Self-Learning Skills and Problem-Based Learning in Medical Education: Case Study
Habilidades de autoaprendizaje y aprendizaje basado en problemas en educación médica: estudio de caso
Abstract
The present research aims to explore the impact of “problem-based learning” on “self-learning skills” of students in the College of Medicine, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University. We use analytical descriptive method and applied the scale of “self-learning skills” on the study sample including 114 students from Medicine College divided into two groups. The first group is consisted of 63 students from third and fourth levels who are taught through problem-based learning. The second group is comprised of 51 students from fifth and sixth levels who are taught through traditional methods. The results of the study have showed that statistically significant differences are found between the both groups and put problem-based learning is found superior over the traditional one. Moreover, we find that the effect degree of strategy on the self-learning skills is varied. The effects are found strong on skill-development of information management and implementation of learning strategies. While, moderate impacts are found on Attitude Towards Learning (ATL), Learning Responsibility )LR(, Motivation and Self-confidence (MS), ability to Plan Learning (PL), ability to Use Learning Opportunities (ULO), Assessment of Learning Process (ALP) and evaluation of learning of success/results.
keywords
Self-Learning Skills, Learning in Medical Education, research skills, ability to MI, evaluation of learning success
Resumen
La presente investigación tiene como objetivo explorar el impacto del "aprendizaje basado en problemas" en las "habilidades de autoaprendizaje" de los estudiantes de la Facultad de Medicina de la Universidad Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz. Utilizamos un método analítico descriptivo y aplicamos la escala de "habilidades de autoaprendizaje" en la muestra del estudio, incluidos 114 estudiantes de la Facultad de Medicina divididos en dos grupos. El primer grupo está formado por 63 estudiantes de tercer y cuarto nivel a quienes se les enseña a través de una nueva estrategia de enseñanza como el aprendizaje basado en problemas. El segundo grupo está compuesto por 51 estudiantes de quinto y sexto nivel a quienes se les enseña a través de métodos tradicionales. Los resultados del estudio han demostrado que se encuentran diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre ambos grupos y que el aprendizaje basado en problemas es superior al tradicional. Además, encontramos que el grado de efecto de la estrategia en las habilidades de autoaprendizaje es variado. Los efectos se encuentran fuertes en el desarrollo de habilidades de gestión de la información y la implementación de estrategias de aprendizaje. Mientras, se encuentran impactos moderados en Actitud hacia el aprendizaje (ATL), Responsabilidad del aprendizaje) LR (, Motivación y autoconfianza (MS), capacidad de planificar el aprendizaje (PL), capacidad de utilizar las oportunidades de aprendizaje (ULO), Evaluación del proceso de aprendizaje (ALP) y evaluación del aprendizaje del éxito / resultados.
Palabras clave
Habilidades de autoaprendizaje, Aprendizaje en educación médica, habilidades de investigación, capacidad para MI, ALP, evaluación del éxito del aprendizaje
Introduction
The higher educational institutes and the universities are facing many challenges now-a-days which are due to rapid developments of communication and information technology. There is a need to activate the strategies through which the learning opportunities can be maximized for the future generations to enrich the professional skills for the requirement of 21st Century. The problem-based learning is counted to be one of the modern strategies emerging during the recent past years and is adopted by the modern world (Ayyildiza and Tarhan, 2015). The proponents of this approach believe that through the application of this model, a set of goals and balanced competencies can be achieved. In addition, the students can acquire information and cognitive outcomes in addition to many non-cognitive outcomes such as skills of effective communication, self-learning and life-long learning, critical thinking, innovative thinking and problem solving (Barr and Tag, 1995).
Recently, the interest in the development of non-cognitive outputs has considerably been increased to float the relevant educational policies. The literature has indicated that the success of graduates in meeting their personal needs, in their working life and achieve the requirements of the labor market does not depend solely on the cognitive skills. Rather, the success also depends on the non-cognitive competencies (GOI (Government of India), 2016a; Cheng, 2016; Garcia, 2014).
