New challenges for the defense industrial enterprises of Ukraine in the conditions of the global pandemic
Нові виклики підприємствам оборонно-промислової галузі України в умовах глобальної пандемії
Abstract
The global COVID-19 pandemic has made significant corrections to international trade in many countries around the world. The article is devoted to topical issues of identifying new challenges that have arisen at entities of the defense industry of Ukraine in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Comparative analysis of forced changes in defense budgets of different countries and statistical analysis of industries that are connected by supply chains with enterprises of the defense industry of Ukraine, which suffer from the introduction of quarantine restrictive measures, proves restrictions on interstate trade, disruption of domestic and global supply chains and significant losses in the economy. This situation may have medium-term consequences for the country's defense budget, and the Ministry of Defense of Ukraine will be forced to apply optimization plans for effective measures of such a scale as modern sequestration. India, Thailand, and South Korea are identified as the most risk-sensitive counterparties of Ukrainian defense exporters due to the reorientation of finances to the priority segment of medicine to eliminate the consequences of the pandemic. To minimize the risk of non-performance of contractual obligations, it is recommended to review the basic terms of supply of goods under the contracts with risk-sensitive counterparties and make adjustments to force majeure clauses in regard to epidemics, as well as possible revise the contract's payment terms.
Keywords
defense budget, defense industrial enterprises, defense equipment and weapon, global pandemic, Ukraine.
Анотація
Глобальної пандемія COVID-19 внесла значні корегування міждержавної торгівлі багатьох країн світу. Стаття присвячена актуальним питанням визначення нових викликів, які з’явились у підприємств оборонно-промислової галузі України в умовах пандемії COVID-19. Компаративний аналіз вимушених змін оборонних бюджетів різних країн та статистичний аналіз індустрій, які пов’язані ланцюгами постачання з підприємствами оборонно-промислового комплексу України, котрі потерпають від введення карантинних обмежувальних заходів доводить обмеження міждержавної торгівлі, порушення внутрішніх та глобальних ланцюгів постачання та нанесення суттєвих збитків український економіці. Така ситуація може мати середньострокові наслідки для оборонного бюджету країни, а Міністерство оборони України вимушено буде розробити оптимальні плани ефективних заходів такого масштабу, як сучасна секвестрація. Найбільш ризик-чутливими країнами-контрагентами українських спецекспортерів визначається Індія, Таїланд та Південна Корея у зв’язку з переорієнтуванням фінансів на приоритетний сегмент медицини для ліквідації наслідків пандемії. Для усунення ризиків невиконання контрактних зобов’язань рекомендується перегляд основних умов поставок товарів за контрактами ризик-чутливих країн-контрагентів та внести корегування по форс-мажорним обставинам в умовах епідемій, а можливо і переглянути платіжні умови договорів.
Ключові слова
оборонний бюджет, оборонно-промислові підприємства, військова техніка та озброєння, глобальна пандемія, Україна.
Introduction
The global pandemic COVID-19 has made a significant correction to international trade in many countries. Significant damage to the economies of countries due to the suspension of work of the majority of enterprises in the national defense industry and countries with strong economic potential. Disruption of domestic and global supply chains can have medium-term consequences for the defense budgets of many countries and negatively affect the implementation of international and foreign commercial contracts of special exporters around the world. The question of whether Ukrainian exporters should worry in the face of emergency changes in the defense budgets of counterparty countries is a key aspect of the study in the context of quarantine restrictions.
Ukraine, like most countries in the world, ignored the warning of the catastrophic consequences of a possible global pandemic in 2020, which was published by representatives of the Global Monitoring Council (GPMB), the World Bank, and the World Health Organization in the report World at Risk (Global Preparedness Monitoring Board, 2019) on September 19, 2019. The authors warned of the catastrophic scale of the global pandemic, which could create widespread destruction, instability, and insecurity, and a 5% decline in world GDP because of the high probability of conflict, health problems in poor countries, and increasing migration. Undoubtedly, ignoring such warnings has had devastating consequences not only for the economies of poor countries but also for economic crises in powerful states. This could not be reflected in the enterprises of the defense-economic sector, which faced new challenges and threats of even further existence, especially small and medium-sized businesses, which are represented by more than 150 private enterprises in the defense industry.
