DOI: https://doi.org/10.34069/AI/2021.42.06.14
Investment policy of the banking sector: data from Russia
Инвестиционная политика банковского сектора: данные из России
Abstract
The growing investment activity of banking sector organisations is an important condition for securing diversification of assets and obtaining additional sources of income, as well as maintaining the required level of liquidity. Economic crises and instability of stock markets affect the investment policy of a bank, the quality of its investment portfolio, and the scope of investment transactions with securities. The purpose of the research is to carry out a comprehensive analysis of the investment mechanism of the Russian banking sector and its organisation, to characterise the investment policy and risks connected with investment activities, to determine the criteria for financial instruments included in the structure of investment portfolios of Russian credit institutions. The authors used the analytical, regulatory, comparative, and statistical methods of research to define the dynamics, composition, and structure of investment portfolios and risks involved in the business of financial and credit institutions, in the course of the formation of investment policy. It was concluded, as a result of the research, that enhanced performance, stability, and liquidity of credit institutions were conditioned by the structure and quality of portfolio investments. Improving the efficiency of the banking investment mechanism is a priority area of development, for strengthening the competitive positions of credit institutions in the national banking system. The article presents conclusions regarding the quality of investment operations and transactions with securities effectuated by banks at the present stage. The authors undertook a comparative analysis of indicators characterising the structure of investment assets of the banking sector, grouped by types of investment portfolio. Proceeding from the above, particular directions were developed for practical use, that allow for efficient selection of stock market instruments for inclusion in the investment portfolio of credit institutions in the conditions of high volatility and uncertainty of the financial market.
Keywords: The Bank of Russia, banking sector, banking investments, investment policy, investment risk, investment portfolio.
Аннотация
Рост инвестиционной активности организаций банковского сектора является важным условием обеспечения диверсификации активов и получение дополнительных источников дохода, и сохранение необходимого уровня ликвидности. Экономические кризисы и нестабильность фондовых рынков влияют на инвестиционную политику банка, качество его инвестиционного портфеля и объемы совершаемых инвестиционных сделок с ценными бумагами. Цель исследования – провести комплексный анализ организации инвестиционного механизма российского банковского сектора, дать характеристику инвестиционной политики и рисков, связанных c инвестиционной деятельность, определить критерии финансовых инструментов входящих в структуру инвестиционных портфелей российских кредитных организаций. Для определения динамики, состава и структуры инвестиционных портфелей и рисков, связанных с работой финансово-кредитных институтов при формировании инвестиционной политики использовались аналитический, нормативный, сравнительный и статистический методы исследования. В результате проведенного исследования установлено, что на рост результативности, устойчивости и ликвидности кредитных организаций влияет структура и качество портфельных инвестиций. Повышение эффективности банковского инвестиционного механизма является приоритетным направлением роста для укрепления конкурентных позиций кредитных организаций в национальной банковской системе. В статье представлены выводы, относительно качества совершаемых банками инвестиционных операций и сделок с ценными бумагами на современном этапе Проведен сравнительный анализ показателей характеризующих структуру инвестиционных активов банковского сектора, сгруппированных по видам инвестиционных портфелей. Исходя из этого, разработаны для практического использования направления, позволяющие осуществлять эффективный отбор инструментов фондового рынка для включения в инвестиционный портфель кредитных организаций в условиях высокой волатильности и неопределенности финансового рынка.
Ключевые слова: Банк России, банковский сектор, банковские инвестиции, инвестиционная политика, инвестиционный риск, портфель ценных бумаг.
Introduction
Investment operations, in particular, portfolio investments, represent one of the most profitable activities in the banking sector. Consequently, the organisations operating in the financial market and engaged in providing financial and credit services set sights on becoming participants of the stock market and forming investment security holdings.
An important factor in setting the strategy of a commercial bank in the market of securities is the formation and approval of investment policy which may be characterised as a set of measures aimed at development and realisation of actions for managing security portfolios; identifying the optimal scope of investment resources; assessing the rise in incomes from investment in securities. The main condition for the efficient investment policy of commercial banks is the development of profitable strategy in the stock market and the formation of investment portfolios that will optimally combine the principles of cost effectiveness and profitability.
The scope of resources allocated by the banks for the formation of investment portfolios is evaluated on the basis of mobilised resources gained from other types of banking activities. Investment operations of the banking sector represent one of the important areas of development of the national economy, which accounts for the relevance of the present research. The purpose of the study is to assess the efficiency of the investment policy and the investment potential of the Russian banking sector, as well as the benchmarks for the banks’ portfolio investments. The objectives of the research are as follows:
- substantiation of the relevance of investment business of the banking sector and characterisation of the investment process;
- assessment of investment operations trends in the Russian banking sector;
- analysis of the volume and structure of investment portfolios of organisations within the Russian banking sector;
- assessment of efficiency of Russian banks’ investment activities;
- identification of major problems affecting the efficiency of investment business of the Russian banking sector.
