The effect of e-Learning practices during the Covid-19 pandemic on enhancing self-regulated learning skills as perceived by university students
Abstract
This paper aimed to investigate the effect of e-Learning practices during the Covid-19 pandemic on enhancing SRL skills as perceived by university students. One hundred –eighty students participated. They aged from 19-21 years ( M=20.3 years, SD= 2.01). An electronic questionnaire using (Google doc) was developed, and distributed it electronically via social networking sites, and a total of (180) responses were manipulated. A descriptive and analytical approach was employed, for its relevance to the topic and objectives of the study, as it studies a phenomenon, event or issue that currently exists from which information can be obtained that answers the research questions without the researcher's intervention. It is evident that the score of individuals for the role of electronic teaching practices during the Corona pandemic in enhancing their SRL skills was average at a relative weight (68.42%). There are no statistically significant differences at the level of significance (α≤ 0.05) between the average scores of the sample members ’assessment of the role of electronic teaching practices during the Corona pandemic in enhancing their SRL skills due to the Major variable.
Keywords:electronic teaching practices; Corona pandemic, self-regulated learning skills; university students
Introduction
The Corona virus pandemic in early 2020 was a great impetus for universities and institutions to implement the calls that preceded them to implement e-learning, adopt teaching practices remotely as a substitute for face education, and depart from the traditional pattern of education to the default as a requirement that had to keep pace with digital transformation before it was a forced response to face the repercussions Corona virus pandemic affects different areas of life.
Whereas e-learning with its various names refers to relying on modern technologies in providing educational content in an effective manner and teaching practices characterized by shortening time, effort and economic cost, and with great capabilities that reach a greater number than the perceived learners (Yen, Lee & Enriquez, 2018), in addition to providing an interesting educational environment through which determinants are eliminated Time and Place (Al-Atribi, 2019).
Learning is now considered, thanks to technological development, an ever-evolving and renewed process, and therefore it is no longer acceptable that the goal of education, whether (traditional electronic) is limited to the transfer of information and knowledge, but rather it should grow towards the search for knowledge and learning how to learn (Walid, 2011).
Therefore, all the educational theories emphasized that learning is an individual issue, in which the learner must use his own way of thinking, and thus e-learning will be more needed than traditional education for a learner able to direct his own learning, and to manage the sources of knowledge, organization, control, and self-evaluation. So that he is aware of his role in terms of choosing strategies that enable him to overcome challenges (Abu Hamid, 2013).
The Corona pandemic has posed a great challenge to universities and students in terms of the difficulties facing the education process. At the level of universities that did not adopt e-learning, they are facing difficulties in quality control, training faculty members, technological literacy among students, employing special programs and evaluation and accreditation mechanisms, and on the level of students in terms of providing the capabilities and requirements, and the need to integrate research and scientific skills with strong time management (Basilaia & Kvavadze, 2020).
Accordingly, SRL has become crucial to achieving academic success, because the university student becomes responsible for learning and managing his resources, setting his goals and achieving them (Eissa, 2015).
SRL represented a new and important curve to students' academic achievement. Previously, student achievement was studied in relation to measurements of their ability, the quality of teaching, or the educational and home environment. As for the theory of self- regulated learning, it is concerned with how students themselves activate, adjust and enhance their own learning practices in educational contexts. Especially, flexible time frames, and extensive personal knowledge, which e-learning can require (Ozen & İlke, 2016; Eissa & Ayman, 2020).
The reality of higher education in general appeared, focusing on the traditional method of teaching, which is based on indoctrination (centered around the teacher), and that knowledge is an end in itself, without considering the activity and effectiveness of the student and his way of thinking, and how he acquires information, which increased the gap digital among the skills of graduates and the requirements of the labor market, and thus self-regulated learning has become a necessity for students to learn how to learn?) more than (What do they learn?), and for students to be more free and individual in making decisions, taking responsibility in learning, and using various types of thinking. The rapid response of Egyptian universities to the repercussions of the Corona pandemic, in order to ensure the achievement of the minimum quality of education, has led to the necessity of adopting electronic practices regardless of levels of culture, material capabilities and level of readiness, which necessitated ensuring their role in enhancing self-organized education skills, in light of the lack of face to face learning , as a precaution to prevent the spread of the Corona virus, and the adoption of electronic education as an inevitable coercive measure.
Significance of the current study coincides with the sensitivity of the role of universities and the shift in their performance during the Corona pandemic, and demonstrating the ability of their electronic practices to achieve the quality of education at a time when the influence of the Corona virus on the course of public life has expanded.
Literature Review
The crises caused by the Corona pandemic have become part of people's lives, and a source of concern for officials due to the difficulty in controlling the virus, and the lack of access to a treatment for it until today (Shazia & Sunishtha, 2020). Since universities are like other institutions, they will inevitably be affected by profound transformations that may cause an irreversible rift in their functions if they do not deal with their implications accurately in decision-making, in gathering and retaining information, and how to employ them academically and administratively (Weeden & Benjamin, 2020).