The purpose of the study is (a) to analyze the change in defense budgets of major countries- contractors under international contracts of Ukraine for the supply of military machinery, equipment, and weapons for further forecasting of risks and threats during their implementation in the global pandemic COVID-19; (b) a study of the impact of the new challenges and threats of the global COVID-19 pandemic on the activities of military-economic sector enterprises in restricting interstate trade and disrupting domestic and global supply chains. To achieve this goal in the work it is necessary to perform the following tasks:
- to analyze the changes in the defense budgets of major countries - counterparties to international contracts of Ukraine for the supply of military machinery, equipment, and weapons for further forecasting of risks and threats during their implementation in the global pandemic COVID-19;
- to study the state of defense enterprises at the beginning of 2020;
- to single out the problems of development of the defense-economic sector during the period of quarantine measures;
- to identify new challenges and threats to the global COVID-19 pandemic in the activities of defense enterprises;
- to propose strategic ways to optimize the activities of defense enterprises in the conditions of possible cyclical repetition of quarantine measures in the medium-term forecast.
Thus, the analysis of new challenges and the development of ways to minimize the risks of the global pandemic on the work of defense industry is a topical issue today, which should be taken into account during developing the Defense Strategy and State Defense Plan, the structure of which was approved by the Presidential Decree of Ukraine № 61/2020 dated March 03, 2020 (President of Ukraine, 2020). The results of this study may be relevant in approving the plan of priority measures to ensure the sustainability of the defense-industrial complex of Ukraine in the global pandemic COVID-19.
Literature review
Studies of the impact of the global pandemic COVID-19 on the national defense budgets of different countries are defined in the works of Ukrainian and foreign scientists and military analysts: Badrak, V. (Badrak, 2020), Darling, D. (Darling, 2020), Gilani, I. (Gilani, 2020), Egel, D., Shatz How. J., Kumar Kr.B., Harshberger, Т. (Egel, Shatz, Kumar & Harshberger, 2020), Korb, L.J. (Korb, 2020), Zgurets S. (Zgurets, 2019). The NATO military budget was studied by Tkachenko, N., Kurmaiev, P., Seliverstova, L., Pozhydaeva, M. (Tkachenko, Kurmaiev, Seliverstova & Pozhydaeva, 2020). At the present stage, the issues of development and problems of the enterprises of the defense industry of Ukraine were considered by such scientists and specialists as Begma V. (Begma & Skliar, 2013), Gorbulin V. (Gorbulin, 2019), Tolok P. (Tolok, 2020) and others.
But in the face of rapidly evolving global and national challenges and threats, it is important to shed light on the economic impact of the COVID-19 global pandemic on the activities of defense exporters to possibly address dangerous consequences at all levels.
Methodology
In this article, the authors used a comparative analysis of forced changes in defense budgets of different countries and economic and statistical analysis of industries that are connected by supply chains with enterprises of the defense industry of Ukraine, which suffer from quarantine restrictions. Statistics which are reflected in the materials of SIPRI, defense budgets of NATO countries, Thailand, South Korea, India, China, and Ukraine were used to compile the results of the study, The materials of National Institute for Strategic Studies (Ukraine) were used in the analysis of the state of enterprises of the defense-industrial complex of Ukraine.
