Small and medium-sized businesses in towns of commodity regions as source of diversification and modernization of their economy
Малый и средний бизнес городов сырьевых регионов как источник диверсификации и модернизации их экономики
Abstract
The article presents the results of the analysis of economic indicators of economic entities of the regions with raw materials specialization, from the perspective of the goals and capabilities of medium and small-sized businesses. In modern conditions, due to the achievements of scientific and technological progress, the goals of the activity, and the potential of small and medium-sized businesses, the authors identify and analyze possible directions of diversification and modernization of the economy of these regions. The towns of commodity regions are located mainly in areas of adverse environmental conditions away from large industrial and cultural centers and in many cases depend on the performance of one or two large town-forming companies. Thus, the prospects of maintaining the attractiveness of doing business for small and medium enterprises in the towns of these regions as well as the attractiveness of these towns for the population were revealed and analyzed. As measures to maintain this attractiveness, the authors consider the possibility of diversifying and modernizing the economy of such towns by supporting the activities and development of small and medium enterprises, as well as implementing measures aimed at introducing the technologies of the “Smart City” concept.
It is assumed that to diversify and modernize the economy of the commodity regions, it is necessary to create conditions for the revitalization of many areas of activity. In particular, it can be achieved through the implementation of “Smart City” projects in these regions. This should stimulate the process of activating the most technologically advanced and innovative areas of activity and have a positive impact on the development of small and medium-sized businesses involved in these areas. In turn, the stable and efficient functioning of such enterprises is one of the most significant tools for such transformations and can speed and intensify the efficiency of the implementation of these processes.
At the same time, the use of “smart” technologies for making “smart” decisions, in the process of modernizing the urban economy included, will increase both the efficiency of functioning of small and medium-sized enterprises, and the mechanisms for supporting their activities and development.
Keywords
commodity regions, diversification of economy, modernization of economy, small and medium-sized business of municipalities, “smart” technologies.
Аннотация
В статье представлены результаты анализа экономических показателей деятельности хозяйствующих субъектов регионов, имеющих сырьевую направленность, с позиции специализации предприятий крупного, среднего и малого бизнеса. В современных условиях, с учетом достижений научно-технического прогресса, целей деятельности и потенциала предприятий малого и среднего бизнеса, в статье, выявляются и анализируются возможные направления диверсификации и модернизации экономики этих регионов. При этом производится попытка выявить перспективы сохранения целесообразности ведения бизнеса для малых и средних предприятий в городах этих регионов, а также привлекательности данных городов для проживания населения с учетом того, что такие города расположены преимущественно в зонах неблагоприятных природных условий в дали от крупных промышленных и культурных центров и во многих случаях зависят от результативности деятельности одного или двух крупных градообразующих предприятий. При этом в качестве мер сохранения этой привлекательности рассматривается возможность диверсификации и модернизации экономики таких городов за счет поддержки деятельности и развития малых и средних предприятий, а также реализации мероприятий, направленных на внедрение технологий концепции «Умный город».
Предполагается, что, для осуществления диверсификации и модернизации экономики сырьевых регионов необходимо создание условий для активизации многих сфер деятельности. Что в том числе может быть достигнуто, за счет реализации в этих регионах проектов «Умный город». Это должно стимулировать процесс активизации наиболее технологичных и инновационных сфер деятельности и оказать положительное влияние на развитие предприятий малого и среднего бизнеса, задействованных в этих сферах. В свою очередь стабильное и эффективное функционирование таких предприятий является одним из наиболее значимых инструментов подобных преобразований и способно ускорить и усилить эффективность реализации данных процессов.
При этом, применение «умных» технологий для принятия «умных» решений, в том числе и в процессе модернизации экономики городов позволит повысить как эффективность функционирования субъектов малого и среднего предпринимательства, так и самих механизмов поддержки их деятельности и развития.
Ключевые слова
диверсификация экономики, модернизация экономики, малый и средний бизнес муниципальных образований, сырьевые регионы, «умные» технологии.
Introduction
In recent years, Russian and foreign scientists have been paying much attention to the issues of diversification and modernization of the economy. This is explained by the fact that, in general, the region’s economy largely depends on the state of basic industries, but at the same time, the highly specialized development of the territory makes the region’s budget dependent on the performance of regional and town-forming enterprises. The transition from a one-sided, often based only on the production of one or several products of the regional production structure, to multiproduct activity allows to increase the efficiency and sustainability of the regional economy and improve the environment (Pankova, Boris, 2012). In this regard, diversified regions, as shown by the results of Russian and foreign studies, generally turn out to be more stable and competitive in comparison with narrow focus specialized regions.
