DOI: https://doi.org/10.34069/AI/2021.40.04.12
Nonprofit organizations in Russia: management features and government support
Некоммерческие организации в России: особенности управления и государственная поддержка
Abstract
The article examines the management of nonprofit organizations in the area of prevention and correction of socially dangerous forms of citizens' behavior. The study is of great interest since such organizations have a wide range of tools for addressing social problems of deviant behavior in society. The methodology of this study predetermined the use of system, monographic, structural and logical research methods, along with the interview techniques. Statistical data and interview surveys showed that the state provided little support to organizations under examination. Their main sources of income are customer funds and private donations, which creates barriers to their development. Based on the research results, the authors concluded that the state should support nonprofit organizations in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous forms of citizens' behavior, as they: 1) facilitate the implementation of interests of a large number of participants in public life; 2) address the needs of various segments of the population which require additional support and protection; 3) provide services that meet the specific needs of socially vulnerable groups requiring additional support and protection. Nonprofit executives should develop special tools to improve the quality of social services and increase organizational capital.
Keywords
nonprofit organizations, deviant behavior.
Аннотация
В статье рассматриваются аспекты управления некоммерческими организациями в сфере профилактики и коррекции социально опасных форм поведения граждан. Исследование представляет большой интерес, т.к. данные организации обладают широким набором инструментов для активизации решений социальных проблем девиантного поведения граждан в обществе. Специфика методологии предопределила использование при проведении исследования методов системного, монографического, структурно-логического исследования, метода опроса. Статистические данные и опросы респондентов показали, что государство в небольшой степени оказывает поддержку исследуемым организациям. В основном они существуют за счет средств своих клиентов и пожертвований благотворителей, что создает барьеры для их развития. В результате исследования сделал вывод о том, что государство должно оказывать поддержку некоммерческим организациям в сфере профилактики и коррекции социально опасных форм поведения граждан, т.к. они: 1) выступают в качестве связующего звена при реализации интересов большого количества участников общественной жизни; 2) удовлетворяют потребности различных слоев населения, нуждающихся в дополнительной помощи и поддержке; 3) представляют услуги, удовлетворяющие специфические потребности социально уязвимых групп населения, нуждающихся в дополнительной поддержке и защите. Руководители организаций должны разрабатывать специальный инструментарий для более качественного оказания социальных услуг и наращивать организационный капитал организаций.
Ключевые слова
некоммерческие организации, девиантное поведение.
Introduction
The formation of civil society and its development in modern Russia accounts for the variability of economic forms focused on the solution of social problems, this giving rise to a special social component of the national economy that naturally attracts attention of many researchers. This component is dominated by non-profit organisations that set social objectives not directly orientated at deriving profit. The accelerated development of the social component in the economy preoccupied with non-profit organisations is acquiring priority importance for Russia in the conditions of the growing technological advancement and related socio-economic transformation, which is recorded in the latest target-setting documents of the governmental economic policy.
In the context of strategic orientation of the modern socio-economic transformation processes towards consistent socialisation and improvement of the quality of the social and economic life, as well as the dynamic development of the human-factor creative potential in the economy, the following trends are observed:
- the growing involvement of non-profit organisations in handling the key problems of modern development;
- production of increased range of goods demanded by the modern society;
- a special form of social and economic activity assigned to these organisations – social entrepreneurship.
In recent decades, a number of forms of socially dangerous (deviant) behaviour, destructive for the human factor in the present-day Russia’s economy, are actively developing, the major being:
- addictive behaviour – people’s dependence on the use of narcotic drugs, alcohol and other factors of systemic disruption of the personality structure, people’s health potential and social milieu;
- behaviour deliberately aimed at infringing the current norms of law, which creates threats to the public order, property complexes, other people’s life and health, state security and communities’ life, etc.;
- behaviour orientated at suicide (suicidal behaviour), that generates negative effects that are extremely dangerous for the human factor (deliberate loss of life, abandonment of human potential, involvement of minors and people who have lost support in life in the process of voluntary departure from life, etc.).