Comparative analysis of changes in defense budgets of major countries - contractors under international contracts of Ukraine for the supply of military equipment
In May 2020 the Ministry of Defense of Ukraine has identified areas for the use of budget funds for the development, purchase, modernization, and repair of weapons, military machines, means, and equipment, the planned expenditures are UAH 22.735 million according to the budget program, of which the general fund is UAH 22.703 million, the special fund is UAH 35.812 million (Ukrainian Military Pages, 2020). Special exporters of military and dual-use goods are important actors in filling the state budget of Ukraine. State Concern "Ukroboronprom" announced a record increase of 37% of the state defense order in 2020, compared to 2019. Following the results of 2019, the special exporters that are part of the concern exported products worth USD 908 million (Hordon, 2020). But the company's management suggests that in the long run, defense spending may be reduced due to the priority of funding of the medical segment to eliminate the effects of the pandemic. In addition, the restriction of interstate trade, the closure of borders, and the disruption of global supply chains can adversely affect the implementation of defense exporters' contracts and the early fulfillment of contractual obligations by counterparty countries. To date, the Ukrainian government continues negotiations to purchase three large consignments of weapons from the United States, needed to protect the state in the east of the country (Defense Industrial Courier, 2020). But quarantine restrictions hamper this process and could negatively affect the supply planned for this year.
The main export countries of the Ukrainian defense industry are Thailand, China, Turkey, Pakistan, India, Saudi Arabia, the United States, Azerbaijan, Algeria, Jordan, and the Republic of Korea. Let's try to analyze whether the unstable epidemiological situation in the main contracting countries can affect the performance of contracts of defense exporters of Ukraine?
The global pandemic causes a rapid response of countries and revision of economic budgets not only of underdeveloped countries but also of countries with strong economies. SIPRI experts predict a significant reduction in the US defense budget for the next couple of years, as the US government is likely to spend USD trillions trying to save the economy from the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic (Korb, 2020). Even the largest American corporation Lockheed Martin has suspended production of a new generation F-35 fighter at a plant in Japan due to the threat of the coronavirus danger. Lockheed Martin produces most of the F-35s in the Texas plant, but the fighters, which are exported to the Allies, are assembled in Japan and Italy (Вaltnews, 2020).
Despite loud calls from NATO on increased the risk of new technologies and aggressive behavior by Russia and China, the European Commission has already cut European projected defense spending in the next seven-year budget by almost half from EUR 13 billion to about EUR 6 billion (Erlanger, 2020). Le Figaro notes that “defense loans will take ten years to rise. This fuels the concerns of French arms manufacturers, who have just called for a concrete stimulation plan to support the French and European defense industrial and technological base and to ensure the strategic autonomy of the Old Continent” (Вaltnews, 2020).
The Thai military has cut it's budget and suspended artillery purchases as millions of Thais, suffering from the negative economic consequences of the coronavirus outbreak, expect financial assistance from the government. The Thai Army became the last unit of the armed forces to reduce its budget for 2020 by about THB 10 billion (USD 441 million) in April out of a total of THB 18 billion allocated by the Thai Ministry of Defense (Techakitteranun, 2020).
South Korea has planned a 1.8% reduction in defense spending, amounting to about KRW 900 billion (USD 733 million) in the second supplementary budget in search of funds to mitigate the effects of the economic downturn and social upheaval following the pandemic of the new COVID-19 coronavirus. in comparison with the initial costs for 2020. The main part of the reduction will be the share of expenditures on the purchase of weapons in the amount of KRW 712 billion, and the other part - on operating costs (Darling, 2020).
Despite the fact that the COVID-19 pandemic is forcing governments around the world to slow down spending, India has been able to withhold 15-20% of the funds allocated to the country's Ministry of Defense in the first quarter of 2020. Experts believe that if the cuts continue in the coming quarters of the year, replenishments in the defense budget could fall as much as 40%. Military analyst Ajay Shukla estimates that the defense ministry could lose INR 800 billion (USD 10.54 billion) by the end of the year, most likely due to reduced arms purchases, military modernization, and even existing commitments. And India's foreign military procurement policy in 2020 against the background of restrictive quarantine measures tends to postpone the import of weapons, financing the national economy and concluding new contracts for the purchase of military equipment with domestic manufacturers (Gilani, 2020).
Unlike other countries, China is not going to significantly reduce its defense spending, even with the economic consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to a 6.8% contraction in the first quarter of 2020 compared to the same period of last year. China has announced a 6.6% increase in its defense budget in 2020 (7-7.5% in 2019), the lowest figure in three decades.
