
Indicators of motor activity (time allotted in urban space of a large city and time allotted in mountainous regions). Source: the authors
.png)
 showing the time allotted to motor activity in urban space and the time allotted in mountainous regions.png)
Figure 1 & 2. Comparative figures (diagrams) showing the time allotted to motor activity in urban space and the time allotted in mountainous regions. Source: the authors.
Under the new socio-cultural realities of the Ukrainian Carpathian region development, health-preserving activity of its inhabitants, which is based on the prevailing in the society understanding of the cult of health philosophy, becomes particularly important. Though it cannot properly solve the problem of forming responsible attitude to their own health among the growing generation, not only as a personal value, but also as the valuable heritage of the community, region, country, humanity in general.
One of the reasons for this crisis is that only medical and biological model of health has been realized in the youth environment for many years, which somewhat varies from modern socio-cultural principles of “health” phenomenon interpretation. However, it should be mentioned that in recent years there has been a certain impairment of the significance of these fundamental values of mankind, which raises many strategic issues related to the spiritual, moral and physical condition of a young man’s life, to knowledge and the use of the best achievements of traditional cultural health-preservation in the life of inhabitants of mountainous regions.
In the context of the problem of our research we will analyze the students’ answers to separate questions of the questionnaire: “What, in your opinion, is healthy lifestyle based on?”
1. What, in your opinion, is healthy lifestyle based on (the respondents were able to choose several options from the four suggested indicators): 52 (86,67 %) on the reasonable use of its life potential, as well as observing the scientifically reasonable recommendations of the World Health Organization and other medical organizations; 15 (25,00 %) on family traditions and values; 9 (15,00 %) on the traditional principles and national philosophy of the Ukrainian people; 8 (13,33 %) on medical indicators;
2. What indicators are traditionally attributed to a healthy lifestyle of the inhabitants of mountainous regions: (the respondents were able to choose several options from the five suggested indicators): 58 (96,67 %) physical activity, regime of the day, work and rest; 33 (55,00 %) quality of food; 30 (50,00 %) mental health and emotional stability; 23 (38,33 %) observance of family and religious traditions; 5 (8,33 %) the opportunity to travel and buy expensive things. In order to study the peculiarities of the phenomenon of human life philosophy, through the prism of ethno-cultural traditions, activities and ways of the population of mountain regions of the Ukrainian Carpathians’s life support, we conducted a questionnaire on the topic ‘Preservation and relevance of observance of traditions of healthy lifestyle by the inhabitants of mountain regions of the Ukrainian Carpathians’, in which 60 respondents participated (the students of two groups of Vasyl Stefanyk Precarpathian National University).
In the context of the problem of our research we will analyze the students’ answers to separate questions of the questionnaire. The results of the questionnaire showed that respondents only partially possess the knowledge of healthy lifestyles. While defining indicators of healthy lifestyle and traditional factors that characterize the healthy lifestyle of the Goriany they noted different priorities. In the first case – it is the use of healthy food, and in the second – physical activity, the regime of the day, work and rest.
According to the scientists, “the health situation of the residents in 27 mountain districts of the Ukrainian Carpathians is deteriorating, “due to the insufficient knowledge of fundamental laws of rational formation, preservation and strengthening of their health throughout life among the majority of people, because of neglectful and often irresponsible attitude to this unified ontological value, which nature rewards a person together with life” (Boichuk, 2017).
Health is a certain phenomenon in the philosophy of personality formation. However, in modern life realities (globalization, informatization, digitalization, military conflicts... and other factors influencing its state), the practice of solving the complex problems related to its protection and preservation, appeals to the analysis, which affects not only the socio-cultural or individual level, but also requires research on the theoretical-methodological level.
In the modern paradigm of knowledge the way of life is defined as steady, which appeared under the influence of social, cultural, material and professional circumstances, lifestyle, that manifests itself in the norms of communication, behaviour, mindset, traditions (Boichuk, 2017). From philosophical position the accent is placed on the socio-economic, educational and cultural, psychological and pedagogical, socio-cultural components of the category “lifestyle”. It determines the essential value of these components in the process of forming a person’s individual life style, with the authenticity of socio-cultural space and the way of interaction between man and nature. After all, it (style), according to M. Zubalii (2014) “is personified and determined by historical, national traditions, received education and personal inclinations” (Zubalii, 2014).