The condition status of the banks’ investment business at the present stage is assessed by the authors on the basis of quantitative, comparative, structural and factorial methods. The given research enabled the authors to evaluate the investment strategy and activity of the Russian banking sector in the stock market, as well as to assess the problems of Russian banks’ entering the stock markets as institutional investors. The Russian banking market is characterised by growing competition and increased monopoly of major players. The authors carried out a qualitative analysis of investment portfolios formed by the Russian banking sector, by assessing the volume and structure of borrowings and identifying the extent of their risk. The comprehensive systemic approach to the analysis of the banks’ investment activity trends made it possible to work out a number of recommendations for its improvement, which enabled the authors to identify the promising areas of research.
Literature Review
The stock market, with its extensive scope of investment instruments having high-quality investment parameters, is an important prerequisite and a key indicator of the condition of the banking sector. The banking system of the Russian Federation is one of the main sources of investment resources in the market of governmental, sub-federal, municipal, and corporate securities. Credit institutions, in order to diversify their activities, maintain the required level of accounting liquidity, obtain additional sources of income generation, and invest in various assets of the securities market (Brichkova, 2019). The main goal of bank investments is the formation of speculative income due to foreign exchange gain from the revaluation of securities within the formed portfolios; receipt of interest-, coupon- and discounted yield, dividend payments on equity securities, as well as obtaining other property and non-property income from participation in subsidiaries and affiliates (Mazhigova, 2018).
The investment activity of the banking sector is influenced by a great number of factors. The major macroeconomic factors that have a significant impact on the investment market and the investment policy of the banking sector include:
- political and geopolitical situation, economic development of the country and priority sectors of the economy;
- stability of functioning and development of the national banking system;
- low volatility of marketed securities prices and stock market indicators;
- stability of the national currency;
- dynamics of prices in commodity markets;
- scope of transactions in the money market and capital market;
- monetary policy of the financial market regulator;
- prudential measures regulating the banking sector, etc. (Volodin and Borenko, 2018).
The investment activity of the banking sector is influenced by a number of microeconomic factors:
- scope, dynamics, and structure of the banking sector resource base, which determines the scale of investment activities of financial institutions;
- bank investment quality indicators assessed on the basis of risk, income, reliability, and liquidity of securities;
- costs connected with formation and monitoring of investment portfolios, etc. (Zagashvili, 2017).
The state of the economy has a key influence on the national stock market indicators. The declining macroeconomic development indicators; deteriorated industrial and financial performance of a large number of enterprises; contracted investment resources of both private and institutional investors – all of the above has negatively influenced the formation of the banking sector resource base and the quality of the credit institutions' assets (Volodin and Michalev, 2018).
The investment activity of the banking sector is characterised by the following specific features:
- The sources of bank investments are represented by internal and raised funds.
- Credit institutions face restrictions when choosing financial instruments for inclusion in their investment portfolios. These restrictions are necessary in order to reduce the risks and to maintain the required level of liquidity, to prevent large-scale bankruptcy of credit and financial institutions.
- The bank portfolio investment result is the formation of speculative and interest income (Aliev and Salmanov, 2015).
Credit institutions use various investment instruments in their investment practice, that are classified according to various criteria. Among the most overriding ones are debt instruments and shares traded in stock markets, included in the 1st and 2nd level quotation lists.
Methodology
Purpose of the research:
- to make a comprehensive analysis and to assess the structure and dynamics of the Russian banking sector's investments in stock market instruments, and to propose efficient measures for the optimisation of the investment policy, that would allow maintaining the investment activity in the conditions of uncertainty and instability of the national economy and the stock markets.
The research includes the following stages:
- the first stage is a study that includes a theoretical review of economic, regulatory, educational, methodological, and literary sources delving into the problems connected with investment processes of financial and credit institutions in stock markets. This section sets the goal, objectives, object, and subject of the research, presents general directions of the analytical work.
- the second stage represents an analytical assessment of the obtained results, which includes analysis of the dynamics, structure, and scope of investment in securities by credit institutions; types of formed investment portfolios; assessment of the efficiency of portfolio investments in the banking sector at the present stage. This involves outlining the directions for optimisation of the credit institutions' investment strategy, which makes it possible to secure stable profitability in conjunction with the acceptable extent of investment risk, while maintaining high investment activity, in the conditions of high risks and volatility of stock market indicators.
The analysis of research papers on the problems of formation of investment policy and mechanisms for ensuring due banking investment processes shows that the analysis and prospects of investment activities of banking business have been described quite extensively. However, most of the essays deal with general issues of stimulating and developing investment activities in the banking sector, while the problems of adaptation mechanisms that allow banks to maintain high investment activity in the context of instability of the national economy and volatile indicators of the stock market have not been fully explored.