The growth of China's defense budget will increase spending from USD 167 billion in 2019 to USD 178.2 billion, or about USD 11 billion, which is the fifth-largest growth rate across the country (Yeo, 2020). The country has the second-largest defense budget in the world, second only to the United States.
Problems of development of the military-economic sector of Ukraine
During the continuation of hostilities in eastern Ukraine, the defense-economic sector is in a difficult situation, which includes not only the defense industry but their logistics system, labor and financial resources allocated for defense needs, as well as the system of commercial relations within the defense organization of the state and the relations of this organization with the civil sectors of the economy and international cooperation. Significant destruction of industry in the Eastern regions which used to be the mainstay of the real sector for decades, and the associated negative processes in the military-industrial complex, disruption of logistics trade flows in foreign trade in military and dual-use goods, rapid reorientation of markets, growth of the shadow economy, trade, information and cyberwars, a significant outflow of scientific potential from the country, essentially hampered economic and geopolitical development of the country. At the beginning of 2020, the plan of revenues to the state budget was fulfilled only by 81.8%, and non-fulfillment reached UAH 43.4 billion, with a shortfall in customs of UAH 23.1 billion, and in the tax service - more than UAH 17 billion (Kramar, 2020). According to the operative data of the State Treasury Service for January-November 2020, expenditures on the general fund of the state budget amounted to UAH 940.6 billion, or 90.3% of the schedule of the reporting period. At the same time, social expenditures, defense expenditures, debt service and subventions and subsidies to local budgets are fully financed in accordance with the schedule on the basis of payment orders. In January-November 2020, the state budget was executed with a deficit of UAH 117.2 billion, including the general fund with a deficit of UAH 130.7 billion when the general fund of the reporting period was signed in the amount of UAH 236.9 billion (Ministry of Finance of Ukraine, 2020).
The state of the Ukrainian defense-industrial complex enterprises
Since 2000 Institutional imbalance with repeated changes in approaches to the management of defense industry enterprises in Ukraine has led to a lack of enterprise development strategy, consistent with the national military-industrial policy, and complicated the concentration of financial resources in priority areas. As Gorbulin V. notes, unsystematic measures in reforming the defense industry of Ukraine resulted in a gradual "washing away" of its specific features as a branch of the defense sector, lowing down it to the level of civilian industries. Ukraine's defense industry, in many of its components, has lost the ability to create and mass-produce the latest models of weapons - according to experts, Ukraine could produce in a closed cycle no more than 5% of the range of weapons required by the Armed Forces. Ukrainian arms overhaul enterprises were in a slightly better condition, but they also faced great difficulties, mainly due to the lack of necessary spare parts, in particular traditionally produced in Russia, as relations with Russia deteriorated from year to year, and official relations with the military-technical cooperation has virtually ceased (Gorbulin, 2019).
At the end of 2019, the defense-economic sector of Ukraine included 167 state-owned enterprises and about 150 private companies, more than 130 of which are subordinated to Ukroboronprom, 12 enterprises are subordinated to the State Tax Administration and 8 enterprises are subordinated to the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
From UAH 101 million (USD 3.4 billion) of the Ministry of Defense budget for 2019, UAH 16.3 billion was allocated for the development and purchase of new and modernized weapons and military equipment within the framework of the State Defense Procurement (USD 580 million) (Zgurets, 2019). Taking into account that the military confrontation in eastern Ukraine has demonstrated the inability of the national defense industry to meet the needs of the Armed Forces on a critical range of weapons, such a budget is insufficient for large-scale rearmament of all types of troops in the required number. As of 2019, according to the MOU, completeness with weapons and equipment of combat units was 95%, and the coefficient of technical serviceability of weapons - 85%. The total number of equipment and weapons, which is part of the arsenals of the Armed Forces of Ukraine, according to rounded indicators is tanks - 1100 nos; BMP - 1900 nos; APC - 1500 nos; art systems with a caliber of more than 100 mm - 1800 nos; helicopters - 130 nos; combat aircraft - 180 nos; military transport aircraft - 30 nos; Navy ships and boats - 9 nos. (Zgurets, 2019). Due to the lack of a proper scientific, technological, and production base, Ukrainian defense companies will not be able to provide the Armed Forces with combat aircraft and helicopters, anti-aircraft missile systems, naval weapons, most ammunition, large-caliber artillery systems, and small arms. To date, Ukrainian defense-industrial enterprises in cooperation with relevant research institutions are developing some new and modernizing existing weapons in those areas of the defense industry in which the country has retained the relevant scientific and technical potential: missile, aircraft, and armored vehicles. Volumes of manufactured military products at defense industry enterprises of all forms of ownership in Ukraine in 2014-2019 is presented in Тable 1.