On the basis of generalization of the research results (scientific publications, archival documents, field researches, ethnographic expeditions, recordings of Hutsul folklore, etc.) in the context of solving this problem, it is possible to define such philosophical and psychologico-pedagogical approaches to the analysis of the personality health phenomenon:
- emphasis on the socio-cultural component of the phenomenon of health;
- disclosure of natural-scientific content of the phenomenon of health;
- knowledge of different approaches to the interpretation of the phenomenon of health, in order to use them in practice;
- analysis of medical and biological indicators of the phenomenon of health during the organization of educational process;
- disclosure of the lingvo-didactic content of the health phenomenon;
- description of the moral and ethical approaches to the process of forming the phenomenon of health;
- taking into account ecological and demographic indicators of the phenomenon of health;
- analysis of spiritual and religious interpretation of the essence of the health phenomenon philosophy.
The analysis of the above indicators gives grounds to confirm that the essence of the concept of “human health” as medico-biological, socio-philosophical, psychological and pedagogical category includes the specifics of social relations, socio-cultural conditions of life and natural geographical factors. Accordingly, the universal phenomenon of health as a form of harmonious relations between man and nature, human and society is determined. Researcher R. Vorobiov (2013) introduced to the scientific circulation the concept of health “as the most optimum personal development in the environment”. At the same time, the scientist emphasizes that “health is a phenomenon that defines the life quality and strategies of everything that exists and provides harmonious relations between man, nature and society” (Vorobiov, 2013). The determined indicators give an opportunity to outline the basic criteria of the cult of healthy human life, formed on the key values of traditional culture, and thus, to build a kind of health triad: positive thinking – proper nutrition – optimum motor activity.
The phenomenon of the cult of healthy lifestyle, the uniqueness of the customary culture of health-preservation as the authentic life philosophy of the Goriany requires a special analysis to use its best practices in the educational process of the institutions and in organizing the inhabitants’ vital functions in other regions of the country. We are convinced that wellness tasks should be implemented in the educational space (family, educational establishment, extra-school education, church) with the direct participation and interaction of parents, pedagogical staff and the public (family-socio-school interaction) based on the principles of partnership pedagogy. Unfortunately, we may observe the tendency of lack of life landmarks and readiness for independent activities among young people; they are characterized by information of interests and initiatives, low level of motor activity, inability to exercise.
We adapt approaches and reflections of this groundwork to the subject and objectives of our research. There is no denying the fact that every nation has its own socio-cultural experience, which is conveyed from generation to generation as a valuable legacy of the older generation to the younger. Due to some ethno-cultural traditions, craftsmen’s continuity, the Goriany support the connection of times and generations, which in some way helps their region and country to avert the cultural disaster. The formation of the health philosophy in ethno-cultural traditions of the mountainous regions’ inhabitants – is a complex centuries-old process of reproduction in the following generations the best qualities and features that were produced and tested by the mountain inhabitants during the whole period of their existence. Their basic philosophical and pedagogical purpose is to direct the younger generation to personal development and socially useful way of self-improvement and determination of value priorities.
Almost all ancient cultures conveyed to our days the idea of a healthy lifestyle embodied in art, rituals and symbols in the inseparable unity of man and nature. This unity is reflected in the philosophers’ thoughts from antiquity to the present day. Folk knowledge about the physical development of a person and his bodily education among the inhabitants of mountainous regions was rationally thought of and related to difficult conditions of the mountain environment. Folk traditions and customs formed throughout the ages were the defining factors that contributed to the adequate bodily and spiritual education of a person, forming a healthy nation through traditional folk healthy lifestyle.
In Goriany’s families the formation of a cult of health philosophy as a vital philosophy, started from an early age, by involving children to participate in family customs, some labour and fortifying against the cold (girls assisted the mother in cooking food, cleaning the house, and the boys worked with the father in the field, helped with the family traditional crafts). It formed the cult of the native home, respect for family, family traditions, love of the native land that in future constituted a basis for further becoming of a young person a part of his community, land and nation. Today, the science has proved the rationality of the national knowledge, firmly established in the customs of the Goriany associated with the human health. The heritage of folk physical culture of mountainous regions’ inhabitants is an inexhaustible source of knowledge, which was formed during the whole history of their livelihoods. Knowledge of spiritual, moral and mental, bodily nature of man, the need for its understanding and constant improving is one of the most significant conditions of personal development. Cohesion and resistance are inherent in the customs and traditions of people living in high-mountainous areas which the residents of flat areas mostly lack.