In the course of the study of the investment activity in the Russian banking sector, an array of analytical data posted on the official website of the financial market regulator was used, along with the financial accounting data of particular credit institutions.
The following was used in the process of exploring the posed problem: theoretical and empirical methods, including theoretical analysis, monographic survey, synthesis, analogy, scientific generalisation, the graphical method of economic research, assessment of the banking sector's investment activity results, and other methods.
Results and Discussion
The Russian banking sector demonstrates the following dynamics of assets and capital growth, as based on the official data published by the Bank of Russia in the form of analytical reports for the period from 2016 to 2018 (Figure 1).
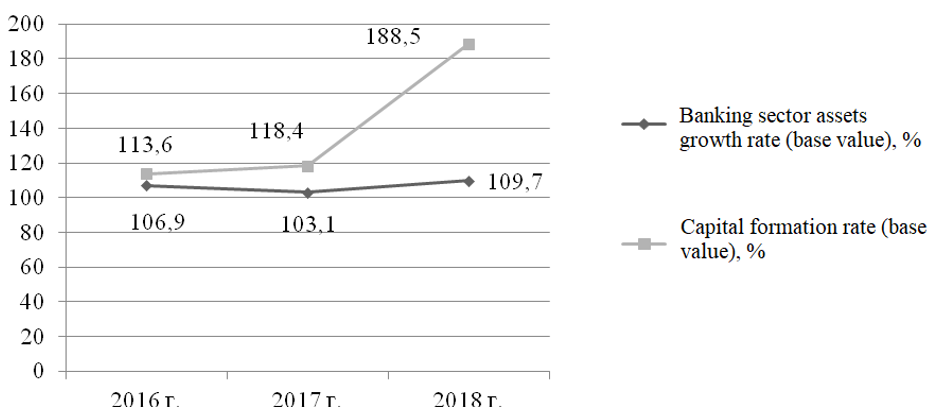
Figure 1. Banking sector assets and equity growth rates in the Russian Federation in 2016-2018
Source: Central Bank of the Russian Federation (2021)
The situation in the financial market improved by the end of 2018-2019, which is characterised by the relative stability of the national currency exchange rate and other indices reflecting the efficiency of the pursued monetary policy (Abramov et al, 2020). The process of investment policy formation involves the accumulation and processing of information that reflects the macroeconomic situation, industry performance, issuer's profile, financial instrument quality rating (Belousova and Kozur, 2016).
This analytical information is formed in blocks:
- dynamics of macroeconomic indicators and investment climate;
- dynamics of indicators of economic sectors' investment prospects;
- indicators of development for individual segments of the financial market;
- indicators of dynamics and quality of stock market assets;
- dynamics of securities issuers' behaviour;
- regulatory documents governing the investment process (Khasyanova, 2018).
The results obtained by specialists working for investment units and departments of credit institutions serve as guidelines for investment transactions and operations (Komolov, 2016).
The key element of investment activity is the development of investment policy aimed at efficient management of the investment portfolio (Figure 2).
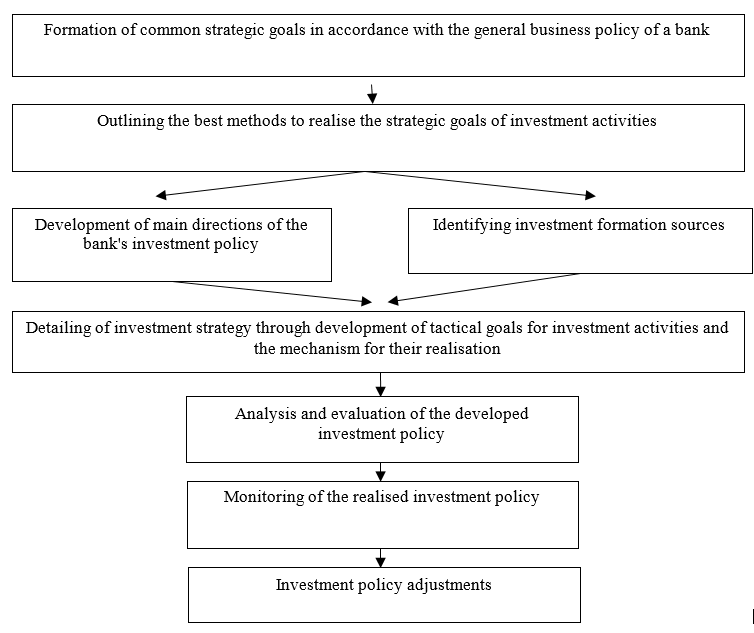
Figure 2. The mechanism for the formation of the investment policy of a credit institution
Source: authoring development
Investment policy, as an element of organisational activities of credit institutions, is a set of measures related to the formation, monitoring, and diversification of investment portfolios formed by banks. The key line of a bank's investment policy is to provide the optimal scope and structure of investment instruments, stable growth of yield generated by them, with a minimum level of risks (Turunceva and Zyamalov, 2016).