Table 1.
Indicators of manufactured military products by defense industry enterprises of all forms of ownership in Ukraine in 2014-2019, UAH million.
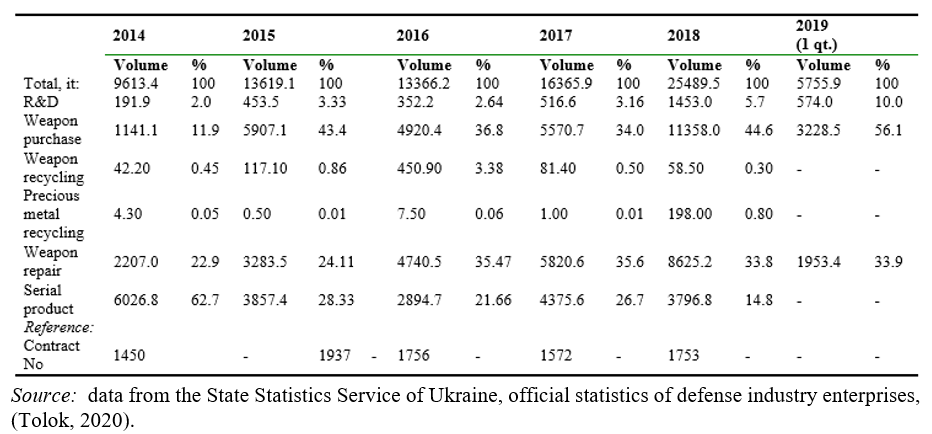
According to the analysis of military products indicators at the enterprises of the defense industry, the insufficient level of serial production is determined (28.33% in 2015 and 14.8% in 2018), the R&D low level of financing for the development of new equipment by enterprises (including insufficient funding from the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade of Ukraine to production preparation for new military equipment), the intersection of R&D and serial production at one enterprise, which reduces the quality of research and development or increases the cost of production (Tolok, 2020).
Out of the 167 state-owned enterprises of the defense industry, which are concentrated in the State Concern "Ukroboronprom", only 57 are profitable enterprises. Wage arrears at unprofitable enterprises of the state concern as of September 2019 - UAH 1.1 billion (Zgurets, 2019), which led to a significant outflow of highly qualified personnel in recent years. Thus, according to the trade union of aircraft manufacturers, 1515.8 thousand people worked in the defense industry of Ukraine in 1993, in 2003 this number is 356.8 thousand people and 133.6 thousand people in 2018 (Trade unions of aircraft builders of Ukraine, 2020).
The priority areas of State Defence Procurement (SDP) for 2019 were the completion of the development of the latest weapon, modernized models of existed armaments and military equipment, their adoption and supply to the Armed Forces. These are missile systems, self-propelled artillery howitzers, multiple rocket launchers, reconnaissance and artillery guidance means. But not all projects were completed in full (manufacture of new armored vehicles BTR-4) (Zgurets, 2019).
In 2014-2019, the private sector of the defense industry had been actively developed (more than 150 enterprises at the end of 2019, manufacturing 2/3 of the total product). A decrease of 22% in the performance of State Defence Procurement works by the enterprises of Ukroboronprom in 2016 was determined (38%) compared to 2015 (more than 60% of works). And 69% of the volume of State Defence Procurement was performed by private enterprises in 2018. This trend has continued to this day.
