The Influence of Social Factors on Business Performance: A Study of Middle Level Managers of Textile-Based Organizations
Соціальні фактори та їх вплив на майстерність творчості: Дослідження менеджерів середнього рівня в організаціях на основі текстилю
Abstract
The study has its focus on influence of social factors on business performance with mediating role of creativity skill of middle level managers, because enterprise does not compete itself without creativity and innovative skill. Therefore, social factors have important influence on individuals’ behavior and leave positive and negative effects on creativity of middle managers and performance of enterprise. To examine the aforementioned aims study used primary data and 120 respondents were interviewed through a self structured questionnaire and question statements are derived from past literature and developed hypothesis to check the association between independent variables (strict control, encouragement, professional attitude, interaction with top managers and colleagues) and dependent variable (creativity skill). The analysis was performed by using descriptive and inferential statistics through SPSS (20). The results of the study showed positive relationship between independent and dependent variables. The current study recommended that valuable tactics in challenging tasks, deliberating ownership of managerial skills can produce creativity in positive ways. It is also suggested that creativity can be attained and polish through providing learning environment.
Keywords
Creativity skill, Social Factors, Strict control, encouragement, professional attitude, Middle level manager.
Аннотация
Дослідження фокусується на соціальних факторах та їх впливі на майстерність творчості менеджерів середнього рівня, оскільки підприємство не змагається без творчості та інноваційних навичок. Отже, соціальні фактори мають важливий вплив на поведінку людей та залишають позитивні та негативні наслідки на креативність менеджерів середнього рівня та результати діяльності підприємства. Для дослідження вищезазначених цілей у дослідженні використовувались первинні дані, і 120 респондентів були опитані за допомогою самоструктурованого опитувальника, похідного з минулої літератури та розробленої гіпотези. Аналіз проводився з використанням описової та випадкової статистики за допомогою SPSS (20). Результати дослідження показали, що позитивний зв'язок між залежною змінною (майстерність творчості) та незалежними змінними, як суворий контроль, заохочення та професійне ставлення, взаємодія з топ-менеджером та колегами. Поточне дослідження рекомендувало, що цінні тактики при вирішенні складних завдань, обмірковуючи володіння управлінськими навичками, можуть створювати творчі здібності позитивно. Також пропонується досягти творчості та поліпшити її завдяки забезпеченню навчального середовища.
Ключові слова
Навик творчості, Соціальні фактори, Суворий контроль, заохочення, професійне ставлення, менеджер середнього рівня.
Introducción
Global enterprise demands creativity and innovation for its success (Gehani, 2011) so the creativity” is something almost accessible in its nature, the word creativity refers to bringing new ideas in the organization (Kremer, Villamor, & Aguinis, 2019). A creative idea is marked by three attributes: it must be original, it must be useful or appropriate for the situation in which it occurs, and it must actually be put to some use’’(Botella & Lubart, 2019). According to (Prabhu, Sutton, & Sauser, 2008) “, it is a set of skills, capacities and traits including ability to work independently, unconventional thinking, tolerance of ambiguity, curiosity and openness to experience (Albert, 1996; Price, 1998). Creativity is not only helpful in problematic tasks of daily life but also has its space in social and business matters. In order to enhance creativity in business, three elements were needed: creative thinking skills, motivation and expertise. Creativity has two phases: first the generative phase in which an individual constructs mental depictions called structures before inventions and second an explanatory phase in which these structures are used to create creative ideas. As the term “creativity” means the tendency to create or recognize new concepts, opportunities or alternatives that can be helpful in communicating with others, solving problems as well as providing entertainment for yourself and others. To be creative, you must be able to see the things from different perspective or in a new way. You must be able to generate new possibilities among other things.
The art of creativity has allowed many brands to be different in time. Consumer would not know the difference between McDonald’s and Burger King without such titles. It helped define corporate institutes using image and color. It would be helpful for consumer identify itself with these brands. For instance, what brand do you consider when you are going to cook your favorite spaghetti? If you don’t like to step foot in kitchen, what restaurant would you choose to satisfy your hunger for spaghetti? Being able to use creative mind has helped the customers to differentiate brands as well as create a sense of trustworthy for many. If you look quickly around you then you can identify which people follow trends and which create their own atmosphere. Fashion has allowed creating a trend or following it. It’s as simple as finding inspiration that can find a way into the mainstream of pop culture (Wheelihan, 2011).