The key principle of banking investments is the optimal combination of risk and return on assets. The greater the security of a financial instrument, the lower the investment risk, respectively (Mandron et al, 2019).
The banking investment portfolio includes the following structural elements:
- securities measured at fair value through profit or loss accounts;
- securities measured at fair value through another cumulative portfolio;
- securities measured at fair value;
- portfolio of participation in subsidiaries and dependent joint-stock companies, unit investment trusts (Kalyagin et al, 2017).
The dynamics of credit institutions' investment scope in the context of the formed investment portfolios that meet IFRS requirements are shown in Figure 3.
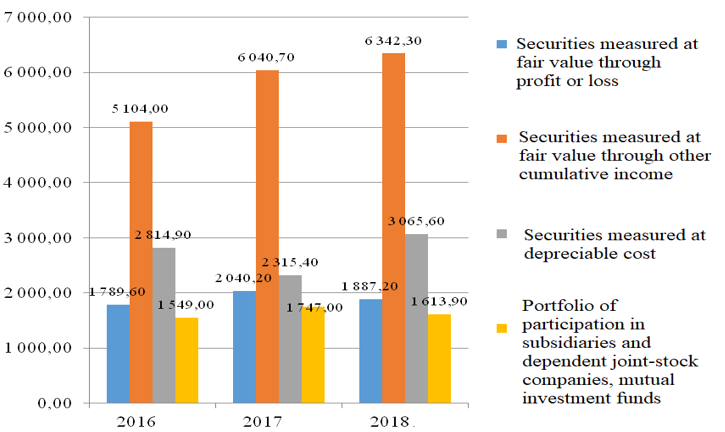
Figure 3. Commercial banks' investment in securities in the context of the formed investment portfolios in 2016-2018, billion rubles
Source: Central Bank of the Russian Federation (2021)
The largest share in banking investments is represented by securities measured at fair value through other cumulative income. The share of this type of investment portfolio in 2016 amounted to 45.3% (or 5,104.00 billion rubles), in 2017 – to 49.6% (6,040.70 billion rubles), in 2018 – to 48.9% (6,343.20 billion rubles).
The securities in the portfolio structure measured at depreciable cost accounted for 25.0% in 2016 (or 2,814.90 billion rubles), in 2017 –19.0% (or 2,315.40 billion rubles), in 2018 – 23.6% (or 3,065.60 billion rubles).
The share of investment securities portfolio measured at fair value through profit or loss amounted to 15.9% in 2016 (or 1,789.60 billion rubles), in 2017 – to 16.8% (or 2,040.20 billion rubles), in 2018 – to 14.6% (or 1,887.20 billion rubles).
The portfolio of participation in subsidiaries, dependent joint-stock companies, and mutual investment funds amounted to 13.7% by the end of 2016 (or 1,549.00 billion rubles), in 2017 – to 14.4% (or 1,747.00 billion rubles), in 2018 – to 12.4% (or 1,613.9 billion rubles).
Commercial banks are classified as institutional investors and adhere to conservative investment strategies. Securities in the conservative portfolio are distributed by financial institutions in such a way that a larger share is represented by bond issues and only a small fraction is represented by equity instruments. The inclusion of a large number of bonds in the structure of a banking investment portfolio allows the bank to efficiently manage the risks connected with the high volatility of market rates; at the same time, investments in shares of major issuers provide for the formation of speculative gains (Volkova, 2018).
Figure 4 demonstrates the scope of investment by the Russian banking sector in debt and equity markets instruments. Consequently, the Russian Federation banking sector adheres to conservative investment policy, so the overwhelming stream of investments is made in bond-secured loans – more than 80%, while the share of investing in shares is slightly over 3%. The data on investment in securities are given without regard for debt security market (bill market) instruments.
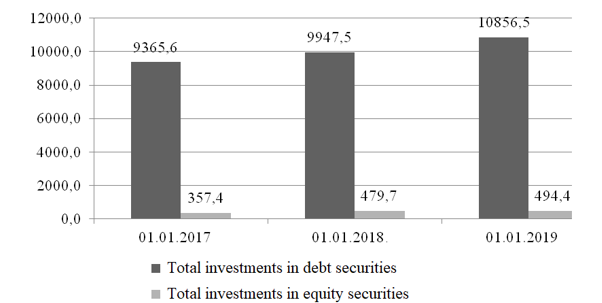
Figure 4. Credit institutions' investments in debt and equity securities in 2016-2018, billion rubles
Source: Central Bank of the Russian Federation (2021)
In 2016, the investment in bond issues amounted to 83.9% (or 9,365.6 billion rubles) in the structure of banking investments, the investment in shares – 3.22% (or 357.4 billion rubles). In 2017, the banks invested 9,947.5 billion rubles in debt securities and 479.7 billion rubles in shares, which accounts for 81.7% and 3.94%, respectively in the structure of bank investments. In 2018, Russian banks made investments in bonds in the amount of 10,856.5 billion rubles, in shares – 494.4 billion rubles. In percentage terms, banking investments in bonds amounted to 85.72%, in shares – 3.9%.