In connection with the development of the above forms of (deviant) behaviour, it becomes necessary to study the work of non-profit organisations focused on the mission of preventing and correcting the socially dangerous forms of behaviour. These organisations as a management object have a number of specific characteristics:
- focus on changing certain parameters of behaviour of individual groups within the civil society and of their position in the socio-economic system, which brings the management of these organisations closer to public administration;
- reliance on public initiative impulses, which makes their management much similar to self-government;
- creation of mixed benefits addressed to groups in need of correction, which accounts for participation of representatives of these groups in goal-setting and control of activity results;
- formation of a resource base through voluntary contributions and payment for ordered benefit packages, which implies the use of budgeting as a basis for managing resources and performance results.
The specificity of activities of non-profit organisations necessitates in-depth development of the theory and practice of their management with regard for the peculiarities of work of these organisations.
Literature Review
Nonprofit organizations are an integral institution of civil society in Europe and the USA. They account for a large share in the economies of developed countries (6-7%) and are characterized by specific features that distinguish them from other commercial and government organizations (Felix et al, 2017). Nonprofit organizations can be considered efficient providers of a wide range of social services with higher quality than the state services ensuring the creation of new added value due to infrastructure development (Valentinov et al, 2015).
Modern trends in the development of the global community aimed at humanizing society, developing human capital, improving the quality of life of the population, require increasing the efficiency of nonprofit organizations (Surovneva, 2017). These trends are most relevant for the Russian Federation, as, despite the abundance of mineral resources (gas, oil, minerals, etc.), a significant part of Russian citizens still face a difficult financial situation.
It should be noted that nonprofit organizations have a wide range of tools for addressing social problems in the country. The authors believe that nonprofit organizations contribute to:
- generation of social innovations aimed at resolving important social problems;
- improving the quality of provided social services and the constant "heating" of public interest in addressing socially significant issues;
- increasing the employment of socially vulnerable groups through the creation of new jobs (Bilodeau and Steinberg, 2006).
Of all the nonprofit organizations operating in the territory of Southern Russia, the authors selected nonprofit organizations (as an object of study) that ensure the prevention and correction actions to socially vulnerable groups. The nature of activities of nonprofit organizations in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous forms of behavior generally is of interest to pedagogical, medical and legal specialists, undeservedly "ignored" by academic economists in their studies. Nonprofit organizations that provide preventive and corrective services to the population are those that implement activities to correct the behavior of socially vulnerable segments of the population, namely, people with drug and alcohol addiction.
In addressing nonprofit organizations in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous forms of behavior, it is worth noticing several specific features of organizations involved in this type of activity (Kulkova, 2016):
- it is important to consider the "subtlety" of working with patients of these organizations – those are primarily patients, not clients as in other organizations. Therefore, such organizations must be licensed to provide medical services;
- as a rule, the organizations under investigation are contacted by relatives of those who find themselves in a difficult life situation; it is relatives who conclude social services contract, which might lead to a denial of services by a person undergoing the behavior correction procedures;
- to provide services in the field of prevention and correction of patient behavior, the studied organizations need to have sufficient economic space, buildings and facilities, which implies certain costs and risks to such organizations.
The study of nonprofit organizations generally involves addressing the issues of state support, the methods of psychological assistance to socially vulnerable segments of the population, and preventive measures for citizens who might be at risk. Therefore, all conducted scientific studies can be grouped into the following categories:
- research on psychological and pedagogical issues related to the prevention and treatment activities for vulnerable populations;
- research on medical issues related to removing victims of alcohol or drug dependence from the risk zone;
- studies of economic issues related to government support for nonprofit organizations.
