A design of Turnover Intention antecedents and their relation on work design for Firms
Un diseño de antecedentes de Intención de Rotación y su relación con el diseño del trabajo para Empresas
Abstract
Most of the time Employees turnover intentions has been examined with the level of Human Resource Practices (HRP) in previous studies. Present study added social and Job characteristic study of 214 employees and managers from a fast food – outlet of Pakistan retail food service. Employee’s turnover intention was significantly associated at firm level and individual level factors and demonstrates the upgrading of food quality and service in the chain. The regression analysis was used to measure the relationship and significance among the observed constructs using SPSS 26. Job characteristics explains within-store variance. The hypothesis statement of the study projected that turnover intention has significantly affected due to individual level and firm level constructs setting in this situation. Outlet variance is described in adding to compensation, transformational leadership among employees in perspective of age and tenure similarity in the firm employees. Further research, limitation are managerial implication and theoretical framework can be discussed in detail.
Keywords
Work design; HR practices; individual and Firm-level factors; Turnover intention; Job characteristics.
Resumen
La mayoría de las veces, las intenciones de rotación de empleados se han examinado con el nivel de prácticas de recursos humanos (HRP) en estudios anteriores. El presente estudio agregó un estudio de características sociales y laborales de 214 empleados y gerentes de un establecimiento de comida rápida de Pakistán. La intención de rotación de los empleados se asoció significativamente a nivel de empresa y factores a nivel individual y demuestra la mejora de la calidad y el servicio de los alimentos en la cadena. El análisis de regresión se utilizó para medir la relación y la significancia entre los constructos observados utilizando SPSS 26. Las características del trabajo explican la varianza dentro de la tienda. La declaración de hipótesis del estudio proyectó que la intención de rotación se ha visto afectada significativamente debido a los constructos a nivel individual y empresarial que se establecen en esta situación. La variación del mercado se describe agregando a la compensación, el liderazgo transformacional entre los empleados en perspectiva de la similitud de edad y antigüedad en los empleados de la empresa. La investigación adicional, la limitación son las implicaciones gerenciales y el marco teórico se puede discutir en detalle.
Palabras clave
Diseño de trabajo; Prácticas de recursos humanos; factores individuales y a nivel de empresa; Intención facturación; Características laborales. Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan.
Introduction
Valued employees have strategic human capital for the organization and high replacing cost. Turnover issues required an esteem and focus in the organization (Holtom, Mitchell & Inderrieden, 2005; Shahzad et al., 2018; Lee & Maurer, 1999). Organizations have valuable human capital, for those firms who have knowledge and experience employees. Organizations allocate millions of dollars on recruitment, selection and training & development for new employees (Rosch, 2001). Human Resource (HR) practices saved the huge cost for the companies to retain the valuable employees (Mathis & Jackson, 2003). How organizations stopped the turnover and discover the effective employees, why employees thinking about leaving and move to another organization.
Actual employees’ turnover doesn't tend in all turnover intention. An important outcome variable found intention to leave in the organizations. Employees’ turnover behavior is not goods signed for organization in the presence of competitive labour market. During some labour conditions like the downturn in the market, it is highly alarming for the management (Allen, Weeks, & Moffitt, 2005). Organizational effectiveness is affected due to turnover intention. Employee’s realization about turnover and other unfavorable behavior in working environment cases the lot of negative withdrawal of working behavior. Organizational performance causes the financial loss and consequently loses the valuable employees. Firstly, on the priority bases pointed out the antecedents of turnover intention. Therefore, avoidable visible and invisible costs reduce to gain the competitive advantage of the companies through expansion of suitable interventions.
An antecedent of employee turnover intention depicts the productive finding in previous literature. Present study elaborates in three directions in connection to past research. Humphrey, Nahrgang and Morgeson (2007) draw a sketch of work design framework first time. In context of past studies that is not to be exploring in literature which adds in our study with new concept of social side. Secondly, work design models approach tests at single level instead of work design antecedent in food industry relevant firms. Our study investigates the work design antecedent on specifically food chain outlets in Pakistan. Thirdly, turnover intention has not been tested in same fashion and more specifically in non-united stated environment.