Small and medium-sized businesses have a significant impact on the development of the economy of administrative-territorial entities and the improvement of their social indicators, which characterizes the level of living standards. At the same time, the activities of small and medium-sized enterprises, the specialization of which is focused on activities that are significantly different from the specialization of large-scale enterprises, is one of the main possible factors for diversification and modernization of the economy of these municipalities.
Within the study of a project carried out with the financial support of the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, the issues of introducing “smart” technologies into the functioning of modern administrative-territorial formations of raw material regions are considered. The use of such technologies helps to facilitate the interaction of the population with the authorities and, thereby, leads to an increase in the living standards of these entities. Municipal formations of commodity regions, which are monotowns to a greater extent, have specific features of functioning that influence the development of the entire region.
Currently, the scope of the problems studied in this area is extensive and is devoted to various aspects of the development, testing, and implementation of “smart” technologies in the activities of municipalities and the population living in them. The authors presented the results of the study of the implementation of the “Smart City” project in previous works. Some works were devoted to studying the possibilities and prospects of implementing the “Smart City” project in Russia in the context of such a strategic indicator as the quality of life (Zubareva, Kuramshina, 2018), the others studied the diversification of the economy of commodity regions in the paradigm the concept of “Smart City” to improve the living standards, including the possibilities of digitalization (Zubareva, Kuramshina, 2019). However, measuring the scale of the digital economy is complicated by the difficulty of determining its boundaries, the lack of reliable data, pricing problems, and the “invisibility” of most types of digital economic activity. Scientists Rumana B., Richard H. claim that “the digital economy, according to our definition, makes up about 5% of the global GDP and covers about 3% of the world labor market” (Rumana, Richard, 2018). Moreover, in the face of increased international competition for technology, investment capital, highly skilled labor resources, a lot for developing countries will depend on their ability to provide a further influx of new knowledge and investments in their fast-growing high-tech industries (Ivanova, Mamedyarov, 2019). All this predetermined the objectives of the given research: to study, consider and analyze various aspects of small and medium-sized businesses of municipalities in commodity regions as one of the factors of diversification and modernization of the economy of these regions.
Theoretical framework
The study of the types and indicators of the activity of small and medium-sized enterprises of municipalities of raw material regions was carried out based on the official data of the Federal State Statistics Service. The indicators under consideration were the volume of shipped goods of own production, the share of certain types of activity, labor productivity index, and other individual indicators of activity of small enterprise business.
Methodology
The paper presents the results of the analysis and processing of official data and the conclusions obtained in previous studies through logic, using such statistical methods as analysis, synthesis, analogy, generalization, forecasting, hypothesis, as well as obtaining new data using empirical methods such as description, comparison.
Results and discussion
Firstly, it was revealed that small and medium-sized businesses have a significant impact on the development efficiency of both the country's economy as a whole and the economy of administrative-territorial entities, in particular. Small and medium-sized businesses concentrate mainly in the field of trade and the provision of various kinds of services in areas different from the specialization of large enterprises and have a relatively lower level of profitability. Currently, small and medium-sized businesses are facing an ever-increasing number of problems and challenges. Accordingly, its effective activity needs support from the state and requires the creation of special operating conditions. To a certain extent, such special operating conditions can be ensured during the implementation of “Smart City” projects.
The economy of commodity regions is more focused on large commodity business. The development of monotowns providing these enterprises with labor is also dependent on the large raw material business. The directions of development of such towns are related to providing the population with a decent standard of living, which facilitates the development of infrastructure for servicing the workers of these enterprises and the entire population. The use of the potential of small and medium-sized enterprises, which are sufficiently mobile and actively able to start operating in popular unoccupied "niches" of services, is one of the factors of diversification and modernization of the economy of commodity regions. Secondly, considering the production potential of enterprises of raw-material towns, it is worth noting the significant depreciation of fixed assets. This is also characteristic of many enterprises in the country. Using the potential of small and medium-sized businesses in the “Smart City” project paradigm will strengthen the economy of these regions and improve the quality of life of the population. Thus, the diversification and modernization of the economy of commodity regions is possible and largely depends on the production and other types of activities of small and medium-sized enterprises.
Diversification of the regional economy is understood as the burden-sharing of the development of the cyclical nature of the regional economic system related to the situation, specific resources, geopolitical, infrastructural conditions for the functioning of the socio-economic system of the region. According to the typology of the regions, Kofanov A.A. classifies raw materials regions as regions with moderate, excessive, and critical specialization (2011).