COVID-19 influence on the defense Industry Enterprise аctivity results
In 2020 the outbreak of a global pandemic has highlighted new challenges for all branches of military leadership. Rapid change of a number of ministerial positions, the inconsistency of administration in the Armed Forces, the introduction of quarantine measures, for which no branch of the Ukrainian government was ready, ignoring the warning Global Readiness Monitoring Council (GPMB) of September 19, 2019 (Global Preparedness Monitoring Board, 2019), led to:
- the need for emergency decrees to protect the personnel of the Armed Forces,
- delays in signing contracts with suppliers of the Armed Forces,
- slowing down the government's work on strategic issues,
- untimely formation of the main and real factor in the preparation of the defense of the future State Defense Order 2020. By Decree of the President of Ukraine No 59/2020 of 27.02.2020(President of Ukraine, 2020) approved only the main indicators of SDP -20, the rest must be finalized in the process of work, followed by dispersing and unbalancing of all components of the state security,
- distinguishing and unbalancing all components of the security sector.
In 2019, despite the availability of significant financial resources provided to the MOU for the implementation of state programs for the development of armaments and military equipment, the Defense Ministry has effectively blocked the use of funds for these purposes. Multibillion-dollar funds were not used to develop and purchase new and upgraded weapons. Only due to the accumulation at the end of 2019 several billion unspent hryvnias, in the absence of State Defence Procurement 2020, some defense industry enterprises were loaded during quarantine measures. On budget funds for 2019, the Lutsk missile cluster of the Luch State Design Bureau is operating in full mode in 2020. But many companies are almost completely destabilized: the 410th Aircraft Repair and Kharkiv Aircraft Plant; Chuguiv Aircraft Plant work one day a week, producing four products ordered by the military for the allocated money; HC Ukrspetstechnika was forced to go into full quarantine before the appearance of State Defense Procurement 2020 (Badrak, 2020).
The situation is similar in the private sector. Only those private enterprises with which the contracts of the Ministry of Defense were concluded at the end of 2019 or those that perform long-term contracts of previous years are in a part-time working week. Under quarantine measures, defense industry enterprises suffer significant losses, including due to restrictions on international trade, disruption of domestic and global supply chains. The reasons for this situation are that the defense and economic sector, which includes not only enterprises of the defense industry, but also their material and technical support system allocated for defense needs in labor and financial resources, as well as the system of economic relations within the state defense organizations and the organization's relations with the civilian sectors of the economy and international cooperation. Industries that are connected by supply chains with defense industry enterprises and the system of defense logistics that suffer from the introduction of quarantine restrictive measures are listed in the Тable 2.
Table 2.
Industries that are connected by supply chains with defense industry enterprises that suffer from the introduction of quarantine restrictive measures, Ist quarter 2020.
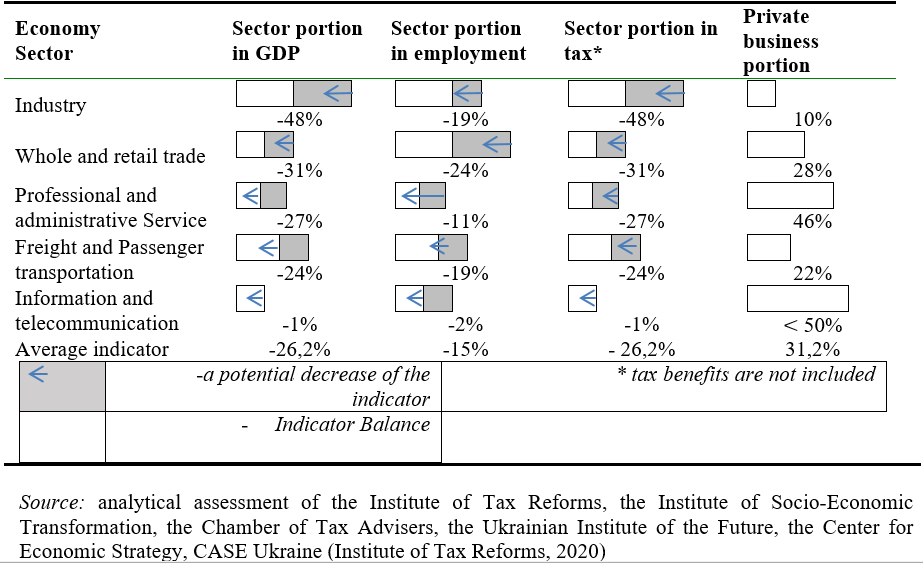
According to the Chamber of Commerce and Industry, at the beginning of May 2020 about 600-700 thousand enterprises, small entrepreneurs, and educational institutions, which employ 3.5-4 million people, stopped working due to quarantine. This is about 1% of all businesses and employees operating in Ukraine.