The main function of this research is conducted in to two levels. In first stage, this research inked the micro and macro level investigation at individual level and store level in perspective of job characteristics, social relationship and HR practices. The purpose of this study is taken empirical evidence lower employee turnover intention. Secondly, current research examines level of interaction between individual and store level. It focused on job characteristics effects on turnover intention in one context to other.
In addition, it is too much significant to judges the employee’s turnover intention in the present context. In work design and job characteristics based model constituted through this study. The main contribution is to forecast employee turnover intention to adopt the approach of interaction between employees and stores level. Most important is future turnover intention finding in a given framework. An empirical testing of proposed research model is based on Pakistani setting. Before this, it would authenticate the measurement of validity to compare the earlier studies conducted mainly in United States framework.
Theoretical framework
A deliberate compliance of employees that leave the firm is definitely the turnover intention (Tett & Meyer, 1993). It is final stage in series of withdrawal cognition since emerging the thought of leaving from the organization. Turnover intention is accounted in period of interval in different organizations (Mobley, Homer, & Hollingsworth, 1978). Past studies have been acknowledged the various antecedent of turnover intention. Mostly scholars originate and predict the turnover intention relation with job sovereignty, social support and job satisfaction. In previous studies mostly scholars are focused on the organization commitment, tenure and demographic variables impact on turnover intention. We reviewed twenty articles on turnover intention. We found three on job autonomy, six fair rewards, three training and development and five controlled on supervisor and employees’ relation.
Job characteristics and motivational characteristics have a sound connection to forecast turnover intention established by the previous studies. Social characteristics are ignored or underemphasized work-context perspective in the research (Morgeson & Campion, 2003). This Study model anticipates HR practices, social relationship, work-context and social characteristics. Employees turnover critically affected through a single intent center on the somatic aspects of labor/work environments, supervises the coordination side of work contexts (Wayne, Shore, & Linden, 1997). In previous studies address the framework of employee behavior in which human management function such as job design, reward systems as well as managers and workfellows (Werner & Desimone (2006). All persuade through employee assertiveness and behavior. Work-design antecedent’s related issue is highly considered. Psychological factors like job satisfaction, organizational commitment and external environment like market conditions and perceived mobility is disqualified by present scholars. Previous Framework designed is based on predictor of job fulfillment, organization commitment and same to turnover intention. Organizational commitment, job satisfaction and attitudinal outcomes are ignored. The study focuses to develop the mechanism for the antecedents of turnover intention and related plan of work design characteristics at individual and the firms’ level.
This study pointed out the significance of high to down cross-cultural level appropriate effects on below level occurrences. It is played contextual factors and effective role in facilitating the persuade of job characteristics to measure the employee performance (Fried and Ferris 1987). The perception of the cost of job change, job alternatives inside an organization and job alternatives outside an organization literature are describe in three prominent contextual factors in the turnover intention (Kammeyer-Muller, Wanberg, Glomb, & Ahburg, 2005). Felps et al. (2009) reveals that a multilevel analysis in coworkers’ Job search behaviors detail different individual voluntary turnover. To attain the better indulgent of employee-turnover intention, employees to employees’ matter of interaction clarify by the researchers. We find out the two-level study comparisons at different situational factors in the current study. Turnover intention affects the relationship binding between HR practices and social relationship to examination of top to down effects.
A number of studies have established the link between turnover intention job characteristics. In connection Li, Wang, Sun, Jiang and Cheng (2018) stated in favor of turnover intention is task of job characteristics. Turnover intention is too much to consider with job characteristics to organizational commitment and job satisfaction. In previous studies job characteristics is treated a single construct, now predict to attitudinal or behavioral outcomes (Slattery et al., 2010). McKnight et al. (2009) establish the five constructs of job characteristics with similar direction. We treated the five pertinent job characteristics into one identified Job characteristic construct. It is use to examine the motivating potential score. Robbins (2005) stated that turnover intention was decline if job score is high on motivational potential. In present study, there are motivational characteristics and job characteristic as whole. Therefore, this study suggests the underline stated hypothesis.
H1: Job characteristics are adversely associated with turnover intention.