Awareness, understanding, techniques and self-actualization (AUTA) a four step model of creativity development developed by Davis (1982). Generally, the model suggests that you must become a creative person (a) increase your creativity, (b) understand the subject of creativity, (c) use standard as well as personal creative thinking techniques and (d) be self-fulfilling. This also covers different societies as well as cultures. On a day to day basis, we inspired by different cultures. That is the most essential driving factor when we observe behavior and contemporary culture. If we stop for a moment, you will notice that everything around us is from clothing to ads, websites, magazines, movies and photos etc (Davis,1982; Rimm,1985).
Middle level managers are responsible overall activities to be performed in business enterprises. They monitor where change is needed and provision of better environment is also the demand of enterprise. Implementation of organizational strategies and practices are functional under the supervision of middle level managers who are first level supervisors but below in the level of top managers (Wooldridge & Floyd, 1990). They are professionals provide healthy environment and committed to perform their role as a bridge between top managers and employees for business success (Banumathi & Samudhararajakumar, 2008).
Main Purpose
The main purpose of this paper is to study the social factors as well as its effects on creativity skills of middle level manager, who monitor the overall activities in textile-based organizations. It also examines the ways that how people can be creative under these circumstances and further investigate if creativity is only caused by social factors.
Objectives of the study
- To understand socio-demographic status of middle level managers.
- To examine social factors of creativity skill.
- To understand the effects of social factors on creativity skill of middle managers.
Study Limitation
The focus of this study was on middle managers in textile based organization due to limited resources and time bounded academic activity. The results of the study may not be generalized except and unless the research is repeated on another sector of business.
Literature Review/Theoretical Framework Strict Control
Strict Control
Van der Kolk et al. (2018) argued that control over employees motivate them to participate in organizational activities that lead to enhance employee performance.
Amabile (1988) stated that employees are assumed to act opportunistically, so management control systems are implemented to control employee behavior and also relevant for creative employees. With emphasis on the particular importance of intrinsic task motivation for employee creativity, the “hidden cost of control” will be the focus of research. The principles of cognitive evaluation theory and the componential theory of individual and organizational creativity will be taken into account in the analysis of the effects of different control mechanisms on intrinsic motivation and consequently, on creativity.
Malmi and Brown (2008) theorized that incentive and reward controls intend to ascertain equivalence between the goals of the business and those of employees by encouraging them by means of, for instance, bonus payments, Kang & Snell (2009) argue that incentive and reward controls can also sustain exploration via an “error embracing” control system and developmental performance appraisal.
Professional Attitude
George (2001)Washington University to conduct a multisite national study with the aim of measuring the impact of professionally conducted community based cultural programs on the general health, mental health, and social activities of older persons, age 65 and older.
The study takes place in three different sites across the country—the metro Washington, DC area; Brooklyn; and San Francisco. Each site involves two groups—(1) the Intervention Group, comprised of older individuals involved in a weekly participatory art program, and (2) those involved in a Control Group, comprised of individuals involved in their ongoing activities as usual known as professionals. Each site recruited at least 100 older persons—50 participants in the Intervention Group and Control Group alike. The overall study has had 300 participants—150 in the Intervention Groups, 150 in the Control Groups. The average age in all three sites, Intervention and Control Groups alike, was approximately 80 years of age, the age range has been 65-103 years. Approximately 30 percent of the participants reflect racial and ethnic minorities.
Encouragement
Azeem et al. (2019) stated that encouraging and motivation of employees enhance creativity that is also good for attracting and retaining quality of employees as well as performance of the organization, it always retain an issue even in struggling economy. Motivating employees to think creatively also helps to ensure that ideas stay under your roof, instead of having them take their ideas somewhere else or start a competing business. There are other components of creativity--domain-relevant skills, quality processes and intrinsic task motivation--according to a componential theory of creativity, environmental factors such as freedom, support and positive challenges also play a key role in fostering creativity (Amabile, 1997).
Interaction with top Managers and Colleagues
The Author theorized and found that transformational leaderships and educational specialization heterogeneity interacted to affect team creativity is such a way that when transformational leaderships was high ,team with greater educational specialization heterogeneity exhibited greater than creativity . In addition, team creative efficacy mediated this moderated relationships among educational specialization heterogeneity, transformational leadership, and team creativity. The Author discusses the implication of these results for research and practice. Shine and Zhou (2007) investigated three factors and their effect on workplace creativity as co workers, managerial feedback and creative personality. Zhou surveyed 123 hospital employs, such as registered nurses, pharmacists and administrative personnel. Participants filled out surveys assessing three factors: supervisor managerial style, co workers creativity and their awn tendency to innovate at work. Zhou says she was able to get a detailed picture of number of factors affecting creativity. In addition to being income , pressure from a micro managing boss my cause employees , especially people who are not naturally creative , to simply mimic the behavior of their creative co workers” that is not creativity ,” Zhou explain , an employees must be gain space and the time to learn creativity strategies used by their innovative challenges , such as brainstorming.