Problem Statement
The development of educational practices is initiated in the College of Medicine, Prince Sattam Bin Abduaziz University during the academic year 2017-2018 to apply the problem-based learning as a teaching strategy. This aims to achieve a set of objectives and outcomes which includes providing the students with competencies and non-cognitive skills which are necessary for a successful medical doctor in the 21st century. These are the most important self-learning skills which have become one of the most important learning outcomes identified by prestigious medical education institutions such as the General Medical Council (GMC) and the academic accreditation institutions as well. But, some studies have shown that there is no complete agreement on the effectiveness of problem-based learning in the development of self-learning skills as it is not the only or always a better way to develop those skills (Strobel and Barneveld, 2009). Frambach et al. (2012) argued that the expected outcomes and effectiveness of problem-based learning and their impact on the development of self-learning skills are varied across the cultures and the extent to which teachers and students are aware of the difference between the modern strategy and traditional education tactics. Premkumar et al. (2018) investigated the influence and the role of the prevailing culture in both teachers and students in developing the self-learning skills. They found that there was a difference between the students in the Middle East to apply modern strategies from Asian students and European students. The European students were found more receptive to apply the modern strategies.
Considering the above arguments, the present study attempts to discover the impact of the application of the problem-based learning on the development of self-learning skills of medical students at Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University in Saudi Arabia.
Research Questions
- Are there significant differences between the group who have studied using problem-based learning and their peers in the second group who have studied using the traditional model of self-learning skills i.e. (Attitude Towards Learning (ATL), Learning Responsibility )LR(, Motivation and Self-confidence (MS), ability to Plan Learning (PL), ability to Use Learning Opportunities (ULO), Assessment of Learning Process (ALP) and evaluation of learning of success/results and total self-learning skills scale?
- Is the impact of problem-based learning on the development of self-learning skills significant among the students of College of Medicine at Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University for above mentioned skills?
We aim at to discover that whether there are significant differences between the mean of students who studied using problem-based learning and the students who studied through traditional model in the self-learning skills scale, we try to discover the effect of problem-based learning on the students of College of Medicine at Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University in acquiring the self-learning skills mentioned above in the research question 1.
Further, we also aim at to find the impact of PBL on the development of non-cognitive outcomes including self-learning skills which is one of the important objective of educational systems and higher educational institutions in this modern era. It is thought to be that the results of the current study would draw the attention for an effective educational process in medical education. These would also be helpful to aware the requirements of development of prevailing culture among the beneficiaries of the development process i.e. students, faculty and parents/guardians. We may train the teachers to serve the propose as they may play a great role in the success of any attempt to achieve the development. The present study is first study, to the best of our knowledge, which is aimed at to discover the impact of problem-based learning on the development of self-learning skills in the medical institute of Saudi Arabia.
Literature Review
Self-Directed Learning (SDL)
Recently, many researchers are interested in assessing the success or capacity of institutions and the strategies to enrich the students to acquire the non-cognitive outcomes or the so-called soft skills or the skills of 21st century. These skills are expected to raise the ability to communicate, critical thinking, innovative thinking, decision-making, self-learning, problem solving, work effectively with teams, self-control, self-management in addition to cognitive skills (Garcia, 2014). Self-Directed Learning where learners are expected to do planning, implementing and evaluating and worked independently or in teams as well to achieve the pre-determined objectives learning (Williamson, 2007). The SDL is defined as a person initiatives to analyze learning-need, frame learning-goal, recognizing resources, learning from other or their materials, selecting and applying suitable learning tactics and assessing learning outcome (Silong, et al 1998; Knowles, 1975).
SDL skills are gaining the special importance in the adult education and in the higher educational institutions. It enhances the learner’s skills to plan and to manage the learning activities to get the knowledge and information and to acquire the specific skills (Abubakar& Arshad 2015). It is considered as one of the requirements of adaptation to the cognitive explosion in the age of rapidly changing technology and it also enhance the ability to acquire the lifelong learning. The SDL is emerged as one of the most important Outcomes of medical education as it is a fundamental requirement for the continuous professional development of a medical doctor. It is an ability to keep up with modernity, continuous development, to solve the problems of patients and to improve their conditions. This has been asserted by many health and medical associations at international level like the General Medical Council (GMC), and the Associations of Academic Accreditation (Shokar et al., 2002). In 2015, the World Federation of Medical Education (WFME) announced continuous professional development standards to improve the quality of medical education (World Federation of Medical Education, 2015).