In general, the concept of “diversification” of the economy is based on the opinion that the production of goods (goods, works, and services) is not concentrated, but scattered across various types of activities. At the same time, sustainable socio-economic development of both regions and the country as a whole involves the use of opportunities that are available when diversifying territorial entities of different levels. It makes sense to assess how the situation is developing in Russia as a whole. Currently, the opposite situation is observed in the country's economy - production and sales of products are concentrated in individual segments, which is supported by the data in Table 1.
Table 1.
Shipped goods of own production, performed works and services on their own by type of economic activity in the Russian Federation in 2016.
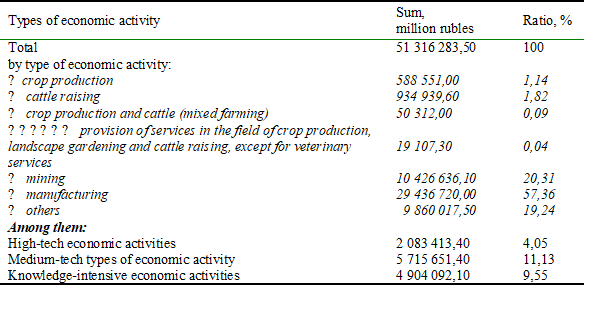
As you know, the concentration of production even at the level of one enterprise gives effects only until optimal sizes are reached, and then, as a rule, they decrease. One of the consequences of concentration may be monopolization. These processes are closely interrelated. Although there is a close relationship between diversification and concentration of production, it is also associated with the simultaneous development of heterogeneous industries. In the course of diversification at the macro level, diverse types of economic activity appear and develop, which gives positively directed results, which include obtaining synergistic effects. Besides, there are other positive factors aimed at success.
Studies have shown that diversification can reduce the dynamics of the development of economic security risks in a country and a region. Diversification involves both the full use of resources and the most complete leveling of risks. Diversification is also an instrument of the antitrust policy of the state.
According to the data presented by the Federal State Statistics Service (Table 1), the largest ratio in the output of products (works, services) is made up of manufactured products (food production, including drinks, and tobacco). Metallurgical products and the manufacture of finished metal products also hold a large ratio. Mining takes second place. All other industries are very poorly represented in this rating. The result of data analysis shows the concentration of activity in individual sectors and the lack of diversification. In addition, there are low indicators in high-tech, high- and medium-tech types of economic activity. Moreover, the share of innovative goods (works, services) in the economy as a whole is 8.5% (The official website of the Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved from: https://www.gks.ru/folder/11189 - date of treatment .09.12.2019).
As studies show, the main goals of diversification in the economy of the region and its business entities include increasing the competitiveness of the region; business risk reduction; increase in profitability; growth of companies’ number in the region, improving living standards in the region (Pankova, Boris, 2012).
The incentives for regional diversification and modernization are increasing transaction costs in the market, increasing the efficiency of internal use of resources, creating an effective internal system of capital investment and capital flow (Momotova, Vorontsova, 2011), improving socio-economic indicators of the condition and development of the region.
As a tool to ensure the competitiveness of problematic regions of Russia, along with maintaining traditional priorities, diversification contributes to the formation of a new framework structure of the regional economy through the creation of cluster groups, faster growth of small and medium enterprises, and the creation of various development institutions in the region based on public-private partnerships. Moreover, diversification can have a positive impact on most of the basic parameters characterizing the competitiveness of regions (Dolgikh, 2013).
As has been demonstrated globally, in modern competitive conditions of world development, diversification is impossible without modernization of the economy. Modernization can be effective if it is carried out mainly through democratic mechanisms and institutions, that is, the modernization of the economy is associated with the use of scientific and technological progress, the use of modern “smart” technologies, and the adoption of “smart” decisions (Ivanovskiy, 2011). In his Presidential Address to the Federal Assembly on November 12, 2009, D.A. Medvedev proclaimed a course towards the modernization of Russia: “... Russia's well-being in the relatively near future will directly depend on our successes in developing the market of ideas, inventions, discoveries, on the ability of the state and society to find and encourage talented and critically minded people, educate young people in the spirit of intellectual freedom and civic engagement”.
At the same time, as the main goal, D. Medvedev noted the reorientation of the Russian economy to the real needs of people (Presidential Address to the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation. RTQUESTION MORE. Retrieved from: https://www.rt.com/russia/medvedev-annual-address-full/#1), which are related to ensuring security, improving health, access to energy, and information. This determines the choice of strategic areas of modernization - development of medicine, energy industry, information science, nuclear, space, and telecommunication technologies.