Thus, one can observe increased investment in equity and debt instruments by banking sector organisations; however, credit institutions limit investments in equity securities, which is accounted for by high volatility of their marketable value, as well as by instant reaction of the stock market to changes in economy and geopolitics.
Figure 5 shows the total investments in securities by the Russian banking sector. The chart demonstrates the dynamics of commercial banks' investment in stock market assets. These dynamics are connected with commercial banks' more active investment in debentures and equity instruments and with the income generated from participation in subsidiaries and dependent joint-stock companies.
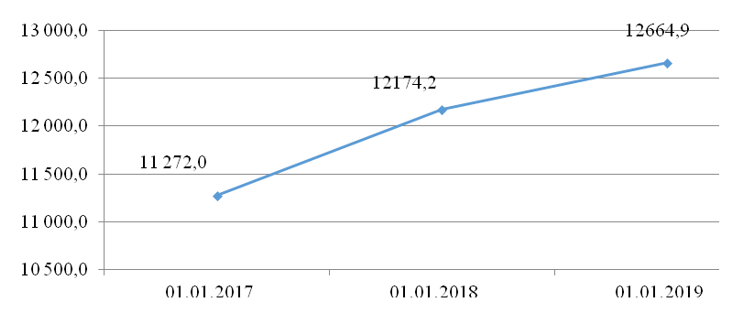
Figure 5. Dynamics of the Russian banking sector's investment in securities in 2016-2018, billion rubles
Source: Central Bank of the Russian Federation (2021)
In 2016, the banking investments amounted to 11,272.0 billion rubles, in 2017 – to 12,172.4 billion rubles, in 2018 – to 12,664.9 billion rubles. Over the period from 2016 to 2018, the scope of banking investments increased by 1,392.9 billion rubles or 12.36%.
The investment activity of the Russian banking sector is characterised by a significant amount of funds allocated for bond-secured loans, while only a minor part is invested in shares of major Russian and foreign issuers (Mandron and Letyago, 2019; Zverev et al, 2018).
Bonds have certain investment parameters which serve as a basis for their inclusion in the structure of being-formed securities portfolios by credit institutions. These parameters are as follows:
- bond-secured loans are deemed to be an instrument of reliable assets traded in the organised and over-the-counter stock market; they assume the formation of interest and (or) discounted income, without fail, within the term set by the issuer; expected payments and proceeds are already known at the time of the investment transaction;
- the bonds issued by first-class issuers with high credit rating are classified as guaranteed and liquid investment assets;
- the costs connected with monitoring of the securities portfolio and analysis of the stock market are reduced due to the low volatility of the market rate (Suchkova and Masterovenko, 2017).
The analytical data demonstrating the scope and structure of investment in debt securities by banking sector organisations are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Scope and structure of investment in debt securities by the Russian banking sector in 2016-2018
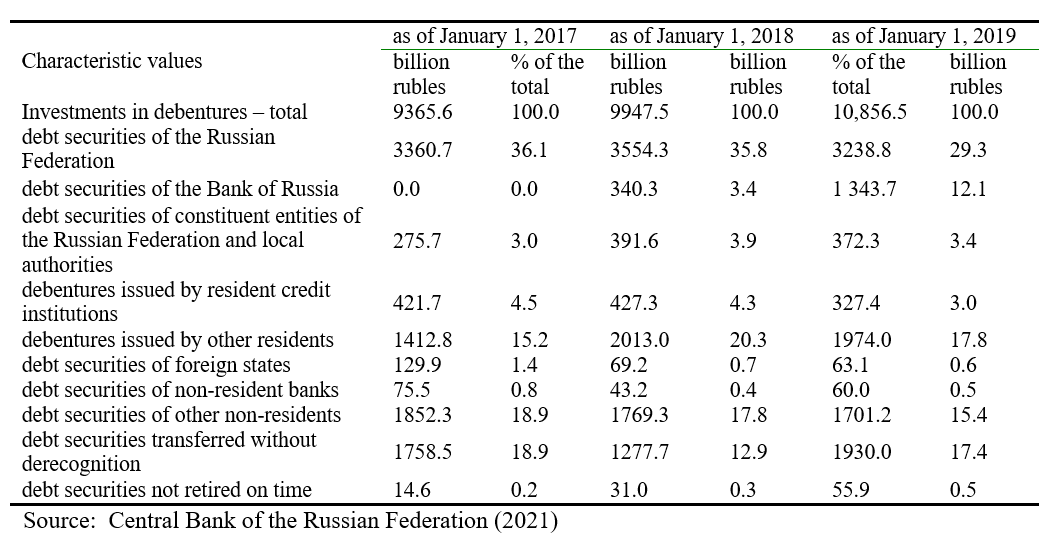
Credit institutions pertain to the conservative group of institutional investors, therefore in 2018, the largest share in the structure of banking investment in debt instruments was represented by debt securities issued by the Central Government of the Russian Federation (2016 – 36.1%; 2017 – 35.8%, 2018 – 29.3%). By the end of 2018, investment in debt securities of the Bank of Russia amounted to 12.1%. In 2018, the banks invested 17.8% of the total portfolio investments in debt securities issued by residents (except for credit institutions). In 2018, the banks assigned 15.4% of their investment funds for non-residents' debt securities (except for credit institutions).