The publications of the National Center for Academic Accreditation and Assessment also demonstrate that the efficiencies of graduates of medical colleges to lifelong learning is one of the main out comes of the programs offered by any medical colleges in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. It also included a frame of reference for students' competencies in medical education defined by the National Center for Academic Assessment and Accreditation (2017). Therefore, many institutes of medical education are seeking to apply the teaching strategies and approaches which can contribute to the development of medical education. Several medical colleges have implemented the problem-based learning approach. Many studies are also aimed at to discover the most important factors which may have the impact on self-learning. These can also be helpful to measure and detrmine the skills that should be possessed by the learner who is able to practice the process of self-learning. The ability to lifelong learning through the scales of self-learning skills is also becoming the need of this modern age. The important scales of self-learning are provided by Knowles (1975), Guglielmino (1977), Candy (1991), in addition to the scales of Ayyildiz and Tarhan (2017) which are the focus of this present study.
Problem-Based Learning (PBL)
PBL is a student-centered approach which is resulted from the engagement of the students during the work in order to understand the problems and their solution. It starts once a teacher is presenting a real problem and the students should practice without any prior information (Barrows and Tamblyn, 1980). It requires the small groups of students to define the problem, to identify the ideas and information involved in the problem, to develop the hypotheses or to suggest the possible solutions to the problem through identifying the educational needs i.e. what should be learned to solve the problem (learning topics) and through development of an action plan to reach a solution. It can also be applied to explain the causes of the problem and to reach the solution (Barrett et al., 2005).
Some scholars considered the PBL as a complete strategy learning (Maudsley 1999; Barrett et al., 2005). The PBL consists of four main components which are philosophy, planning & designing, teaching and evaluation. The theoretical foundations of PBL are derived from the modern learning theories like cognitive school and the constructivist school. PBL emphasizes that learning is an active mental process that utilizes the prior experiences of a learner and also develops the connection between the prior information and new information in building and formulating the new hypotheses or the theories. It also connects the facts and theoretical information with the practical dimensions in order to acquire a deep understanding about a concept. The social foundations can also be shown in PBL when peers in the groups collaborate to build knowledge. Thus, it comes into existence as a result of learners' procedures or actions.
PBL is consistent with the modern approaches in building the curriculums to adopt the real problems as the basis for learning process on the one hand and adopting the principles of learning based on the outcomes on the other hand. Where PBL, the planning process starts with identifying big ideas of the knowledge, skills, values (Toohey, 1999) to formulate the outcomes in the form of interesting and professional problems which may challenge the students' minds and motivate them to learn the desired outcomes. This step is one of the most important standards to judge the success of PBL and this is also considered as one of the most important challenges faced by the processes to implement the strategies. The curriculum revolves around a set of core problems (Boud & Feletti, 2017) as the problem is the basic starting point and may represent as the driving force for the learning process. It also directed towards a point which differentiates between the strategies of PBL and the method of learning through problem-solving. The important characteristics of PBL includes that the problem or case is starting point, realistic or simulates reality, integrated and deals with various aspects problem solving needs integrated knowledges of different subjects. In PBL, students play the main role in the learning process; Where they are responsible for determining the problem, knowledge they need, analyzing the existing ideas in the context, and developing an action plan to solve it.
In this context, Dolmans (1994) explained that PBL describes that Faculty goals are decoded into a problem. Then, students examine the problems in understanding the fundamental ideologies. In the same context, Hmelo-Silver (2007) argued that Problem-based learning earns students self-learning skills with objectives of erecting elastic knowledge, evolving operative problems-solving abilities, emerging life-long knowledge skills.