The need for a comprehensive review and implementation of modernization processes is also substantiated by scientists A. A. Belykh and Mau V.A. in their studies. They note that “at all stages of the country's development, priority was given to national policy and the system of public administration. Political and military factors (priorities) almost always dominated the economy. Cost-effectiveness issues usually receded into the background. For the reforms to be successful, their basis must be the interconnection of economic and political transformations. This means recognizing the need for an integrated approach to modernization” (Belykh, Mau, 2020: 41). The process of modernization contributes to a significant increase in all economic indicators.
The ability of the economy to improve its basic characteristics, i.e. to increase its efficiency, is connected with the growth of such key basic system indicators as energy and resource efficiency, and, undoubtedly, labor productivity. Introducing modern technologies in the economy of the administrative-territorial entities and improving its basic indicators mentioned above, increasing the share of innovative products, using modern organizational and economic methods in management, creating conditions for activating the main processes are hot topics in modernizing the economy of administrative-territorial entities and the most important condition for creating a competitive economy within the country as a whole.
High-tech types of economic activity include such industries as the production of pharmaceutical products, office equipment, andcomputers, electronic components, apparatus for radio, television and communications, medical devices; measuring instruments, control, management, and testing; optical instruments, photo and film equipment; watches, aircraft, including space. Medium-tech activities include such activities as chemical production (excluding the production of gunpowder and explosives); production of machinery and equipment (excluding the production of weapons and ammunition); the production of electrical machinery and equipment, automobiles, trailers and semi-trailers, railway rolling stock, motorcycles and bicycles, other vehicles and equipment not included in other groups. High-tech industries include activity in the field of telecommunications, and the field associated with the use of computer technology and information technology; research, and development.
Undoubtedly, sustainable socio-economic development involves the diversification of the economy as a whole and, in particular, of its sectoral structural elements. Today, the value of many indicators listed is not very high. This is confirmed by the data of the Federal State Statistics Service.
Table 2.
The Share of individual activities in the Russian Federation by type of economic activity for 2011-2016.
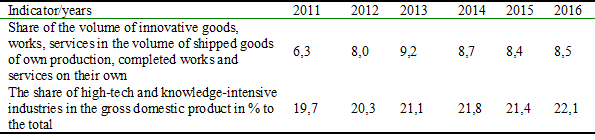
According to the data in Table 2, the share of the volume of both innovative products and products of high-tech and high-tech industries in recent years, although insignificantly, tends to increase.
Let’s consider the labor productivity index for the economy of the region as a whole, which, according to the Federal State Statistics Service, is calculated as the quotient of the division of the physical volume indices of GRP and the change in total labor costs. Table 3 shows that the change in levels has a negative tendency in decreasing in Russia in general, and in the Tyumen region in particular.
Table 3.
Labor productivity index for 2010-2017, %
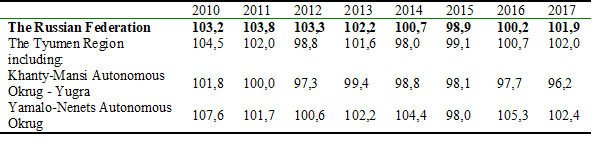
Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug are raw material regions. But in these regions, which are associated more with the production of products in the fuel and energy complex, a decrease in labor productivity is also observed.
As the governor of Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug-Yugra, Natalia Komarova noted in her annual report on the results of the Government of the Autonomous Okrug, “the oil industry is the core of the economy of Russia and Yugra. The forecasts of leading energy agencies and companies agree on the main point: even in the most difficult-to-implement scenarios, the level of demand for hydrocarbons will be higher by 2040 than today. The medium-term growth potential of the industry is estimated by independent experts at 2 percentage points of the country's GDP. About 60% of the residual recoverable oil reserves of Russia are concentrated in the West Siberian oil and gas province” (Annual report of the Governor of Yugra on the results of the government of Autonomous Okrug and appeal to residents, deputies and members of the public, 2016).
This fact suggests that the region lives off oil revenues. In the case of unfavorable development, in case of reduction or even production go-off, lower energy prices, etc., the economy may “collapse”. Therefore, it is necessary to diversify the economic sector in this raw material region. Small and medium enterprises will help to develop non-primary industries. So, in the territory of Surgut, there is a great number of enterprises in the service sector - medical, educational, social, etc.