Such characteristics are caused by the ideological outlook, life philosophy of the Goriany and belonging to a particular region. It should be noted that in the Goriany’s beliefs and folklore there is a lot of interesting information on medicine, folk treatment, nobility, connected with the practice of economic activity, everyday life, training of physical endurance and stability. Calendar and household rituals, which are observed by the Goriany in their lives, are the ground for combination and comparison of individual and group identity, because a person through various rituals selects the components which are the closest to him. In the mountains, this manifests itself during the performance of folk dances (‘Gutsulka’, ‘Resheto’, ‘Arkan’, ‘Gutsulskii ples’, etc.) celebrating various religious holidays, in particular Christmas and Easter. It is vividly seen in the youth’s ignition of ritual fires, caroling, joint performances of ritual songs, dances, various exercises, the organization of competitions on agility, speed, accuracy, etc. Many folk games reflect the labour activities of the Goriany, ‘Sow the Cucumbers’, ‘Oak’, ‘Bokorashi’, ‘Koval’, etc.
In the Steppe Ukraine, where there is a lot of equal space, games with a wide field for playing activities were distributed, whereas in mountainous areas prevailed games to balance, drag a rope, jump and throw objects to the target (‘Pull the Beech’, ‘Throw an Axe’, ‘Pull the Rope’). The effectiveness of folk traditions regarding the Goriany’s attitude to health and healthy lifestyles contributes to the formation and preservation of collective memory of its predecessors, provides the transfer of their achievements through the educational process and upbringing of growing generations as a sort of ethno-pedagogical code, which transformed into a complete system of knowledge of a certain people. The basis of the traditional culture of the Goriany, according to E. Prystupa & V.Pilat (1991), is “the organic combination of rational and irrational information from various branches of knowledge acquired during the millennial historical development of the nation” (Prystupa & Pilat, 1991).
The traditional system of national knowledge about human health includes: traditional medicine and veterinary (healing, curing, sayings), the People’s calendar (‘Hutsul Kalendar’), folk omens and beliefs about weather phenomena (Lunar Kalendar), folk knowledge about certain professions and handicrafts, national pedagogy (ethno-pedagogy), knowledge about folk clothing (‘Hutsul Uberia’). Among these components of the national knowledge we should note the whole layer of knowledge and centuries-old experience, which relate to specific patterns and rules of human upbringing related to its glazing and rehabilitation. Peoples heritage popularizes the traditional cult of health philosophy among the inhabitants of mountainous regions, characterizes the patterns of human life through the prism of social, moral, spiritual and mental manifestations of man, focusing on the formation of human bodily indicators (physical perfection and biological activity). The analysis of authentic folk traditions of the Goriany, related to health, healthy lifestyle and everyday activity, certifies great potential of the Goriany’s cult of vital philosophy, which was formed in modern socio-cultural space on the basis of customary culture, traditions and rituals. The Goriany live close to nature, so the whole life cycle of their activities and work, the formation of worldview are connected with natural phenomena. The most typical feature and the result of the beliefs of the Goriany was the cult of nature and health. Life in a unique nature contributed to the formation of a harmonious cheerful outlook among young people, strengthened their connection with the land, forest, valleys, rivers and lakes. Hard daily work (sheep breeding, cattle breeding, beekeeping, farming and other activities) alternated with various entertainments during religious holidays and free-from-work days.
National pedagogical traditions were manifested in all spheres of human life and activity, transforming in the worldview and reflecting in the system of values of the mountainous regions’ inhabitants. Determining the priority of lifestyle indicators that affect their health, respondents' answers were distributed as follows in Table 2.
Table 2.
The priority of lifestyle indicators that affect Inhabitants of the Ukrainian Carpathians’ Mountainous Regions health. Source: the authors.
