Digitalization of Higher Education and Professional Development of Educators: Technologies and New Opportunities
ABSTRACT
Nowadays, the development of the digital environment and the global network covers almost all spheres of life. That is why special attention is focused on the provision of the educational process with appropriate teaching aids and curricula, so that schools, universities, educators, and professional development of educators meet modern national and global challenges and provide support in the field of digital technologies, developing and shaping modern digital competencies. The article presents an analysis of digitalization in higher education and the necessity to improve the professional development of higher school educators and professional development technologies related to this process. Based on an expert survey, educational trends in the era of educational digitalization, innovative pedagogical technologies, and teaching methods are determined. The results of the survey, related to the introduction of new pedagogical and digital technologies in the educational process, allow the authors to design a model for the professional development of educators in the direction of the digital transformation of the educational process.
keyword
higher education, digitalization, educators, professional development, digital competence.
Introduction
The features of the modern development are caused by processes that emerged at the turn of the millennium and widely developed at the beginning of the 21st century. They include the transition to a knowledge economy and information society, as well as the strengthening of digitalization (digital transformation), which determine the economic and social type of the development of national and international economies, individual regions and cities. Neo-industrialization (reindustrialization), informatization, emergence of new technologies, and mobile automated high-tech industries have led to radical changes that continue to shape the economies of developed countries and have a significant impact on the formation and implementation of human capital (Tsvetkov et al., 2020; Danilina et al., 2020; Trubilin et al., 2020).
The concept of digitalization has become relevant in modern society. The study of the definition of digitalization and its derivatives proves that it has become relatively established in the scientific community and is associated with the large-scale penetration of information and communication technologies into the everyday life of modern society. This issue captured the scientific community very quickly and scholars have identified a large number of individual areas where its aspects are considered.
Thus, some issues related to the scientific understanding of this category, its structure and specific features caused by the rapid development of modern information and communication technologies are reflected in scientific developments (Banning, 2016; Olbert & Spengel, 2017; Gbadegeshin, 2019; Srai & Lorentz, 2019).
The enrichment of the real world with electronic digital devices, facilities, and systems and the establishment of electronic communication exchange between them leads to the digitalization of education as a component of the digitalization of society as a whole (Helsper & Eynon, 2010). To achieve the goal of digitalization, which is to achieve the digital transformation of existing and new sectors of the economy, as well as the transformation of life spheres into new, more efficient and modern ones, the education system should play an important role (Ugur, 2020).
The works (Bleiklie & Kogan, 2007; Neier & Zayer, 2015; Thompson et al., 2014) raise the issue of reforming and modernizing the existing higher education system in accordance with the challenges of the present time.
According to T.V. Nikulina, educational digitalization is its modernization, reformation, and transformation, as well as problem-solving and decision-making with the help of digital technologies (Nikulina & Starichenko, 2018). According to researchers, digital technologies should be implemented in all spheres of education, educator training, educational infrastructure, methodology (pedagogy), and teaching resources, as well as leadership and management at all levels and sectors of the education system (Fevolden & Tomte, 2015; Lipinsky et al., 2019; Dudin et al., 2019).
According to N.S. Ilyushenko, digital technologies provide an opportunity to intensify the educational process and increase the level and quality of perception, understanding, and assimilation of knowledge. With the help of media and interactive tools, it is easier for educators to use an approach based on the implementation of innovative approaches, including the use of cases, experimental and research work, and business games. As a result, students absorb information much better and form appropriate skills, being in an emotionally comfortable environment, do not lose the desire to learn, generate ideas, and create (Ilyushenko, 2019; Veselovsky et al., 2019).
According to I.V. Robert, digital technologies provide several new opportunities, both for educators and students. They include: pleasure from the fascinating process of communication and learning; automation of most of the teaching work, freeing up time for searching, communication, self-improvement, and individual work with students; providing feedback; correction of the individual development of future specialists; improvement of the management of the educational process and education in general (Robert, 2014).
D.K. Grigoryeva believes that the main areas of higher education digitalization in Russia should be:
− the creation of educational resources and digital platforms with support for interactive and multimedia content for the general access of higher education institutions and students, particularly, automation tools for the main processes of universities;
− development and implementation of innovative computer, multimedia, and computer-oriented teaching aids and equipment for creating a digital learning environment (multimedia classes, STEM research centers and laboratories, inclusive classes, blended learning classes);
− organization of free access to the Internet for students in classrooms;
− development of distance education, using cognitive and multimedia technologies (Grigoreva, 2019).