Despite the facts, the researchers are agreed on the merits of PBL. However, there are several challenges in which the most important are the lack of learning resources, the weakness in teachers’ training and the lack of researches which may examine the nature of problems that can be presented to learners. In addition to, confusion between learning through problem-solving and PBL (Boud and Feletti, 2013). "The type of prevalent culture in the educational community either they believe that it is teacher-centered education or student-centered learning and the role of teachers in guiding students to implement the new strategy, accomplish the tasks assigned them and achieve the desired goals" (Premkumar et al., 2018; Barrows and Tamblyn, 1980).
Methodology
Population and Sample
The population includes all students of College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University. The sample is consisted of 114 students during the academic year 2019-2020.
Method and Procedures
The development of educational practices is initiated in the College of Medicine, Prince Sattam Bin Abduaziz University during the academic year 2017-2018 , where applied the problem-based learning as a new teaching strategy, to discover the impact of new strategy on self-learning skills of the students, the present study uses the analytical descriptive method. It applies the scale of “self-learning skills” in the end of second semester of academic year 2019-2020 on the sample of study in order to discover the differences between the two groups of the study. The first group (63 students) using “problem-based learning” and consisted of the students of third and fourth level. Whereas, the second group (51 students) studied using the traditional method and included the students of fifth and sixth level. The results were analyzed in the light of relevant literatures and studies.
Tools of the Study
The present study used the Self-Learning Skills Scale of Tarhan and Yyildiz (2015) because of its modernity and its reliance on the previous self- learning scales that are popularly and largely used in the recent literature (Aydede and Keserciog˘lu, 2009; Fisher et al., 2001; Guglielmino, 1977; Williamson, 2007). Using this scale, we address the deficiencies that have been emerged in those scales including the lack of inclusion of all dimensions and skills of self-learning. The scale consists of forty questions distributed on eight dimensions as shown in table 1. uses a five-point Likert scale (1= Strongly Disagree, 2=Disagree, 3=Partially Agree, 4=Agree, 5=Strongly Agree). The total scores range from 40 (least-ready for SDL) to 200 (most-ready). To ensure that this scale is appropriate for application in Arab students in Saudi Arabia, we conducted a pilot study on a sample of 35 students from the study population to calculate the validity and reliability of the test.
Statistical Methods
We utlize the SPSS 24 to calculate the mean, standard deviation, Pearson correlation coefficients for validity of internal consistency, coefficients of Cronbach's alpha for reliability,independent samples t-test for the significant differences between the experimental and control groups and Cohen equation (1988) for the two independent samples to measure the effectiveness of strategy used.
Data Analyses
Validity and Internal Consistency of Tool
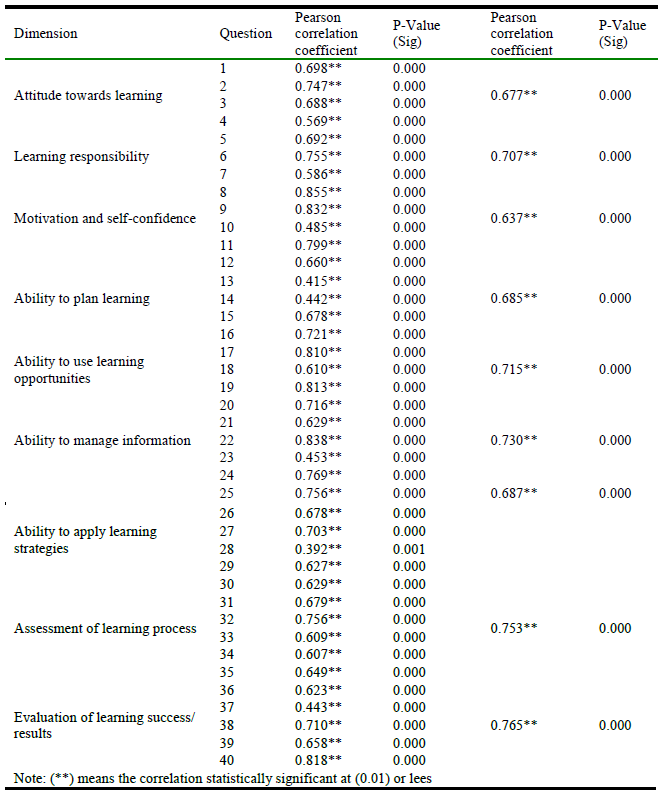
We calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient between each statement and its construct. To know the validity and internal consistency of the tool, the questionnaire was designed and correlation coefficients are showing reasonable magnitudes and statistical significancy to proceed, in table 1.