HR Practices
HR practices are highly related to increase the positive work environment. Past studies depict lower turnover due to constructive work climate (Huang, Ma, & Meng, 2018; Allen, Shore, & Griffeth, 2003). Turnover intention has directly and negatively relation with competency development, nonmonetary appreciation, fair reward and data distribution practices (Paré & Tremblay, 2007). HR practices have four dimensions like training & development, performance appraisal and compensation factors. Turnover intention is highly associated with HR dimension, theoretical and empirical findings have conferred in the past studies. HR practices will increase the employee’s belief to do extremely well for the organization. Organization is focused on employees care and self-respect to do better for the firm. In result of employer commitment turnover intention is reported very low (Wayne et al., 1997). Irregularity of organizational presentation provides the HR practices investigation in the studies.
H2: HR practices are adversely associated with turnover intention.
Social Relationships.
Social characteristics have significance components of work. The relationship of work components has related with determinant worker willing to do work perfectly, to most important thing workers want to show meaningful work (Humphrey et al., 2007). Group intention and commitment play important role in determination. Individual’s perception about his or her group role to leave the group (Whiteoak, 2007; Arokiasamy & Tat, 2019). Present study investigates the social aspects, transformational leadership of manager and similar attributes of colleagues, employee turnover intention information is received from vertical and horizontal relationship of employees (Dupré & Day, 2007).
In this study, one of the fundamental questions are addressed in direction of transformational leadership. To extent, find out the follower personality, followers characteristics have biased by the leadership perceptions (Felfe & Schyns, 2006). Leadership has needed and owned by the followers. The research shows a leadership behavior instead of perception of leadership (Schyns, Flfe and Blank, 2007). Job satisfaction and organizational commitment is achieved through social interaction among peers in the organization. Low rate to leave an organization can decrease along social interaction (Yang, 2008).
We confer the theoretical and empirical relationship of turnover intention with transformational leadership. Albrecht (2005) addressed the recent development in transformation leadership and how to come close together. Organizational Citizenship behavior, work innovation, work effort and work-related effectiveness is measured numerically, theoretically and reliable binding with transformational leadership in many previous studies (Martin & Epitropaki, 2001). Burns (1978) stated in the study and provided the evidence about factors to inspire followers and leadership contribution to make the followers effective for organization. Distinction between transactional and transformational leader was introduces by Burns.
After some time, Bass (1985) conducted the research to recognize four transformational-leadership (TL) behaviors:
- Idealized influence
- Inspirational motivation
- Intellectual stimulation
- Individual consideration
H3: Social relationships are adversely associated with turnover intention.
Organizational behavior refers to meaning of situational opportunities and constraints to affect the behavior in given situation. Also, at low level context build the relationship among level of occurrences (Johns, 2006). Before going to final conclusion, job characteristics and outcome have demanded more exploration to investigate the relationship of contextual factors; previously few researches have investigated the contextual factor relation between job characteristics (Fried & Ferris, 1987). Job characteristics model has used in the findings of past exploration. In the work environment context job intervention has become alternative tool of success for contextual factors. Therefore, individual level variables are influenced the organizational level variables. This study adopts the organization to individual or a top-down process research strategy to quantify this relation. That is, the firms-level dynamics particularly address the study of human resource activities and social relationship. They can support to form a condition that turnover intention and job characteristics to constraint the relation among the factors.
As we discussed in previous section of the study, employee’s perception has changed to use of HR practices in the organization, regarding their welfare, health cares and personal contribution in the organizational behavior (Wayne et al., 1997). Employees’ loyalty with their organization shows positive sign; provide the evidence existence of HR practices and job characteristics that motivate the employee to do more for organization. When organization realized that employees did not perceived the job characteristics in the job environment. Organization operated the substantial HR practices to lead down the turnover intention factor. Turnover intention reported very low where organizations apply the substantial HR practices. In view of fact that organizations have invested more money on HR practices to enhance the employee’s perception. That investment cultivated the organizational values from human capital. Lack of information about their own job, experience will be treated as compensation, and then employee intention to move is relatively low.
In perspective of social relationship, Harris and Harvey (2008) stated that turnover intention is strained by the relationship of supervisor and subordinate. Employee’s perception is highly associated with their work-based group; Intention to leave the organization, their level of commitment has determent the employees’ role in the organization (Whiteoak, 2007). Employees feel comfortable in the environment. When they exist in favorable social relationship and core job characteristics associated situation. When employees do not consider the job characteristics, they only focus their job context. In that result a positive strong relationship prevails at workplace. Social relationship with experience has significantly negative account with lower turnover intention in those organizations where employees experience is inversely associated. A negative work outcome may be reduced for positive social interaction with supervisor or colleagues like work stress, over load job can create the thinking for leave the organization. But employees have liked to want do more at the organization. Negative social interaction must characterize in that case.