The banking sector's investment in shares is relatively insignificant. The data for analysis of investment in shares by the Russian banking sector are presented in Table 2.
Table 2.
Scope and structure of commercial banks' investment in equity securities in 2016-2018
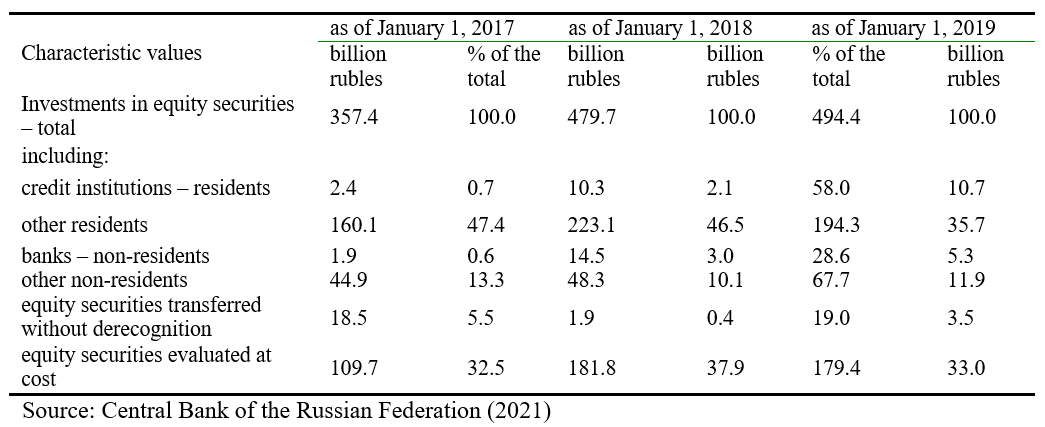
The dynamics of investment in shares by credit institutions have an upward trend. By the end of 2018, commercial banks' investments in equity securities amounted to 494.4 billion rubles. Investments in securities of resident and non-resident credit institutions had a positive growth trend throughout the analysed period. Equity securities transferred without derecognition decreased in number over the last three years. The data characterising the scope of credit institutions' investing in bill market instruments are shown in Figure 6.
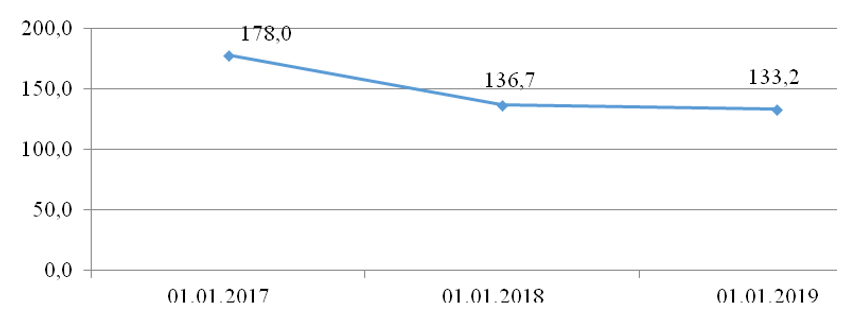
Figure 6. Data on the dynamics of investment in bills by credit institutions in 2016-2018, billion rubles
Source: Central Bank of the Russian Federation (2021)
Investments in bills are decreasing with each analysed year. In 2016, the funds allocated for the purchase of bills amounted to 178.0 billion rubles, in 2017 – to 136.7 billion rubles, in 2018 – to 133.2 billion rubles. The reduction of investments in this type of non-equity formed-to-order financial assets amounted to 44.8 billion rubles or 25.2%.
The credit institutions' investments in non-equity financial instruments decreased. Basically, Russian banks invest in bills of resident credit institutions (2016 – 49.3%, 2017 – 57.7%, 2018 – 61.7%) and in bills of other non-residents (2016 – 49, 3%, in 2017 – 41.0%, 2018 – 36.8%).