Woodman et al., (1993) studied to present the basics for understanding to create in a relational setting. This paper defined organizational content such as product, service, concept process or motion to create an important strategic value, project, concept or process by a team working on the comprehensive power of public relations systems. The interactive model of creative behavior developed by Woodman and Schoenfeldt (1989) had been provided the starting point for their theoretical development. This sample was used in its supporting literature on creative practice and its design to develop a collaborative approach to design. The three thought processes has been summarized by three strategies that can guide the development of hypothesis.
Rubenstein et al., (2018) in their mixed method study examined teachers’ perceptions of creativity using social factors of cognitive theory these were personal, behavioral as well as environmental. In describing barriers to creativity, teachers often conversed macro-environmental factors, but when enlightening or defining creativity, teachers often used personal also behavioral traits. That was not uncommon for teachers to have very little idea of who can do what or what creativity always brings products; however, some two-dimensional teachers were vague about guiding natural orientation. Compared to in-service teachers, pre-service teachers showed more optimism in their future conservational support and lower self-efficacy in developing creative thinking.
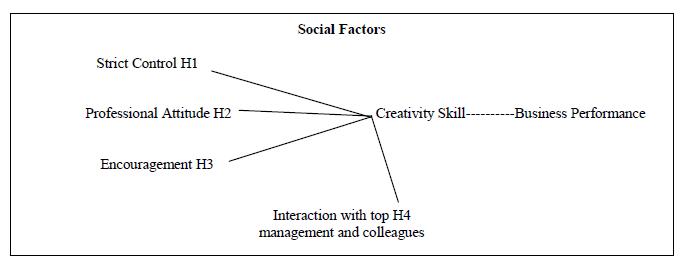
Theoretical Model
Hypothesis development
H1: Positive association between strict control and creativity skill of middle managers.
H2: Positive association between professional attitude and creativity skill.
H3: Positive association between encouragement and creativity skill.
H4: Positive association between interaction with top managers and colleagues to enhance creativity skill.
Methodology
Quantitative descriptive research method was used. Universe of present study was based on middle managers of three textile based organizations who have the responsibility of overall flourishing capacity of the organization. Simple random sampling technique was used to draw sample from the population, for this purpose a list of middle managers employees was obtained from every textile base organization, and targeted sample was consisted of 120 respondents. As a data instrument, structured questionnaire was prepared based on study objectives and variables as social factors i.e. strict control, professional attitude, encouragement, interaction with top managers and colleagues with five statements are constructed based on these variables. The each item of questionnaire was constructed on five point likert scale that contained five options and this was indicated as (agree, strongly agree, undecided, disagree and strongly disagreed), creativity skill valued as (low, moderate and high). Survey method was used to collect data from the respondents with face to face interaction. Verbal consent of respondents was taken during data collection. Pre-testing of the questionnaire was done on 30 respondents, these questionnaires were excluded in final data collection phase, after pre testing some statements are manipulated and then alpha value was obtained to check the reliability of the instrument aiming to know the consistency and relevancy of each question based on study variables, Chronbach alpha values was 0.70≥0.8. Data was analyzed through SPSS, this was consisted of two phases, first one was about descriptive analysis of variables and second was about inferential statistics by using chi square test to check the association between variables.
Results and discussion
Table 1.
Reliability of Instrument.
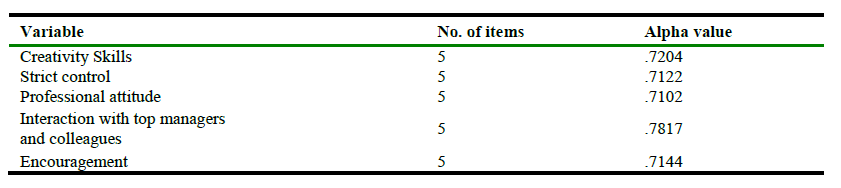
Table 1 shows reliability of questionnaire, it is a test measure to check the consistency of the items in an instrument. The most common test is Chronbach’s alpha which is used to check the reliability of data. If the value of alpha is equal to .70 or above the result is satisfactory (Hair Jr, Hult, Ringle, & Sarstedt, 2016).