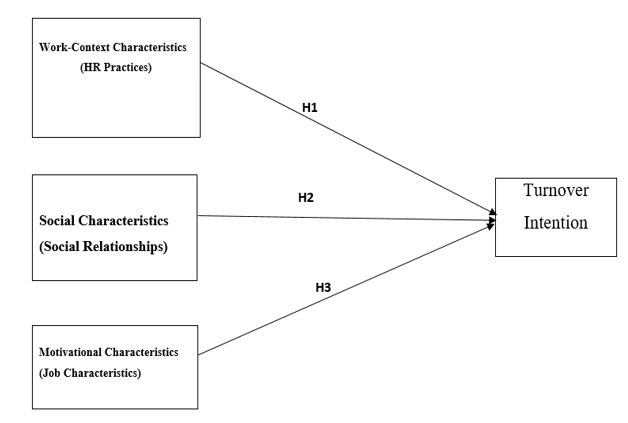
Figure 1: Theoretical Framework of Study
Methodology
Sample
Seventeen Pakistan-based fast-food chain centers, Brand chain, were requested to participate in the research survey. Fast food chain was selected for achieving the desire result. Firstly, it is noted that food chain adopts different franchise point from the same brand. Rather than comparing the firms, brand offers standardize operating control (Glebbeek & Bax, 2004). Second, even though it precedes centralized strategy to maintain the quality, the outlet center encourages the owners to maintain their own freedom to deal every day management issues regarding communication, evaluation, training and development and compensation. Third, Service industry was used to measure the turnover intention in the past studies, it is totally contrast of previous studies (Yang, 2008), low skilled participants reported in most of the current research. Participants have possessed relevant knowledge of their firm and expertise. They have detailed information of customers and convey immediately. Employee characteristics go, mutually inspire and capability to cooperate with customers. The work place characteristics factors became too much critical for firm performance, when workers parting from the firms can perpetrate on it together evident and unseen damages.
An identical number of employees selected in survey package. Equal numbers of managers were selected for sample. A cover letter conveys the purpose of study, questionnaires delivered to participant along with this letter. All information regarding this will contain confidentially. Questionnaires were delivered to each participant personally and collect after one or two hours. Total 240 questionnaires were forwarded to the participant and 215 questionnaires received from the survey. We managed the survey personally. After collection of data, during the analysis process only complete questionnaires were accepted. Missing data is not entertained in final sample.
Measurement scales
Turnover Intention (TI)
Brislin, Lonner and Thorndike (1973) stated the pure concept of firms leaving factors to measure. Turnover-intention (TI) was well-defined as an employee’s inclination to leave the firm (Brislin, 1980). They were explained to measure in the following statements:
TI1 I often think of leaving the organization.
TI2 It is very possible that I will look for a new job next year.
TI3 If I may choose again, I will choose to work for another organization.
Five-point Likert type scales ranging from strongly disagree (1) to strongly agree (5) were used to measure.
Job Characteristics (JC)
Five basic dimensions ware used to measure job characteristics. This scale adapted from a study done by Hackman and Oldham in 1976. Participants were responded to on a five-point Likert scale ranging from strongly disagree (1) to strongly agree (5). The dimensions were stated in the following numbering;
JC1 The job requires me to use a number of complex high-level skills (variety of required skills)
JC2 The job provides me the chance to completely finish pieces of work I began (task identity)
JC3 The job is very significant and important in the broader scheme of things (task significance)
JC4 The job gives me a considerable opportunity for independence and freedom in how I do the work (task autonomy)
JC5 After finishing a job, I know whether I have performed well (task feedback). The sum of scores on the five items gives the job-characteristics score.
HR Practices (HRP)
Supervisors are prospective and well informed, then workers to implement the Human Resource activities at the workplace (Gerhart, Wright, McMahan, & Snell, 2000; Batt, 2002). In current study, food chain managers were provided the information regarding training and development, performance appraisal, compensation, and communication. The elements were adjusted from a study done by Huselid (1995) and Snell and Dean (1992).
A five-point Likert scale ranging from strongly disagree (1) to strongly agree (5). Following 8 elements were constructed.