As the governor also noted in a previously noted document, small and medium-sized businesses make a significant contribution to the development of the labor market. Table 4 presents the data on the turnover of medium-sized organizations by constituent entities of the Russian Federation. So, in the Tyumen region in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug this indicator increased by 53% in 2016 compared to 2015, although in Russia as a whole the growth is lower - 43%. Currently, in a pandemic, indicators, as economists predict, will decrease significantly, since the quarantine regime has more affected the activities of small and medium-sized enterprises.
In 2018, the entrepreneurs of Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug created 3200 permanent workplaces, 400 new small enterprises were formed. To maintain positive dynamics in this direction, it was decided to extend the reduced rates for small businesses using a simplified tax system. “In 2018, every fourth ruble of the consolidated budget was directed to support industries. These are investments in jobs, in the localization of strategic competencies in Yugra. The list of government support measures has been expanded, easy loans have been introduced on the conditions of federal-regional co-financing for projects that increase the level of localization of final Russian products” (Annual report of the Governor of Yugra on the results of the government of Autonomous Okrug and appeal to residents, deputies and members of the public, 2018).
Among the new industrial enterprises of Yugra, there is the Chinese holding “Hilong” in Surgut, which created a plant for applying a protective polymer coating to the inner surface of oil assortment pipes. The company “Epik 380” opened a plant for the production of pumping units for hydraulic fracturing in Izluchinsk. The company “Baker Hughes” opened a plant for the production of electric centrifugal pump units for the mechanized extraction of mineral resources in Nizhnevartovsk. According to investors, the digital technologies that will be used in the production of plants will increase the efficiency of oil and gas field development (Panova, 2018).
In addition, to diversify the economy of Yugra, the launch of significant projects was approved. Among them are the metalworking complex of “Severstal”, “Yashel Park Sibir”, specializing in the processing of industrial waste; production and logistics industrial park "Yugra", focused on the production of goods and equipment for energy companies.
Let’s consider the indicators of goods shipped by medium-sized organizations by type of economic activity (Table 4).
Table 4.
Shipped goods of own production, performed works and services on their own (excluding VAT, excise taxes and similar obligatory payments) by average organizations by type of economic activity in the Russian Federation, in current prices, billion rubles.
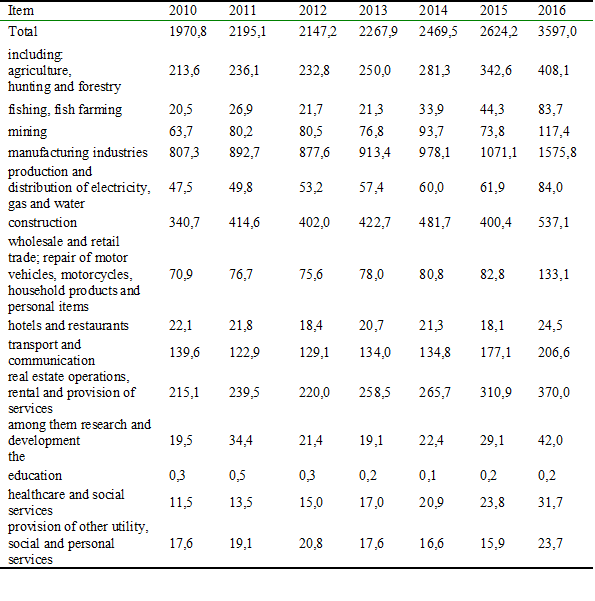
In 2016, the largest share is medium-sized enterprises operating in the field of manufacturing and construction. At the same time, the same specificity is observed in the economy as a whole.
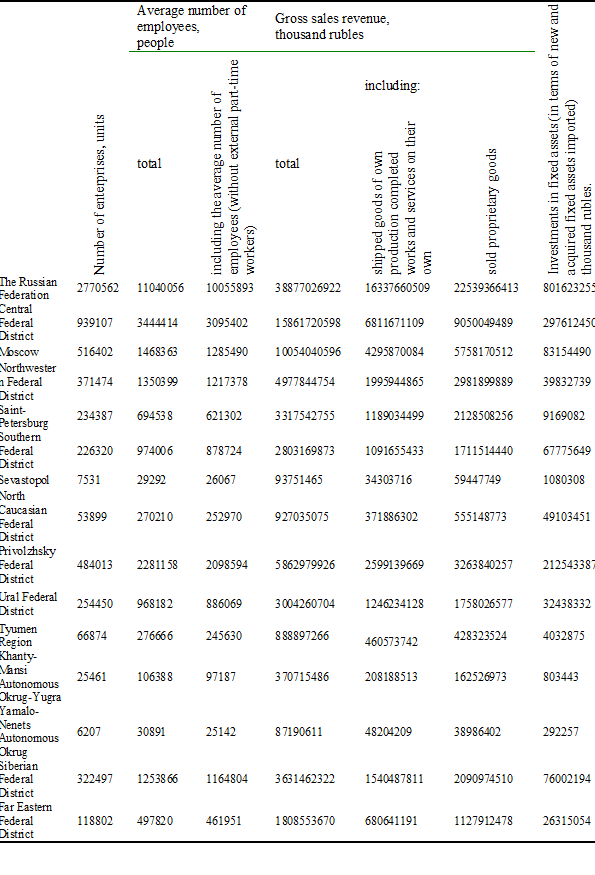
Considering the activities of small enterprises in Russia, it is possible to admit their differentiation by regions according to the official data presented in Table 5. These indicators also include the results of microenterprises.