According to the analytical assessment of the Institute of Tax Reforms, the Institute of Socio-Economic Transformation, the Chamber of Tax Consultants, the Ukrainian Institute of the Future, the Center for Economic Strategy, CASE Ukraine, the continuation of restrictive quarantine measures could lead to the economic decline of more than 4-5% (Institute of Tax Reforms, 2020).
Ukrainian defense industry enterprises work at the world armaments market in the segment of aircraft construction, armored vehicles, and ammunition. In recent years, Ukrainian goods have been represented in the shipbuilding markets only by the export of components to hovercraft.
During 2018-2019, the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade of Ukraine focused on the implementation of key goals and objectives of strategic directions of development of the defense and security sector of Ukraine. The total volume of exports of weapons and services of public and private defense enterprises amounted to about USD 1 billion, of which USD 766.3 million accounted for the export of enterprises of Ukroboronprom. In 2018, the key exporters were Ukrspetsexport (USD 256 million) and SE "Antonov" (USD 223 million). In the total volume of exports of SE "Antonov" 88% of revenues are air transportation services (Zgurets, 2019). In 2019, Ukroboronprom's exports amounted to USD 908 million, which is 19% higher than in 2018.
In early 2020, the management of Ukroboronprom predicted an increase in exports by 30% (up to USD 1.18 billion) but does not rule out the negative impact of restrictive quarantine measures in Ukraine and around the world (Badrak, 2020). This is due to the restriction of interstate trade, disruption of domestic and global supply chains, and possible revisions of military budgets of counterparty countries. Thus, the management of the Concern may face not only problematic issues related to the planned reorganization of six corporations instead of Ukroboronprom, specialized in missile construction, aircraft construction, armored vehicles, radar, and marine systems and aircraft repair, but also pandemics overcoming a challenge, especially if during 2020 the experts' predictions about the recurrence of the epidemic outbreak are confirmed. To minimize the risks of international contract breaches, the concern's management must take into account the instability of the epidemiological situation in the main countries-counterparties of defense exports: Thailand, China, Pakistan, India, Saudi Arabia, USA, Azerbaijan, Algeria, Jordan, Republic of Korea. To avoid unnecessary penalties and late fulfillment of obligations, it would be advisable to review in advance the basic terms of the supply of goods under contracts and make adjustments for force majeure in epidemics.