However, all these studies seem to ignore the hybrid nature of social entrepreneurship. This results in contradictions in the mission of socially oriented nonprofit organizations, which seek to solve their problems based on the principles of self-sufficiency and profit:
- on the one hand, they are intended to make a major contribution to addressing urgent social problems, to provide targeted assistance for insufficiently protected social groups, to reduce social tensions and overcome constraints on the development of these groups;
- on the other hand, they are supposed to ensure sufficient profits from resolving these problems, required for business development and creation of additional business value.
Nonprofit organizations that provide preventive and corrective services to socially vulnerable groups of the population also remain beyond the scope of scientific research. This type of nonprofit organization is lost among other nonprofit organizations. As a rule, researchers pay particular attention to the activities of charitable foundations, inpatient medical institutions, and nonprofit organizations protecting representatives of certain ethnic groups.
To resolve this contradiction, it is necessary to consider nonprofit organizations involved in the preventive and corrective activities provided to socially vulnerable populations in terms of their management. This involves conducting systematic studies, in contrast to studies affecting financial, medical and other issues.
Using statistical data and interpretation of results of the sociological study conducted by the authors, the article identifies factors affecting the management of nonprofit organizations in the Russian Federation and considers the need for their state support. The acquired scientific knowledge will help the management of nonprofit organizations to determine the "growth points" and the "bottlenecks" that need to be addressed to ensure the effective operation of such organizations to the benefit of society.
The main findings and recommendations of the study can be used for further development of management mechanisms and strategies for the development of socially oriented nonprofit organizations, as well as for strengthening those mechanisms and modernizing socio-economic policies aimed at various aspects of the Russian social economy.
The development of civil society in Russia brings to life various types of organizations whose basic objectives are to help vulnerable segments of society through implementing social projects. Active development of such economic entities results in the strengthening of the nonprofit sector of the economy. Omelchenko and Gimazova (2014), Myronchuk and Khutyz (2017) note that in modern Russia, different groups of processes proceed in parallel. Some of them are aimed at enhancing the competitive advantages of Russia under the growing technological shifts, others – at strengthening the development of the social component of the economy and nonprofit organizations as its main subjects.
The authors consider the studies conducted by Kulkova (2016), examining the provision of services to the population by socially oriented nonprofit Russian organizations, valuable. Using the methods of sociological studies, the researcher accesses the sustainability of these organizations and determines the vectors of their further development, enriching the practical understanding of the activities of Russian nonprofit organizations.
The Russian government needs to address several issues in implementing social projects: activating the creative potential of the country's population, increasing volunteerism, and creating effective communication platforms (Putin, 2018). The nonprofit organizations under study play an essential role in all these processes. The works by Sesavin (2015), Shibaeva, Bychenok and Tsukarev (2016) focus on the impact of socially oriented activities on the content of the organization's management process. It is necessary to note the diversity and variety of approaches to the disclosure of individual aspects outlined in the study of topics. However, so far, the theoretical, methodological and applied aspects of studying management processes of nonprofit organizations in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous forms of behavior as economic entities of the third sector of the economy remained on the periphery of scientific research.
The purpose of the study is to analyze the activities of nonprofit organizations in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous forms of behavior in the South of Russia and suggest ways to improve the efficiency of their activities. The objectives of the study include:
- identifying the highest priority tasks of managing nonprofit organizations in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous forms of behavior;
- determining the creative potential of the studied organizations, the willingness of participants in nonprofit organizations to take risks in the implementation of their activities, the degree of professionalism and the need for special competencies among employees of nonprofit organizations;
- accessing the possibility of predicting the results of social projects and the likelihood of their consolidation among the beneficiaries of social services, the degree of government support for the organizations under study;
- revealing the factors involved in the management content of the studied organizations.
Methodology
In the first phase of the study, the authors identified the factors of the external and internal environment affecting the activities of nonprofit organizations using systematic, monographic, structural and logical methods.
In the second stage of the study, based on the results of the authors' previous scientific studies and the data of the Russian Statistical Yearbook (Russian Statistical Yearbook, 2018), they revealed a high demand for nonprofit organizations in modern Russian society using systematic and structural-logical research methods.