In general, the traditional distribution by regions is observed. The data in Table 5 make it possible to state that the largest share of small businesses is concentrated in the Central Federal District as a whole, and Moscow in particular. An insignificant number of small businesses is in Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug and Sevastopol. The same specificity of distributions observed in other indicators.
Table 5.
Performance indicators of small enterprises by constituent entities of the Russian Federation for 2016.
The gross sales revenue of products (services) of small businesses, including the activities of micro-enterprises, and individual entrepreneurs by regions in dynamics over 2013-2016, is presented in Table 6.
The data makes it possible to state that the structure remained unchanged, although there was an overall increase in value indicator.
Table 6.
The gross sales revenue of products (services) produced by small enterprises at current prices, thousand rubles.
 produced by small enterprises at current prices, thousand rubles..png)
Speaking about the modernization of the economy, it is worth paying attention to the indicators characterizing the renewal of fixed capital. Table 7 presents the indicators of the investment volume in fixed assets by regions of the country.
Table 7.
The investment volume in fixed assets (excluding budgetary funds), thousand rubles.
, thousand rubles..png)
The data presented in Table 7 shows that the tendencies as a whole by the regions remain traditional. So, the Central Federal District leads the list of regions by the volume of investments in fixed assets as well as in small businesses (Table 5. Investments in fixed assets). The last position is the North Caucasian Federal District.
Considering the activities of small businesses, it is important to study its distribution by type of activity shown in Table 8, also including the activities of microenterprises.
According to the Federal State Statistics Service (The official website of the Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved from: https://gks.ru/free_doc/new_site/business/inst-preob/tab-mal_pr_m.htm- appeal date. 12/09/2019), it can be stated that small enterprises by type of activity are also concentrated in specific industries, and the potential of these enterprises differs somewhat from the potential of medium and large business organizations. The same tendency is observed in other indicators. In particular, the number of enterprises of small businesses is concentrated in wholesale and retail trade, provision of services in the metallurgical industry, production of coke, and petroleum products. This makes it possible to assume that the possibility of diversification, the use of the potential of the areas of activity of small and medium-sized businesses, the use of the existing potential of small and medium-sized businesses, and the digitalization of areas of activity will increase the efficiency of the economy.
As the study of statistical data shows, activation of small and medium-sized enterprises, the creation of conditions for its development, is a significant source of development and the economy of the whole country in general. Moreover, to accelerate the growth rate of labor productivity, it is necessary not only to increase the number of small and medium enterprises, but also to create conditions for their active growth, in particular, to ensure the availability of opportunities (favorable business climate) and incentives for it (competition), and overcoming regional, institutional and financial restrictions - a necessary measure to create an environment that would be favorable for the growth of new enterprises (Bessonova, et al., 2020: 98).
It is also worth noting that the role of a competitive procedure in Russia is small. This is reflected, firstly, in the low role of the redistribution of market shares (overflow of labor resources) from less to more productive companies in the decomposition of aggregate labor productivity and, secondly, the explanatory ability of productivity factors to increase the sales of firms is very small (Savin, et al., 2020: 121).
However, this is of particular relevance for monotowns and, in particular, for raw-material towns. The current situation in the municipalities of raw materials orientation is another incentive for diversification and modernization of the economy of these regions. Perhaps small and medium-sized businesses can be one of the sources of such transformations. But this activity today is associated with many problems resulting in the occurrence of entrepreneurial risks. Some economists, speaking of commodity regions, note that, as a whole, in these regions, there are monotowns that are the legacy of the Soviet economy. They account for about 40% of the total GRP of the Russian Federation. From 1095 towns of Russia, about 440 meet the criteria of a monotown (data as of the end of the 1990s) (Abramova, Pechenina, 2009).