Discussion aspects of the Ukrainian strategy for minimizing post-pandemic threats for enterprises of the defense-industrial sector
According to the authors, post-COVID rehabilitation of enterprises of the Ukrainian defense industry can be extended to several steps. To optimize the work of enterprises of the defense industry in today's conditions and to minimize possible economic and security threats in the operation of enterprises, it is proposed:
- at approving the plan of priority measures for sustainability of the defense-industrial complex of Ukraine, to accelerate the placement of orders of State Defense Procurement (SDP), including the conclusion of state contracts with suppliers at tentative prices. This will eliminate the next round of "price wars" and will help to advance the tasks of the State Defense Procurement within its indicators without their exceeding;
- in the Strategy for the development of defense industry, to provide for hedging of financial risks of enterprises, to minimize risks in epidemiological conditions and the application of quarantine measures, in particular, the starting 80 percent advance for work under contracts. it is proposed to increase the advance to 100% for priority defense projects within the framework of the State Defense Procurement;
- to launch the possibility of applying the mechanism of concluding forward contracts at the level of the Ministry of Defense of Ukraine. Forward contracts stipulate the obligation of the customer to purchase a certain lot, subject to confirmation of the necessary haracteristics of the General Staff of the Armed Forces;
- to load the enterprises of the defense-economic sector with the state defense procurement orders against the objective fall of market demand for civilian products, including the definition of contractors which provide the activity of executors of such order;
- for developing the State Defense Procurement Plan, to take into account the proposals specified in the Sectoral and cross-sectoral export strategies under the program Export Strategy of Ukraine for 2017-2021 (Ministry of Economic Development, Trade and Agriculture of Ukraine, 2019), which determines the identified barriers and tools to support the export of engineering, aircraft, and transportation, the priority list of measures to stimulate exports in Ukraine and the projected impact of export promotion measures on exports in sectors, with an assessment of the impact of these measures on Ukraine's economy.
Areas of further authors’ research are aimed at studying the experience of European countries in optimizing the work of defense sector enterprises, determining patterns of behavior of major players in the world arms business in foreign markets, and systematization of economic and mathematical methods of pandemic crisis risk assessment.
Conclusion
Examining changes in the national defense budgets of major counterparties of Ukrainian defense exporters under the influence of measures aimed at overcoming the global COVID-19 pandemic, it is determined that the "corona crisis" causes significant damage to the defense industry of any country regardless of their economic level. After the first quarter of 2020 most Asian countries already had reduced their defense budgets and cut funding for military equipment and procurement programs. India, Thailand, and South Korea are identified as the most risk-sensitive counterparties of Ukrainian defense exporters due to the reorientation of finances to the priority segment of medicine to eliminate the consequences of the pandemic. The defense budgets of China and the United States are more stable, though further aspects of our research will be long-term forecasts of timely fulfillment of obligations under contracts with Ukrainian defense exporters, under the cyclical recurrence of the epidemic outbreak. Considering the significant penalties normally imposed under contracts for the supply of military equipment and dual-use goods, armaments, and components, and aiming at the elimination of the risks of default, it is recommended to impose the analysis review of the basic terms of supply of goods under contracts to risk-sensitive counterparties. and to make adjustments for force majeure clauses in epidemics, and to possibly revise the terms of payment of contracts.
According to the analysis of the activities of enterprises of the defense-economic sector of Ukraine in 2019-2020, the following challenges were identified in connection with the global COVID-19 pandemic:
- the inability of the authorities to respond quickly to epidemiological threats and reformat budgets into priority areas to ensure the necessary security not only of the Armed Forces but also for defense enterprises;
- lowered interest of the state and scanty funding of scientific potential of enterprises - developers of new technologies needed to ensure the state's defense capabilities, which may lead to an inability to perform complex design tasks and loss of competitiveness of Ukrainian defense enterprises in foreign markets, which may have the greatest added value;
- deepening of the crisis of providing enterprises of the defense industry with high-tech personnel, the consequences of which may be not only the inability to fulfill contracts but also the flow of technology in connection with stimulating the migration of such personnel abroad;
- violation of supply chains of goods necessary for the functioning of defense enterprises both internally and externally, which contributes to the destabilization of enterprises, break of contracts for defense orders. In an attempt to escalate the war in Donbas and planned creation of two new missile brigades and a motorized infantry division near the occupied territories of Donbas, delays in the implementation of contracts could lead to military threats of losing the country's defense capabilities;
- the possible recurrence of quarantine restrictive internal and external measures requires a revision of the terms of foreign trade contracts in terms of conditions of supply of goods and force majeure clauses to prevent and avoid unnecessary penalties and late performance of obligations with foreign counterparties-special exporters.
The results of this study and proposals for optimizing the work of enterprises in modern conditions may be relevant at elaborating the plan of priority measures to ensure the sustainability of the defense industry of Ukraine in a pandemic crisis and post-pandemic recovery.