In the final stage which took place in the fall of 2018, the authors conducted a sociological study. The survey allowed analyzing the interaction between state and nonprofit organizations providing social services, along with the specifics of managing nonprofit organizations. Evaluation of expert opinions allowed identifying the key aspects of managing nonprofit organizations in the field of prevention and correction of the socially dangerous behavior of citizens, as well as the perception of nonprofit organizations by the public authorities. At the third stage of the study, the authors developed a questionnaire and selected a sample that included 51 representatives of nonprofit organizations of the Southern Federal District of Russia.
The questionnaire used closed-ended questions. The sample included representatives of nonprofit organizations that volunteered to participate in the survey. The leaders of socially oriented nonprofit organizations providing social services in the territory of the Southern Federal District of Russia acted as the main informants.
To define the key aspects of managing nonprofit organizations in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous forms of behavior, the authors conducted an online survey of 51 representatives of these organizations performing in the Southern Federal District: Rostov-on-Don – 15 respondents, Krasnodar – 18 respondents, Volgograd – 10 respondents, Astrakhan – 8 respondents. Of these, 32 respondents work in nonprofit organizations performing activities to correct the behavior of socially vulnerable segments of the population (people with drug and alcohol addiction), 19 respondents work in nonprofit organizations performing preventive activities among socially vulnerable segments of the population.To process the initial information, the researchers used the Microsoft Excel and SPSS software.
Results and Discussion
The totality of the studied factors, which allow determining the content of managing nonprofit organizations, can be divided into two groups: 1) external environmental factors and 2) internal environmental factors affecting these organizations. First, let us present a brief description of the external environmental factors. The study should begin with the analysis of megatrends – global sustainable long-term tendencies determining the development dynamics of all aspects of human life (Figure 1).
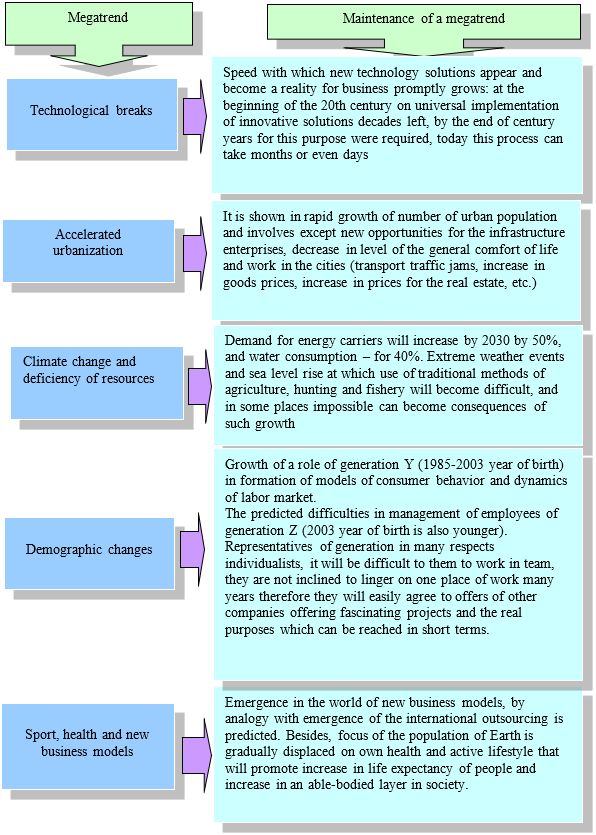
Source: compiled by the authors, based on Goodiev (2019)
Figure 1. Major megatrends in the main areas of socio-economic development till 2030
The presented trends can obviously be probabilistic in nature. However, they allow identifying a certain tendency for the emergence of a "new reality". Each of the megatrends carries future opportunities and threats to the life of contemporary people. Let us consider how these megatrends affect the activities of the organizations under consideration. Omelchenko and Gimazova (2014) note that the growing number of people with socially dangerous (deviant) behavior creates nonprofit organizations operating in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous forms of citizens' behavior. Let us show how the megatrends presented in Figure 1 affect the activities of the studied organizations.