In the development zone, which occupies the northern and eastern territories of the Russian Federation, most monotowns are located, specializing in primary processing of raw materials: Surgut, Nizhnevartovsk in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, Novy Urengoy in Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Usinsk in the Republic of Komi, etc.
Zemtsov S.P., Chernov A.V. in their research (Zemtsov, Chernov, 2019) note that “in Russia, in the context of low economic growth rates and low investment activity, the opportunities for non-resource-based growth are largely determined by access to foreign markets and increased government participation. Structural policies will require efforts to expand the presence of Russian companies in international markets, as well as stimulate entrepreneurism in large corporations by creating corporate venture capital funds, identifying divisions for promising products, buying startups, supporting research and development costs, and improving management skills. Particular attention should be paid to the building up of fast-growing technological startups, including the formation of intellectual property markets and entrepreneurial ecosystems in the regions” (Zemtsov, Chernov, 2019: 90).
As the study of statistical data shows, the activation of small and medium-sized enterprises and individual entrepreneurs positively affects the development of regions and municipalities, since taxation of small and medium-sized businesses in the form of special taxation regimes, on the one hand, is a form of support for small and medium-sized businesses, on the other hand, it is one of the tax sources of local budgets. Therefore, the directions for the development of their activities should be a priority when developing a strategy for the development of municipalities, since to some extent the flow of funds of municipalities depends on their quantity and development.
Modern economic and political discussions and problems are focused on two factors: technological trends leading to a radical and rapid renewal of all aspects of society, as well as the socioeconomic and political discomfort generated by them for various social groups (Mau, 2020: 6). At the same time, the development of small and medium-sized businesses can be closely related to the development of “smart” technologies, with lean manufacturing to ensure the development of the economy of regions, towns, and to provide services to large enterprises in terms of the development of digital technologies.
It is interesting to study fast-growing firms. In their development unlike other small and medium-sized enterprises, they rely on domestic technologies and solutions, including their development. Therefore, for the successful development of dynamic companies, state support for Research and Technological Development is of great importance. The state support is related to the creation of new production technologies, including those implemented by companies for their needs. However, while measures for reducing barriers to exports are relevant for ordinary exporters, such measures are not enough for fast-growing companies; promotion of the respective brands in the target markets, stimulation of their recognition and trust in them, and support for regular technological updates are also required (Kuzyk, et al., 2020).
The socio-economic development of municipalities in the northern territories largely depends, as was noted, on the activities of large town-forming companies, specializing mainly in raw materials. In the given paper a town-forming company is defined as an industrial facility, whose work is crucial in the field of employment, affects social problems and their solution largely determines the condition and development of town’s infrastructure (Town-forming company: significance, development. Retrieved from: https://fb.ru/article/223737/gradoobrazuyuschee-predpriyatie-znachenie-razvitie). But the presence of a town-forming enterprise on the territory of a municipality, as studies show, often leads to the emergence of various kinds of problems. The solution to these problems can be taken up by small and medium-sized enterprises due to greater mobility, shortening the time needed to resolve various issues that arise, etc. In recent years, professional managers and managers of these territories have begun to pay attention to these enterprises and their support. They associate the prospects for the development of such cities with the massive development of medium and small enterprises. The list of town-forming companies of the Russian Federation was adopted by the Russian government. It included industrial facilities, whose activities are important for the welfare of the vast majority of the population in certain settlements. The list of town-forming enterprises included: OJSC “Altai-кoks”, JSC “Karabashmed”, JSC “SUEK-Kuzbass”, PJSC “MMC “Norilsk Nickel”, PJSC “KAMAZ”, LLC “Zharkovsky DOK”, OJSC “Rosugol”, OJSC “Mechel” and others (Town-forming company: significance, development. Retrieved from: https://fb.ru/article/223737/gradoobrazuyuschee-predpriyatie-znachenie-razvitie).
In recent years, there has been a transfer of administrative resources of northern town-forming enterprises from northern cities to large cities in the European part of Russia. And this leads to the emergence of a “niche” previouslyoccupied by these enterprises. Therefore, one of the areas of economic development of the territory within which the town-forming company operates may be the revival and (or) reorientation of industrial facilities. If a settlement has a certain kind of resources, sufficiently large but unused production capacities, then it is possible to form a practically new production base on this basis. However, inefficient activities of representatives of government bodies, or influential groups of territories, corruption activities in the personal interests can lead to the squandering of available resources. Examples of this are easy to find in the open information space. In this regard, the joint activity of the local administration and entrepreneurs based on, for example, public-private partnerships is of great importance for the development of promising sectors. The government regulation of these relations also serves these purposes.