It should be noted that the current study adhered to the same dimensions of Tarhan and Yyildiz, 2015’s scale.
Table 1.
Pearson correlation coefficients between each statement and the total degree.
Statistical Reliability
Table 2.
Reliability coefficients Cronbach's alpha.
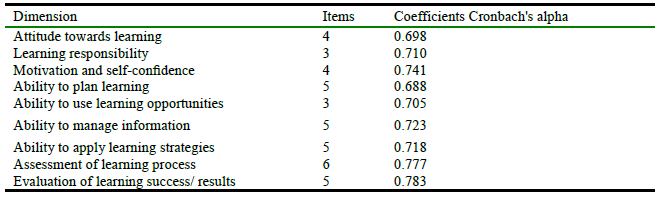
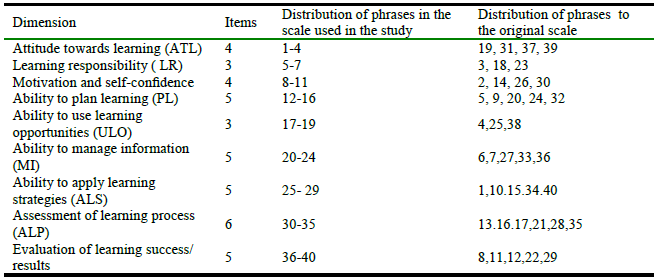
Table 2 showed that overall reliability coefficient is 0.885. It indicates that the tool is characterized by great stability and achieves the purposes of the study. Therefore, the further statistical analysis using these constructs are reliable After calculating the reliability and stability of the scale, the items of the scale (40) are distributed to each construct in table 3.
Table 3.
Distribution of ítems.
Results
At first, we test out first research question. Are there any statistically significant differences between the group who have studied using problem-based learning and their peers in the second group who have studied using the traditional method of self-learning skills i.e. ATL, MS, ability to PL, ability to ULO, research skills, ability to MI, ALP, evaluation of learning success/ results and total self-learning skills scale? The t-test for two independent samples is used to identify the significant tatistical differences between the mean scores of the experimental and control groups for the self-learning skills. The results are reported in table 4.
Table 4.
Results of independent samples t-test for the significant differences between the experimental and control groups.
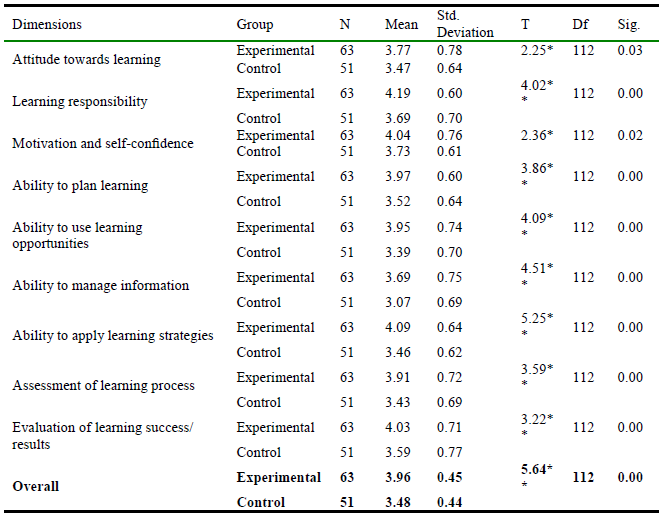
In the table 4, it is clear that statistical significance p-values are less than the level of significance of 5%. Therefore, results favor the mean of experimental group.