The investments in bills of other non-residents are insignificant, their share in bill market instruments in 2016 amounted to 1.3% or 2.3 billion rubles, in 2017 – to 1.3% or 1.8 billion rubles, in 2018 – to 1.4% or 1.8 billion rubles. More detailed information on the structure of investments in bill market instruments by the Russian banking sector is shown in Table 3.
Table 3.
Dynamics and structure of investments in bill market instruments by the banking sector in 2016-2018
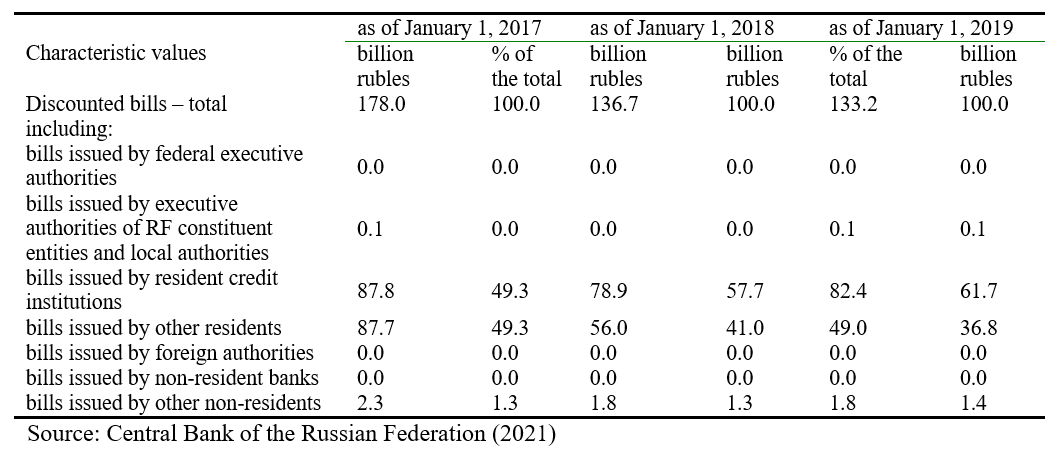
Figure 7 presents the data showing the book profit from transactions with securities by the Russian Federation banking sector.
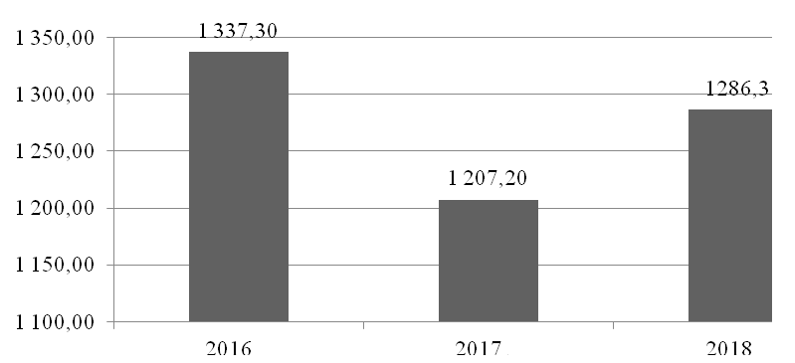
Figure 7. Income gained by the Russian Federation banking sector from transactions with securities, billion rubles
Source: Central Bank of the Russian Federation (2021)
The income from transactions and operations with securities in 2016 amounted to 1,337.30 billion rubles, in 2017 – to 1,207.20 billion rubles, in 2018 – to 1,286.3 billion rubles. The profitability of banking operations with securities decreased in the period from 2016 to 2017 by 9.73%, while it increased by 6.55% in the period from 2017 to 2018.
Based on the research results in respect of the scope, dynamics, and structure of investment in securities by credit institutions, the following trends were identified:
- first, one can observe steady growth in the banking sector's investing in securities throughout the whole analysed period, along with the extension of investment activity, which confirms the fact of the stability of the national economic system;
- second, the banking sector adheres to conservative policy in the formation of portfolio investments, therefore one can see steady growth of investment in stock market instruments, with certain proportions maintained in the structure of the securities portfolio. Debt instruments in the investment portfolio in 2016 accounted for 83.09%, in 2017 – 81.71%, in 2018 – 85.72%. Equity instruments in 2016 accounted for 3.17%, in 2017 – 3.94%, in 2018 – 3.90%. The calculation of data was made without account of instruments of the bill market;
- third, the share of government bond-secured loans, bond issues of the Bank of Russia, and bonds issued by corporate issuers in the structure of formed portfolios decreased. The share of debentures issued by the Russian Federation Government decreased in the period under review from 36.1% to 29.3%; the investment in bonds of the RF Central Bank increased to 12.1%; in 2016, credit institutions did not invest in bonds issued by the financial market regulator. Investments in corporate bonds in the structure of debt securities increased from 15.2% to 17.8%, which testifies to the increased role of private issuers and further development of real sectors of the economy; moreover, this also shows that the stock market is on the path of stable development (Sidorov, 2019);
- fourth, the development of investment activities of commercial banks in the stock market leads to increased concentration of the banking sector, so investments in securities are made mainly by major commercial banks, the largest in terms of assets; the principal geography of investments is Moscow and St. Petersburg.