For the financial support of monotowns, several options for their support can be distinguished. One of the main ones is government funding. Such support should be carried out in two directions. First of all, it is necessary to provide the city-forming enterprise with the necessary means to develop production itself, expand activities and solve problems in the field of employment of the urban population, and secondly, it is necessary to support the budgets of settlements to maintain the proper list and level of services, developing entrepreneurship (Pankova, Boris, 2012).
The implementation of the tasks mentioned above is ensured, as is known, including through the implementation of state programs. These programs provide an opportunity for town-forming enterprises to take advantage of subsidies that offset part of the cost of paying interest on loans. Besides, enterprises can take advantage of tax deferrals for investment loans and regional fees. The state acts as a guarantor for loans. Financial support for the budgets of settlements is reduced to the following measures: providing additional funds in the process of allocating state loans to the subjects of the Russian Federation from federal funds and subsidies for balancing the budget sphere of the region, and developing public-private partnerships. An example is the implementation of regional investment projects at the expense of the federal fund in the form of subsidies for co-financing capital construction projects of state-owned facilities. Another area is the provision of funds for the implementation of additional programs aimed at reducing tension in the regional labor market, and for the development of medium and small enterprises, including farms. An example is also an additional program aimed at developing and supporting the world of work, which involves training, retraining, internships, and increasing the mobility of citizens to solve employment problems in the territory. The state program provides for the stimulation of the resettlement of residents from problem areas in the event of the transfer or liquidation of a town-forming enterprise.
An important direction is the restructuring, reprofiling and modernization of the production activities of a town-forming enterprise transferred to another city with the use of its material and technical base, as well as stimulating demand for manufactured products by establishing a priority for these enterprises during the placement of municipal, regional, federal-state orders with the rest equal with all conditions.
To improve the infrastructure of a settlement under additional programs, measures are currently being taken to eliminate dilapidated and emergency housing, major repairs of worn-out housing stocks, modernization and reconstruction of utilities, treatment, and water intake facilities, energy and heat supply facilities are underway. Additional development programs also include the introduction of energy-saving technologies in housing and communal services and the manufacturing sector (Town-forming company: significance, development. Retrieved from: https://fb.ru/article/223737/gradoobrazuyuschee-predpriyatie-znachenie-razvitie).
Support for the development of small innovative enterprises is also taking place through the provision of grants to small and medium-sized businesses for the development, creation, and production of innovative products, as well as for research and development, including in the field of sports development, urban environment, ecology, social entrepreneurship. Additional programs are also aimed at organizing the digital eco-space of towns and settlements by uniting the most developed marketing platforms, educational, and information platforms through a unified system of identification and authentication.
The popularization of the activities and significance of entrepreneurship is also the direction of entrepreneurship development achieved through a federal information campaign, including promoting the image of an entrepreneur on the Internet and social networks, as well as relevant regional and municipal campaigns.
Conclusions
Thus, to diversify and modernize the economy of commodity regions, it is necessary to create conditions for the activation of many areas of activity. This will allow small and medium-sized enterprises to develop. Entrepreneurship is one of the engines of such transformations, which will speed and strengthen the development efficiency of this process.
The article attempts to identify prospects for maintaining the feasibility of doing business for small and medium-sized enterprises in the towns of these regions and maintaining the attractiveness of these towns for population living. The authors draw the attention to the fact that such towns are located mainly in areas of adverse environmental conditions away from large industrial and cultural centers and in many cases depend on the performance of one or two large town-forming companies. As measures to preserve this attractiveness, the authors suggest the possibility of diversifying and modernizing the economy of these towns. This can be achieved by supporting the activities and development of small and medium enterprises, as well as implementing measures aimed at introducing the technologies of the Smart City concept.
It was revealed that to diversify and modernize the economy of the resource regions, it is necessary to create conditions for the activation of many areas of activity. It can be achieved, in particular, through the implementation of “Smart City” projects in these regions. This will stimulate the process of activating the most technologically advanced and innovative areas of activity and will have a positive impact on the development of small and medium-sized enterprises involved in these areas.
At the same time, the use of “smart” technologies for making “smart” decisions, including in the process of modernizing the urban economy, will increase both the efficiency of functioning of small and medium-sized enterprises and the mechanisms for supporting their activities and development.