First, there is a "servicing" of society, expressed in the active growth of the services market (Karmarkar and Pitbladdo, 1995; Kim, 2011). New innovative and digital technologies, which are based on the intellectualization of public life, significantly extend the limits of public services delivery and generate new types of services required in a digital society. Even though the nonprofit organizations under study provide social services to beneficiaries free of charge, they still obey the laws that affect the modern service market (Shibaeva, Bychenok and Tsukarev, 2016).
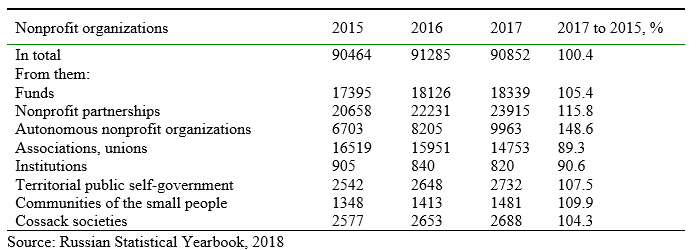
Considering the statistical data (Table 1), it is worth noticing a small increase in the number of nonprofit organizations, which confirms the thesis about their relevance in society.
Table 1.
The number of nonprofit organizations by type (at year-end)
Second, the demand for entrepreneurial qualities and innovativeness in the activities of modern organizations is growing. Studies show that nonprofit organizations employ people who are willing to solve social problems and are ready to sacrifice their most expensive resource – time. Thus, it can be said that only owners of unique competencies and moral qualities can effectively generate social projects, as well as implement them.
Thus, according to the Rosstat data, in 2017 the number of people who received legal assistance on a gratuitous or preferential basis increased by 23% compared with 2016 (from 2.3 million to 2.8 million). The authors note an increase (by 17%) in the indicator "the number of people who received charitable assistance in kind" (compared to 5.6 million people in 2016 and 6.6 million people in 2017) and a 23% increase in the number of people who received charitable assistance in cash (compared to 1.6 million people in 2016 and 2 million people in 2017) (Russian Statistical Yearbook, 2018).
When conducting an online survey in the fall of 2018, the respondents were asked several questions. The first question was intended to outline the range of important tasks of managing the organizations under study. The respondents' answers revealed the highest priority management challenges for nonprofit organizations in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous behavior (Figure 2).
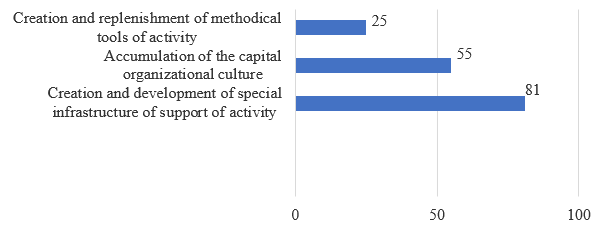
Source: compiled by the authors, based on replies to the questionnaire
Figure 2. Management challenges for the studied organizations according to the survey of their representatives, %
As can be seen, the highest priority management challenges include those that scored the largest number of respondents' votes – 81% and 55%. Therefore, the management of these organizations needs to focus on the development of special tools that allow for better provision of social services, as well as on increasing the organizational capital expansion.
The second question was asked to respondents in order to define the creative potential of the organizations under study (Figure 3).
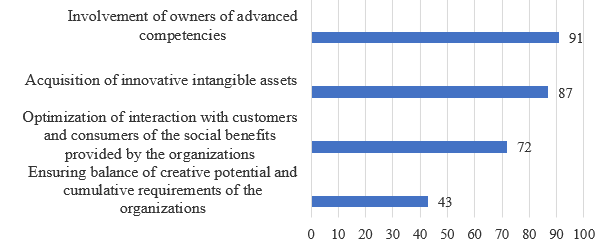
Source: compiled by the authors, based on replies to the questionnaire
Figure 3. Management challenges for the studied organizations aimed at creative capital expansion, %Respondents believe that the involvement of employees, who are carriers of intellectual capital (91% of respondents), in conjunction with the expansion of intangible assets (87% of respondents), enables nonprofit organizations operating in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous behavior to function stably in the market.