The Corona pandemic has caused a shock that is not easy not only at the local level for universities, but also at the global level, which has had a great impact in changing the form of academic work and its priorities (Murphy, 2020). Development and employment of educational theories in the field of making use of technology and interactive tools to enrich the learner experience. Because e-learning as a real practice needs more time in planning and providing means for designing educational materials and evaluation mechanisms (Haleem et al., 2020).
Accordingly, we must realize that this emergency transformation has caused a crisis that has had profound consequences, as the burden has shifted to faculty members and students alike, so the faculty member has become exceptionally demanding of the necessity of a rapid shift towards virtual (distance) education and program learning, and the necessary applications, which is a tedious effort for those who wanted to be devoted in education, evaluation and follow-up (Tadesse & Muluye, 2020).
Although the Corona pandemic imposed a shift in the vision of the universities' mission, by adopting distance education as a basis for maintaining the minimum quality of education (Chick,2020), it is not necessary to consider that the use of modern technologies and electronic media in the teaching and learning process is no longer a luxury, but rather a necessity that requires keeping pace with the age of information through the use of programs, practices and electronic courses partially or completely (Basilaia & Kvavadze, 2020).
In order to ensure the success of these practices, a set of skills is required, the most prominent of which is the learner's ability to direct his own learning as it includes interaction with others, self-monitoring and motivation (ElAdl & Eissa, 2019; Mostafa, 2016; Habib, 2015; Yilmaz & Erkan, 2014), to be more able to control, plan, control and correct, and this of course requires the learner to be aware of his role in terms of choosing the resources and strategies that enable it to overcome the challenges it faces (ElAdl & Yousra, 2020).
Online teaching practices through the university platforms have become inevitable after the Corona pandemic imposed the closure of universities and social distancing, but the matter faced many difficulties, especially since most of the regular universities and their students were not prepared to use this type of teaching and learning. Despite what many studies (e.g. Al-Juhani, 2017 Al-Rashidi, 2020; Mahmoud, 2019) have proven of the effectiveness of e-learning in helping the learner adapt to life to face its problems, and the use of knowledge outcomes in thinking and making immediate and future decisions .However, the level of benefit is often linked to the quality of teaching and evaluation, which was confirmed by the study of Hinnawi (2018) as the matter related to electronic or distance education did not take its luck after the training and spread and the orientation towards it was surprising, it did not exceed digitize content, electronic tests, or simple costs and assignments. The concept of SRL refers to the set of subjective actions undertaken by the learner influenced by self-efficacy (Kilic, Yavuz & Şükrü, 2013; Mostafa, 2018) and cognitive factors, the ability to employ learning strategies and cognitive factors, and the ability to employ learning and meditation strategies to obtain an advanced level of achievement.
Al-Rashidi (2020) indicated that SRL is crucial to achieving academic success, especially in the higher education stage, as it helps students to pursue their educational tasks effectively, and to identify strengths and weaknesses at their level. The Al-Sa`ida study (2015) confirms that students of SRL are described They are highly motivated, because they have a greater willingness to participate for a longer period of time when performing educational tasks, and they also practice their educational experiences efficiently and in different ways, and they have a wide repertoire of cognitive and metacognitive strategies (Abdul Khalik, 2014), and they have the ability to rearrange and organize themselves, and define their goals.
According to the above, the purpose of this paper is to investigate effect of e-Learning practices during the Covid-19 pandemic on enhancing SRL skills as perceived by university students.
Hypotheses
H.1: University students in Egypt appreciate the role of electronic teaching practices during the Corona pandemic in enhancing SRL skills (Cognitive skills; Meta-cognitive skills; Resource management skills, and Motivation effort skills) to a large extent.H.2: There are no statistically significant differences at the level of significance (α≤ 0.05) between the average scores of the sample members ’assessment of the role of electronic teaching practices during the Corona pandemic in enhancing their SRL skills due to their Major (Arts - Science).
Methodology
Sample and Procedure
The study population consisted of all students of the Higher Institute of Social Service in Cairo, the Faculty of Specific Education in Cairo, the Faculty of Pharmacy at Kafr El-Sheikh University, and the study sample was determined in a random way in view of the exceptional circumstances that societies pass through from home quarantine, where the researcher prepared an electronic questionnaire using (Google doc) and distributed it electronically via social networking sites, and a total of (180) responses were manipulated. Students aged from 19-21 years (M=20.3 years, SD= 2.01). Those who answered all the questions of the survey and sent them back were as follows: 90 (50%) students from Faculty of Pharmacy at Kafr El-Sheikh University, 80 (44.4%) students of the Higher Institute of Social Service in Cairo, 10 (5.6%) students from the Faculty of Specific Education in Cairo.