Uni-Variate Analysis
Table 2
Socio-demographic status of the respondents.
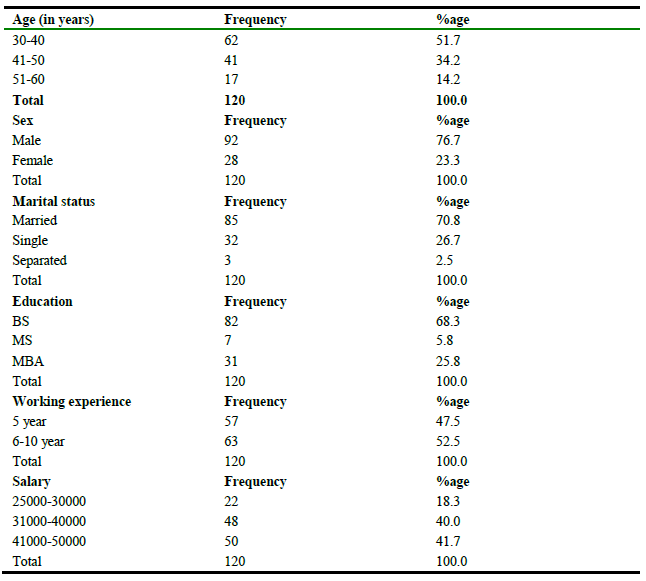
This table 2 gives detail of socio-demographic status of the respondents, that shows majority of the respondents were young as half of sample i.e., 51.7% of the respondents belonged to age group (30-40), while little more than one-third i.e., 34.2 % of the respondents had 41-40 years of age and remaining 14.2 % of them had 51-60 years of age. Table 2 reveals that a large majority i.e., 76.7 % of the respondents was male and 23.3 % of them were female. So it is clear that the majority of the respondents were male. Significant majority of the respondents i.e. 70.8 % of the respondents were married, while slightly more than one-fourth i.e., 26.7 % of them were female and only 2.5 % of them were separated. It also indicates that a majority of the respondents were highly qualified, most of them had BS level of education i.e., 68.3 % of the respondents had education at BS level, while 5.8 % of them had education at MS level and about one-fourth i.e., 25.8 % of them were MBA, while majority of the respondents had 6-10 years working experience i.e. 47.5 % of the respondents had 5 years working experience, while little more than a half i.e., 52.5 % of the respondents had 6-10 years working experience and the majority of the respondents had sound salary package i.e. 18.3 % of the respondents had Rs. 25000-30000 monthly salary, while 40.0 % of the respondents had Rs. 31000-40000 monthly salary and 41.7 % of them had 41000-50000 monthly salary.
Table 3.
Association between strict control and creativity skill.
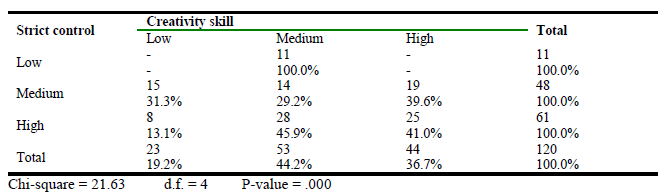
Table 3 shows value of Chi-square (21.63) an extreme level of significant relationship between strict control and defendants’ creativity skill. The hypothesis concluded that strict control is positively associated with the creativity skill is accepted. The guidance and stimulation of employees for organizational performance is studied under the mechanism of HRM, the contol over, check and balance on employees enhance their creativity in real sense, therefore, recently HRM has shifted its focus on employee commitment oriented performance by control oriented performance to commitment oriented (Hauff, Alewell, & Hansen, 2014). Formal and other control practices are important to judge the performance of employees (Sitkin, Cardinal, & Bijlsma-Frankem, 2010).
Table 4.
Association between professional attitude and creativity skill.
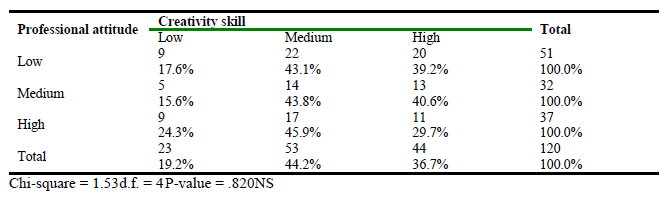
Table 4 shows p values (.820) is greater than the significant values (0.05), there is no relationship between professional attitude and creativity skill and the value of Chi-square (1.53) shows a non-significant relationship between both variables so the hypothesis is “rejected”. The results are correlated with the earlier study of (Wlliam, 2004) asserted that some employees goes from openness to experience or professional behavior having divergent attitude and thinking, rather some employees have negative divergent thinking that impede to employees performance in organization. Professionalism is a commitment to work an employee has and serve it for the organizational performance, fruitful practices of HRM belongs to the performance of the organization (Seeck & Diehl, 2016).