As shown by the data in Figure 4, the state provides insufficient support to the organizations under study: only 35% of the respondents answered positively to the question about state support.
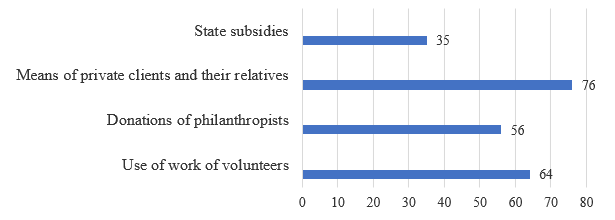
Source: compiled by the authors, based on replies to the questionnaire
Figure 4. Forms of state and public support for the activities of the studied organizations, %
Exploring the publications devoted to operation of non-profit organisations, the authors of the present article concluded that these papers are frequently of general theoretical nature or consider highly specialised issues connected with these organisations’ activities.
For instance, Kulkova (2016) develops the theoretical issues concerning the essence and characteristics of social entrepreneurship, which allowed her to identify the following characteristics of social entrepreneurship in her article: socially responsible risk, social transformation through implementation of social innovations, focus on a target group – people in a difficult life situation. However, the specifics of management of this type of organisations was not explored by her, which does not make it possible to see the nuances that must be taken into account by head managers of non-profit organisations working in the third sector of the economy. At the same time, the scholarly results derived by Kulkova, that might be considered close to the subject of the present research, reflect the following functions of social entrepreneurship, as identified by her: creation of a social value through involvement of a target group in entrepreneurial activity; innovations; altruism. The present study proves the need to involve the customers and consumers of social benefits in the processes of development and control, as concerns creation and distribution of these benefits, with respect to the profile of involved organisations, which makes it possible to achieve positive results.
Sesavin’s essay (2015) focuses on consideration of the conceptual apparatus serving as a basis for the study of the non-profit organisations sector. The researcher considers the core of the concepts “non-profit organisation”, “socially-oriented non-profit organisation” and “the third sector” and clarifies the definition of the “third sector” relative to the Russian realities. His research is undoubtedly relevant in terms of improving the theoretical and methodological platform for management of non-profit organisations; but unlike the study undertaken by the authors of this article, it is purely of theoretical nature and does not consider the specific features of governance of non-profit organisations.
Surovneva’s essay (2017) reveals the complexity of management activities of non-profit organisations, which leads to contradictions between the methods for achieving the set goals, the difficulties in assessing their priority and the achieved results. This position of the author is close to the one voiced in the present article, since it enables a researcher to take into account the specifics of non-profit organisations’ activities and points to the need to develop a special approach to management of these organisations. However, owing to the peculiar features of the explored subject area, Surovneva further substantiates the prospects of applying the principles of anti-crisis governance aimed at sustainable operation of non-profit organisations, which, in our opinion, narrows the range of possible management tools to the level of anti-recessionary management. One can agree with the author that the complexity of the ongoing socio-economic processes in Russia engenders the use of anti-recessionary methods in order to promote the development of non-profit organisations. However, as deemed by the authors of the present article, it is necessary, in addition, to explore the specific features of staff management of these organisations: the personnel must have certain competencies and skills in order to efficiently provide assistance to people in need of this aid in accordance with the goals set by the non-profit organisation.
The results of the research carried out by Shibaeva et al. (2016) are close to those voiced in the present study; the above authors highlight the issues of systemic approach to management of socially oriented non-profit organisations, showing the need for comprehensive account of the key factors contributing to the development and efficient performance of these organisations. In this regard, the cited article analyses the modern aspects of system management. Its authors, analysing the opinions of experts, confirm the relevance and validity of the governmental policy in relation to the “third sector”; prove the need for systemic approach to the realisation of programmes supporting non-profit organisations. This approach is supposed to increase the efficiency of such programmes with a view to contribute to the development of a socially orientated movement and in general, of the civil society, which is consistent with the results of the present study.