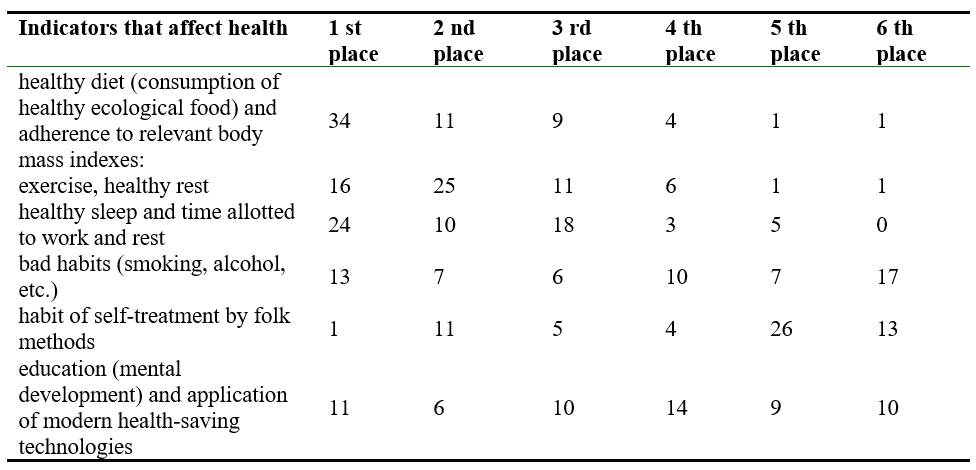
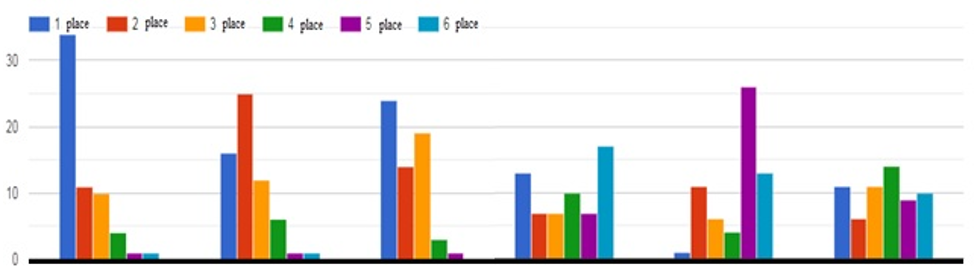
Figure 3. Indicators of a person's lifestyle that affect his or her health level.Source: the authors.
Research and experimental work has confirmed the efficiency of implementation of the ethnopedagogical context in the process of knowledge acquisition on the formation of health of young generation. Thus, most students demonstrate a conscious perception of the domestic achievements on the cultivation of health, substantiate the significance of ethnocultural traditions and the experience of the inhabitants of mountainous territories (Gorian) on issues of health preservation and strengthening for contemporaries, evaluate them as significant in the formation of scientific theory and health-preservation practice. They contribute to the implementation of an effective potential of the environmental approach (mountain environment, climatic conditions, highlands, the length of territories) in the development and preservation of young people’s health. Residents of mountainous areas of the Ukrainian Carpathians “belong to those nations in Europe, whose rites are one of the oldest and richest (Stelmakhovych, 1997: 42).
The results of the questionnaire confirm that folk traditions of the people inhabiting the mountainous regions of the Carpathians, who promote children health culture, can be effectively used in modern branches of health-preservation (propedeutically-hygienic, medico-ehabilitation, еcologico).
Acknowledgment
*We are very grateful to all the Hutsuls who kindly shared their knowledge and practices with us. Information has been provided during ethnographic practice by craftsmen famous in Ukraine and abroad, performers on traditional Hutsul musical instruments, Mykhailo Tafiichuk, the head of the family instrumental ensemble and Roman Kumlyk the founder of the unique museum of musical instruments. (vil. Bukovets, Verkhovyna District, Ivano-Frankivsk Region).
Conclusions
Phenomenology of human health philosophy in ethno-cultural traditions of the inhabitants of the Ukrainian Carpathians is extremely versatile because it contributes to overcoming boundaries between bodily and spiritual, biological and social, individual and global. “Using the results obtained in practice and further exploring the potential of the Ukrainian Carpathian region will allow us to trace the impact of certain factors (both internal and external ones) on the formation of regional socio-cultural environment in order to extrapolate the results of the research to the study of other mountainous regions of Europe and the world” (Chervinska & Chervinskyi, 2020: 110). Cultural and historical epochs and centuries-old experience of the people define the essence of health and healthy lifestyles for the population of some regions. In this period of transformational change, the modern personality finds itself in a situation that causes an identity crisis, which manifests itself in negative independence, reduced efficiency, lack of life plans, frustration with basic needs, blurring of values, uncertainty and disintegration.
We tried to focus the attention on those key aspects that remain stable for centuries and are essential for today’s generations. They include: the integrity of the human personality, which manifests itself in the interrelation and interaction of mental and physical strength of the body; the harmony of psychophysical strength, which increases health reserves, that manifests itself on the physical, psychological and socio-cultural levels; a way of life of a person, which at all times is interpreted as a kind of human activity, the main parameters of which are work, everyday life, educational, socially-useful and cultural activities, various customs, traditions and a person’s behaviour. Respectively, on condition of successful organization and qualitative aims content of these factors, which, in a complex, will promote human health, we may confirm the implementation of a healthy lifestyle. Prospects for further research may be the study of the process of life-aim values formation of the Ukrainian Carpathians’ residents.