HRP1-T Training plans are developed and monitored for all employees.
HRP2-T Good employees are promoted to a higher-level position.
HRP3-P The performance- appraisal process is standardized and documented.
HRP4-P Organization provides employees with a feedback system for performance appraisal.
HRP5-C Wages are tied directly to employees’ performance.
HRP6-C Organization uses incentive pay to boost individual performance.
HRP7-CO Employees’ opinions will be seriously considered.
HRP8-CO Employees know organizational objectives and strategies well.
Transformational Leadership (TL)
Workers were asked to reply to 9 items concerning the employees’ perception of the best leadership behavior in each outlet, again on a five-point Likert scale ranging from strongly disagree (1) to strongly agree (5).
The items were selected from the four dimensions of transformational leadership on the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire (MLQ), Form 5X (Bass & Avolio, 1997). The 3 items helped to measure idealized influence. Two items assisted to measure inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation, and individual consideration, respectively. Sample items are comprised below:
TL1 My supervisor makes me proud by associating with me (idealized influence)
TL2 My supervisor articulates a compelling vision of the future (inspirational motivation);
TL3 My supervisor seeks differing perspectives when solving problems (intellectual stimulation)
TL4 My supervisor treats me as an individual rather than just a member of a group (individual consideration).
For collection of model tested measurement, we use the Amos for CFA model to estimate the independency of Job characteristics, social characteristics, HR Practices and turnover intention constructs resultantly relative from employees. Research model consist of three main variables, which were sure independent as the model specifying three separate factors shows sufficient fit χ2 = 543.50, df = 115, GFI = .94, RMR = .02, RMSEA = .05, CFI = .99), estimate of the construct provide the strong intensity. Three construct relation result to establish the factor model in significant improvement in fit over all, in case of single factor construct model χ2 = 4401.08, df = 119, GFI = .64, RMR = .10, RMSEA = .20, CFI = .89) and a two-factor model combining job characteristics and transformational leadership (χ2 = 2264.16, df = 118, GFI = .71, RMR = .06, RMSEA = .17, CFI = .93
Results and discussion
Result of study stated the means, standard deviations and inter-correlations for all constructs added in the description of the result. Job characteristics were highly related and negative relation with turnover intention (r = −.353, p < .01), tenure, age and gender were considered as controlled variables. The hypotheses of research predicted that both individual and firm level variables have significant impact on turnover intention. Turnover intention in employee had highly related impact on firm level to supported the establish hypotheses. Thus, we calculated a null model by using of HLM, which was not predicting specifically for all function level of the study. In this style Residual variance of intercept (τ00 = .012, p < .01). It is reported significance at firm level and individual level. Variance of .016 present indicated the 16 percent change in employee turnover intention resided to 80 percent change noted within the firm. Hypothesis statement one projected that job characteristics would be correlated to employee turnover intention. Firms level association of job characteristics adversely associated with employee turnover intention. It is expected a framework that specified job characteristics was not established for the model.
Analysis shows that 18.4 percent of variance estimated with job characteristics. Particularly job characteristics had strongly negative associated with turnover intention of employees (γ = −.459, p <.01). Consequently, HR practices, transformational leadership obtained the similar level interception reported in firm level. Result shows that compensation and transformational leadership were accounted respectively (γ = −.365, p < .1), transformational leadership (γ = −.542, p < .01). Compensation and Transformational leadership had significantly negatively associated with employee turnover intention. Employee turnover intention had not significantly related with training and development (T&D), performance appraisal and also gender similarity did not have established the relation with employee intention. Testing the Hypothesis statement three projected that firm level variable would moderate relationship between social characteristics and turnover intention. While firm level variable of this research had examined the potential effects of human Resource practices (HRP), as well as transformational leadership has an effect with turnover intention.
In the present study, data were collected from 214 employees in different franchise outlet. The size of firms was different to other studies, for example, 25 restaurants (Liao & Chuang, 2004) and the 23 Organization (Wu & Chaturvedi, 2009). In the context of present research, the current study has examined a set of key factors and contextual relation of turnover intention with food brand employees working on the operation point. However, there are relevant to the other factors that also influence the turnover intention.
Turnover intention was found significantly in employee intention within and among the firms. Tenure of employee, age, leadership style compensation and job characteristics have explained with a moderate level of variability. In General, organization level is relatively important to effect the turnover intention relation with job characteristics. In same order it is found in employees’ level, managerial leadership and compensation.