Survey
Digital citizenship Survey (By the author). The researcher designed a questionnaire of students ’assessment of the role of electronic teaching practices during the Corona pandemic in enhancing SRL skills, as it consists of two parts: the first part is personal data, and the second part consists of (41) paragraphs distributed into four areas: (Cognitive skills, Meta-cognitive skills, Resource Management skills, Motivation effort skills). The questionnaire used the Likert scale of five ranks ranging from very large to very weak to determine the degree of need so that a certain score was given to each response as follows: very large (5 Ms), Large (4Ms), Medium (3Ms), Weak (2Ms) and very weak (1M.). Thus, the total score ranges from 41 to 205 scores. The reliability of the scale in terms of internal consistency was assessed by Cronbach’s α. α = 0.836.
Design
The researcher followed the descriptive and analytical approach, for its relevance to the topic and objectives of the study, as it studies a phenomenon, event or issue that currently exists from which information can be obtained that answers the research questions without the researcher's intervention.
Results and Discussion
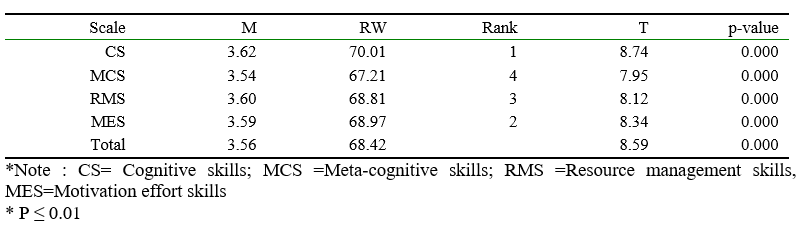
To verify the first hypothesis, which states " University students in Egypt appreciate the role of electronic teaching practices during the Corona pandemic in enhancing SRL skills (Cognitive skills; Meta-cognitive skills; Resource management skills, and Motivation effort skills) to a large extent", mean, standard deviation, relative weight, order, and T-test were used for one sample, as shown in table 1. It is evident from Table1.that the score of individuals for the role of electronic teaching practices during the Corona pandemic in enhancing their SRL skills was average at a relative weight (68.42%). This result goes in the same line with the results from previous research (e.g. Alenezi, 2020; Broadbent & Poon, 2015; Dwi, Nur, Septi & Sanidi, 2020; Green et al., 2015; Poitras & Lajoie, 2018) which have demonstrated a significant positive role for e-learning in enhancing SRL skills. That the great momentum in the use of these practices came recently, despite the fact that recognition of them as a synonym for face education was old, due to the forced circumstance created by the Corona pandemic related to social distancing and the closure of universities, as the level of acceptability, quality and effectiveness of these practices varied by students and faculty members. Cognitive skills came first with a relative weight (70.01%) to a large degree, and metacognitive skills occupy the last place with a relative weight (67.21%) with a medium degree. This result goes in the same line with Al-Ruwaili's Study (2018) which indicates that students are still lagging behind in their ability to handle their own learning, although metacognitive skills help online learners handle their own learning and the approaches they use to interact with specific learning systems (Tsai, 2009).
The reason for metacognitive skills occupy the last place is the fact that these skills relate to higher thinking strategies that students are not used to in traditional education, and that most of the students' responses to these electronic practices came within the framework of fulfilling the requirements for success in the courses offered without careful consideration on the impact of learning or the need to link to previous experiences or predictions based on data, which was confirmed by Al-Rashidi study (2020) which indicates that students are not used to higher thinking strategies.
Table 1.
Mean, standard deviation, relative weight, Rank, and T-test on Digital Citizenship Survey.
To verify the second hypothesis , which states" There are no statistically significant differences at the level of significance (α≤ 0.05) between the average scores of the sample members ’assessment of the role of electronic teaching practices during the Corona pandemic in enhancing their SRL skills due to their Major (Arts - Science)", One Way ANOVA was used , as shown in table 2. There are no statistically significant differences at the level of significance (α≤ 0.05) between the average scores of the sample members ’assessment of the role of electronic teaching practices during the Corona pandemic in enhancing their SRL skills due to the Major variable, and the reason for this may be attributed to the practices adopted by universities were inclusive of all students, with the difference in the method of presentation or evaluation from one college to another, but it was in one learning platform, and one method of communication. This result goes in the same line with the results of Shaheen, &Rayan's (2013) which indicate that There are no statistically significant differences at the level of significance (α≤ 0.05) between the average scores of individuals due to the Major variable.
Table 2.
The results of ANOVA for the differences between the mean scores of the sample due to their Major (Arts - Science)

Conclusion
The results of this study demonstrated a significant positive role for e-learning in enhancing SRL skills. That the great momentum in the use of these practices came recently, despite the fact that recognition of them as a synonym for face education was old, due to the forced circumstance created by the Corona pandemic related to social distancing and the closure of universities, as the level of acceptability, quality and effectiveness of these practices varied by students and faculty members.