Other authors like Myronchuk and Khutyz (2017) explore the problems of non-profit organisations in accord with the positions of the authors of the present article. They define the principles of management of socially oriented non-profit organisations – similar to those used in the present research.
Summarizing the research results and relying on the experience of management improvement accumulated in nonprofit organizations involved in the study of the human factor correction, let us formulate and justify several principles for improving the management of these organizations.
The first principle is to ensure the proportionality of changes in the preventive and corrective branches of activity in these organizations to changes in social needs for relevant benefits. A study of the specific nature of nonprofit organizations showed the predominance of organizations with a corrective branch, which was confirmed by a larger number of nonprofit organizations of this profile. These findings lead to the following affirmations :
- the corrective branch absolutely dominates over the preventive branch, and this dominance is increasing;
- the specified dominance of the corrective branch is based on differences in the mechanisms of resource support of the specified branches. While the corrective branch is financed mainly through the payment of correction contracts by private customers, the preventive branch is funded mainly by private benefactors whose funds are insufficient to solve the existing problems. Public funds for prevention hardly accrue to nonprofit organizations and are spent by structures controlled by government bodies responsible for the corresponding tasks.
The absolute dominance of the corrective branch over the preventive branch of activity in the organizations under study means that they are embedded in the process of expanded generation of addictive behaviors. A clear deficit of preventive activities among young people inevitably leads to the fact that these organizations face with a constant increase in demand for specific benefits of correction for established and fixed addictive behaviors, which is more expensive. This situation is contrary to the global practice, which is characterized by the predominance of a preventive branch in such organizations (see, for example, Nkuba et al., 2019; Jones, 2004; Mares et al., 2016).
The second principle is the involvement of customers and consumers of social goods in the design and control processes for their creation and distribution in accordance with the profile of organizations. Social goods created and implemented by the organizations under study mostly relate to socio-psychological and socio-cultural services. This fact determines the need and opportunity for participation of those who pay for the creation of these goods and those to whom they are addressed at all stages of creating such goods. At the same time, improving the management of organizations implies the active involvement of these entities in the design and control processes for the creation and distribution of goods. The effective design and further creation of social goods that are essential for people entering or involved in socially dangerous behavior embedded in the structure of their personality involves a detailed study of these forms of behavior, and a relevant assessment of the human factor, including with respect to the assessments of those who are closely connected to these people and are willing to participate in the correction process. As provided in the paragraph above, the results correspond to global trends, according to which it is impossible to organize effective treatment for drug and alcohol addiction without the consent and desire of patients themselves. Treatment against their will gives low efficiency (Carr, 2011; Volkow and Li, 2005; White, 2009).
Conclusions
The analysis of responses from a survey of leaders of nonprofit organizations in the Southern Federal District allowed identifying and ranking the priority challenges of managing the organizations under study, which resulted in the following conclusions:
- the majority of experts gave their votes for the challenges of creating and replenishing the methodological tools of activity (81%) and accumulating the capital of organizational culture (55%), which allows qualifying them as primary challenges of managing the organizations under study in this direction;
- less than 25% of experts gave their votes for the challenges of creating and developing a special infrastructure for supporting activities and creating and replenishing the technology portfolio of organizations' activities, which allows attributing them to the ordinary tasks in this area;
- the distribution of expert votes reflects the specific features of activities in the field of human behavior correction – weak interaction between different organizations in the sphere, their desire to act independently from the state and local communities, along with poor technological equipment of organizations and the shortage of employees who are prepared to work with technologies for correcting the human factor.
These results can be used as a basis for international discussion. The authors were unable to find studies regarding the specifics of managing nonprofit organizations in the field of prevention and correction of socially dangerous forms of behavior.