Smyth et al. (2009) have perception to leave their organizations, which consist with the rational of the job characteristics framework establish in the previous studies. Employees were less likely to leave their organization. Transformational leader is negatively related with employee age, tenure and similarity among coworkers. Turnover intention is significantly establishing negative relation with compensation, leadership and tenure. Employees had access to fair and reasonable compensation packages. They have less willing to leave the organization in existing scenario on adequate pay packages. Social interaction is positively related to supervisor or colleagues than coworkers who had low level to connect such access. Previous studies finding supported the research results (Ahuja et al., 2007; Lawrence, 2006). Turnover intention is comprehensive analytical relationship. Particularly, sum up the results of most recent research on turnover intention (Allen, Bryant and Vardaman,2010). Present study shows that Transformational leadership relationship with employees/ coworkers on turnover more as compare to pay packages and job satisfaction. A comprehensive detail shows the actual research estimates of turnover predictors. Pay packages may not be considered permanently to resolved the turnover issues. Another criticism of participant not totally relates the desire level of participants, which is deemed to typical potential sources of common methodology bias (Podsakoff, MacKenzie, Lee, & Podsakoff, 2003). Social desirability is commonly observed as the propensity on the part of individual to present them in a positive light, it is too much difficult to judge the exact feeling perceived to attain the desire results. For example, HR practice items responded through arranged questions asked to Managers. The competent employees are stranded to a high-level position in the organization. Managers might be cautious to these high positions possessed by good employees. They have noted that social aspect can create spacious relationships. Constructs relationship was vague and serving as suppressor variables (Ganster, Hennessey, & Luthans, 1983).
Podsakoff and organ (1986) stated that the recommendations to decrease the biased aspect. Therefore present study in shape of self-reporting and social desirability. The study designed the measured of the forecaster and standard variables from diverse sources, like employees, managers and other informative resources use to eliminate the self-biased factor particularly in present study. The benefit of this procedure is that it constructed according to the mind-set of source person or relate to this method of information judged on constructs relationship between criterion and predictor relationship. A lenient approach and social desirability factor eliminating by used of any tendencies instead of this. Factor Analysis is conducted at initial stage before distributing the questionnaires of main study. Over all Model fit found and provide the significant improvement in research model shown in our analysis. Additionally, if common-method variance had been rated up. The examined relationship would have been estimated against unlikely pattern of observations. As final point, Turnover intention relationship was found empirical, theoretical and consistently in previous studies. Therefore, significance influence of study has founded and appeared in effect of common method effect of study. However, Nederhof (1985) recommended some factors with use of social desirability scaled, the acceptance of forced choice and a random distribution and response methodology alleviate the effects of social desirability are precious components presently as well as ongoing components for future studies.
Conclusion
This study added a study of social and employment characteristics of 214 employees and managers of a fast food establishment in Pakistan. The contribution of this study would provide the guidelines and direction for policy makers. The practitioners should also develop the strategies and organized the programs to overcome employees’ turnover intention at work place. It would help the firms to reduce the turnover issues among the store staff, managers and firm’s level. This research will add the valuable contribution for academia and as well as for industry to increase the firm’s efficiency, effectiveness and overcome the recruitment cost. Consequently, present research suggests that operational managers should deliberate the findings and recommendation to overcome the turnover intention problem to relate the given scenario and take proper managerial actions in light of this study.
Present study has some limitations. The employee turnover intention is independent variable and three dependent variable job characteristics, HR practices and social characteristics are measured through questionnaires. It can be argued that constructs measure with incumbents in the best knowledge of that their manager. This study has another limitation and highly concerns the potential generalizability of the results. Although, manage a point of disposal of unnecessary factors associated with different occupations and firms by bound to a research sample to a limited occupation in two cities same types of organizations. Furthermore, variables estimated can affect the values on the variables. This low variance attenuates the measured the relationship among the constructs. To end with, this study involved a firm level design, making fundamental inferences impossible. Therefore, further research should observe how associations studied in the present research develop the framework and tested in other environments. A worker, who is attending to routine work activities may experience significant stress from remind about quitting the job. An employee is thought about quitting the work place after performing the routine work tasks may experience an intensive work attention.