To answer the second question, the effect of using problem based learning on the development of Self-Learning Skills for medical student, the Cohen (1988) equation is used which is as follows:
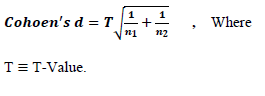
.PNG)
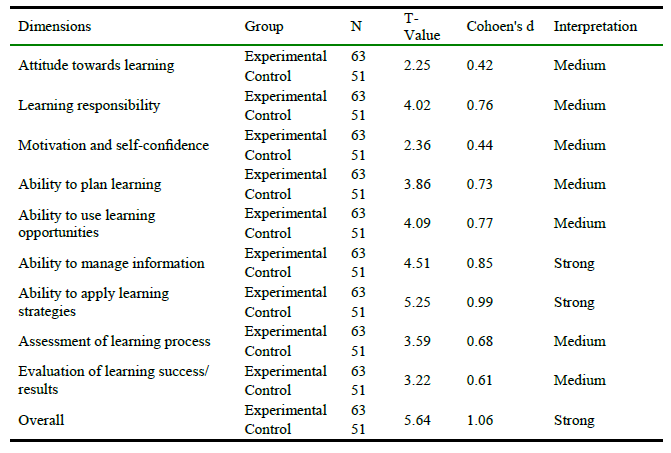
Where, if the calculated value of the effect size is 0.20, the effect size is weak. If the calculated value of the effect size is 0.50, the effect size is medium and if the calculated value of the effect size is 0.80 or more, the effect size is strong.
Table 5.
Results of Cohen equation.
Discussions
The results showed that the problem-based learning is important for the development of self-learning skills. Because, student would be responsible for identifying the gap and learning topics which need to be known and access to the facts and information associated with it. Through specifying the appropriate sources of learning. This is consistent with the results of several previous studies (Nerali et al., 2016; Leary, 2012; Bakr and Arshad, 2015).
There is a strong impact of problem-based learning on the development of self-learning skills. Further, the differences in the degree of impact on different skills are shown in table 4. The impact of using this strategy has been found strong for the development of information management skills and the skills of applying learning strategies. While, the results showed that a moderate impact on the ATL, MS, ability to PL, ability to ULO, research skills, ability to MI, ALP, evaluation of learning success/ results and total self-learning skills scale.
The moderate results may be claimed due to the recent application of the experience, the lack of awareness about the requirements of strategy application and the philosophy based different roles of both teacher and student and the lack of skills of faculty members which are necessary for the application of this strategy. Premkuma et al. (2018) and Frambach et al. (2012) asserted that the prevailing culture in the learning community and the development of faculty’s skills play a vital role in the application and success of modern strategies and changes. We believe that with time, increase of experience and culture prevalent would be completely different from the traditional one. Moreover, there will be less resistance to change that faculty and students may exhibit. The students in problem-based learning are responsible for the entire learning process from planning to evaluation of results. They are not accustomed to and it becomes a cause for a psychological burden on them. That reason has been indicated by a number of faculty members during their discussion in one of the professional development workshops held on the topic of problem-based learning. Moreover, Silen and Uhlin (2008) and Nerali et al. (2016) confirmed that PBL worked well once the students and faculty understand the factors which influence the changing role of a faculty member from that of a guru (sage on the stage).
Conclusions
The problem-based learning is important for the development of students' non-cognitive skills. Specially, it influences the self-learning skills which are consisted of taking responsibility for learning, planning for learning, applying its strategies and evaluating the learning process and its results. However, it is necessary to provide the environment with certain conditions which could help to implement it according to its basic principles which are preparing students, faculty and officials before starting the process of application. The efforts should also be initiated to educate and to train the both teachers and students about their new roles in order to achieve the desired goal. The prevailing culture and past experiences of the usual learning model have strong impacts on students and faculty to accept new models to make them effective.
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Recommendations and future directions
Based on our research, we feel that there should be more studies to discover the factors which are affecting the development of different self-learning skills ,We recommend conducting a study to reveal the students' perceptions about the problem-based learning in order to identify the most important features as well as the obstacles which may prevent the achievement of the desired goals. We also recommend realizing the importance of disseminating culture while developing programs and curriculums to increase the awareness of the beneficiaries about the developmental changes in the educational process and to make sure that faculty is having the necessary skills for its application.