The efficiently structured investment policy that takes all existing economic and political factors into account is the main tool in the realisation of the investment mechanism (Zvonova and Kuznezov, 2017). It is important for credit institutions to comply with the following principles during the process of development and approval of their investment policy in the securities market, in order to maintain financial stability and prevent a decrease in profitability from operations (Nikulina and Baklazhkova, 2016):
- focus of the developed and approved investment policy aimed at the realisation of strategic plans of the financial organisation and enhancement of financial stability;
- account of inflationary expectations in calculating the profitability of particular stock market instruments and investment operations of credit institutions;
- assessment of the expected economic efficiency of investment operations by commercial banks;
- monitoring the stock market and the instruments in the structure of the banking portfolio;
- account of financial market trends, the state of the national and world economy, when forming the structure of investment portfolio;
- evaluation of projects and investments in terms of their relevance and prognosticated efficiency;
- selection of reliable and preferably cheap sources and methods of bank investment funding (Khozyainov and Kvasov, 2015).
When developing an investment policy, it is necessary to take possible market risks into account (Figure 8).
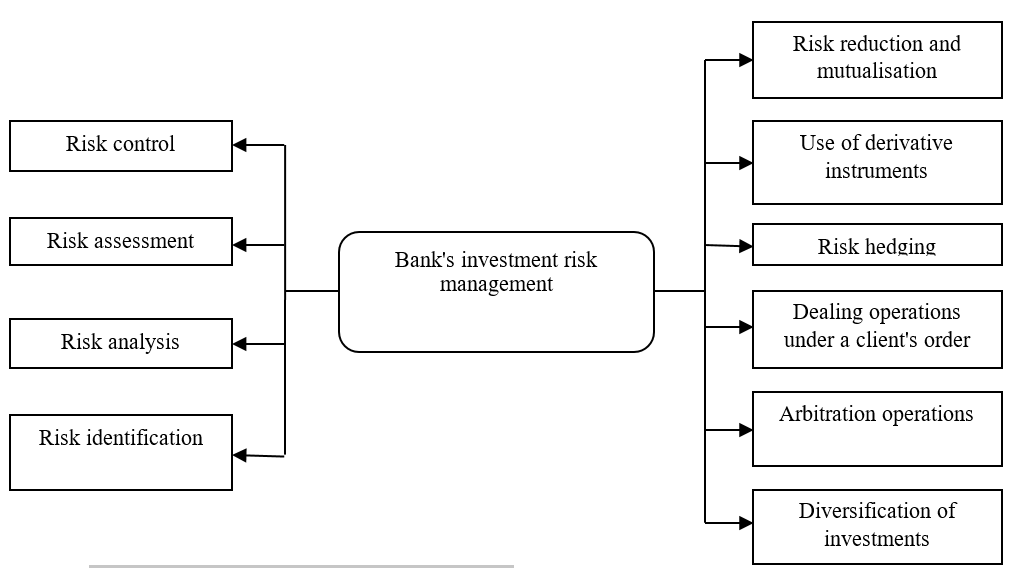
Figure 8. Bank's investment risk management scheme
Source: authoring development
In the periods when stock and foreign exchange markets face financial crises, it becomes relevant for credit institutions to focus on the selection of instruments that fully meet the requirements of the approved investment policy, for inclusion in their investment portfolio (Aganin, 2020). The structural units in charge of the bank's investment business are actively working to study the key indicators characterising the state of the stock market; they identify due instruments, explore their investment parameters and criteria for inclusion in the portfolio structure (Milovidov, 2020).
Consequently, the mechanism for the formation and structuring of investment securities portfolios of credit institutions is formed on the basis of the most reliable, profitable, and liquid securities against the minimum acceptable market risk level.
Conclusions
The main criteria for the selection and inclusion of securities in banks' investment portfolios should be as follows: their maturity period, discount rates for REPO transactions established by the financial market regulator for every issuer, risks identified in accordance with the developed and approved investment policy of a credit institution. The nominal level of profitability in the present-day economic conditions has minor importance for selecting securities and monitoring investment portfolios, since this parameter is not able to take into account the expected risk value comprehensively.
The account of the above factors will enable commercial banks to realise a more efficient mechanism for the selection of financial instruments and will ensure the due formation of the optimal scope and structure of the investment and trading portfolio. This portfolio is supposed to meet the requirements of the actual investment policy and would make it possible to generate maximum speculative and interest income against minimal risk. This, in turn, will ensure the stability and liquidity of the banking sector, along with the stable inflow of investments in the real sector of the Russian economy and in governmental funds.