Table 5.
Association between encouragement and creativity skill.
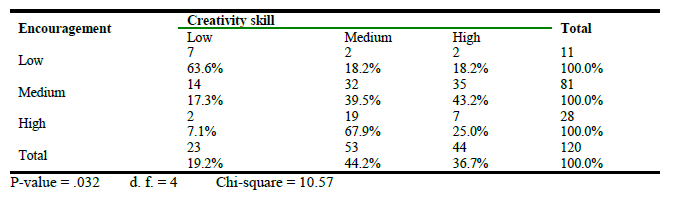
In Table 5 p value (0.32) and chi square value (10.57) indicate positive association between encouragement and the creativity skill so the hypothesis is accepted. Encouragement from employers is inevitable aspect for motivation of the employee, in this connection results are coincided with the work of Azeem, Hayat, Nawaz, Sajjad & Ali (2019) who examined and confirmed that encouragement of employee through motivation is a key to success of any business.
Table 6.
Association between Interaction with top management and creativity skill.
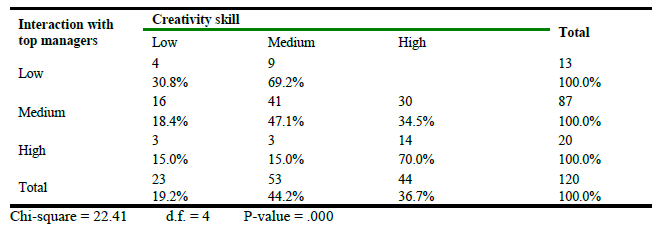
Table 6 shows chi-square value (22.41) and indicates a highly-significant association between interaction with top managers and respondents’ creativity skill. As low interaction with top managers then they had low (30.8%) and medium (69.2%) creativity skill. If the respondents had high level interaction with top managers then they had had low (15.0%), medium (15.0%) and high (70.0%) creativity skill. So the hypothesis “Interaction with top managers is positively associated with creativity skill” is accepted. The results are correlated with the work by Verburg, Nienaber, Searle, Weibel, Den Hartog, & Rupp, (2017) stated that organizational control over employees performance and trust employ positive outcome, better task performance, and organizational citizen behavior.
Discussion
It is hypothetically stated according to the aim of the study that creativity of middle level managers is improved due to influence of social factors as analysis shows multiple indicators i.e. strict control and interaction with top managers have control over the activities of the middle level employees, it builds team work to enhance their work ability and increase business performance, this argument was affirmed and enhancing the existing literature by adding the work of Mayer & Gavin (2005) who found positive relationship between strict control and employees working, by which control was natural and legitimate way to manage employees, this was implemented by top mangers through formal rules and written documents and more informal control was imposed by peers (Baldauf, Cravens, & Piercy, 2005). Moreover, obeying controlling creativity of employees enhanced through professionally motivated HRM and encouragement this was affirmed by (Dunegan et al., 1992; Cheng, et al., 2019), also gets speed up the innovative process for business performance.
Conclusions
It is concluded that business organizations demand high work performance from their employees and also provide complete working environment for utilizing their skills, it is found that individual skills are improved due to organizational performance through encouragement, professional attitude, interaction with colleagues and strict control, in order to ascertain standard creativity from the employers, encouragement and motivation, HRM control practices that focus on deliberated committed efforts and attitude, professional relations of employees with top managers and colleagues who are experienced and part of the organization having full temperament to handle the activities of each employee who is restricted through check and balance on their skills play an important role in good relation of middle managers creativity and enterprise success.
On the behalf of results it was suggested that valuable tactics enacting in challenging tasks, deliberating ownership of managerial skills of employees can be produced through encouragement and interaction with senior colleagues, it also entails creativity in positive ways. It is also suggested that creativity can be attained and polished through providing learning environment. Creativity is essential for success in every field, especially in the high-tech field, where knowledge is the key resource, in order to enhance the knowledge level, there is dire need of employees should be more creative through training and professional motivation.