Digitalization of higher education requires the formation of an appropriate digital competence (DC) among students and, especially, educators. DC, according to researchers, is a broad and holistic concept that describes the skills associated with technology and covers much more than functional digital skills that need to be used in a digital society (Almerich et al., 2016; Melnichuk et al., 2020; Beciu et al., 2019). E. Elstad and C. Christofferson believe that DC is a set of academic and professional practices supported by diverse, ever-changing technologies (Elstad & Christophersen, 2017). V.I. Kolykhmatov understands DC as the use of computers to receive, evaluate, store, create, present, and exchange information, as well as to communicate and participate in joint virtual networks. It requires a critical and reflective attitude to available information and responsible use of interactive media (Kolykhmatov, 2018). I. Alvarez and his co-authors define DC of higher education educator as an opportunity to effectively and critically use information technology for training, self-development, and active participation in society (Alvarez et al., 2009).
In 2017, the EU introduced an updated framework of DC (Digital Competence – DigComp 2.1) (Carretero et al., 2017), which consists of five main blocks of competencies (Table 1).
Table 1. Components of DC.

According to researchers, DC of educators includes several skills that can be grouped into seven elements:
− media literacy – the ability to critically perceive and creatively rethink academic and professional communications in various media;
− information literacy – the ability to find, interpret, evaluate, manage, and share information;
− ICT literacy – the ability to accept, adapt, and use digital devices, applications, and services;
− communication and cooperation – the ability to use digital networks for training and research;
− digital scholarships – participation in new academic, professional, and research practices that are based on digital systems;
− learning skills – the ability to learn effectively in formal and informal technology-rich environments;
− career and management style – the ability to manage digital reputation and identification on the Internet (Gudmundsdottir & Hatlevik, 2018).
N.N. Kondasheva points out that the identification of ways to increase DC of higher education educators is relevant in relation to the process of transformation of modern education. This transformation happens because of the rapid development of technology, intellectualization of labor, increased social mobility, etc. At the same time, according to the researcher, university professors are not always fully aware of the difference between the modern generation and previous generations of youth. A significant distance of the digital generation in possession of modern tools is a challenge to the digital society and educational digitalization, which must be considered both in the organization of the educational process and professional development of educators and educational leaders (Kondrasheva, 2017).
The topical issue of developing DC of educators is not called into question in the pedagogical community. Researchers describe the following challenges posed by historicism of the contemporary moment on this issue:
1. The role of the university educator is important because they contribute to the formation of future specialists in digital society.
2. The level of formation of DC of an educator determines the quality of higher education and the level of readiness of a university graduate to live in a digital society.
3. The system for assessing the level of formation of the educator's DC is important because of its motivational and developing role.
4. The system of advanced training for university professors should include familiarization with trends, technologies, and ICT tools that are relevant for students and educators of a modern university (Aimaletdinov et al., 2019).
The subject of this article is the study of the awareness of university professors about educational trends, innovative pedagogical technologies, and digital tools and their desire to improve their skills to predict the development of their DC in the modern digital society.
Research hypothesis: The development of the model of professional development of scientific and pedagogical university workers is possible based on the study of an educator’s level of awareness about the use of ICT in professional pedagogical activities and personally recognized needs for increasing DC.
According to the results of the study, it can be concluded that the subject set in the study was achieved.
Methods
The study used the following research methods to implement the research goals:
− analysis and generalization of theoretical provisions to determine the state of research on the digitalization of higher education;
− expert survey method to determine educational trends in the era of educational digitalization, and innovative pedagogical technologies and methods. Thirty-four experts took part in the expert online survey – university professors with more than 15 years of experience;
− questionnaire method – a survey of educators and students on the introduction of new pedagogical and digital technologies in the educational process. The survey involved 56 university professors and 160 students. The survey proposed questions related to the understanding of educational trends and their relevance for use in the educational process of a particular university. It revealed the personal attitude of educators to innovative pedagogical technologies and methods and their vision of the need for their use at the university, as well as clarified the level of importance of relevant innovative technologies for students. Thus, we clarified the attitude of educators to the components of DC and determined the need for educators and students to master the skills of digital tools in groups.
Results
According to the experts, considering the rapid changes in society, the requirements for educators are constantly updated and educators need new, more complex sets of competencies. The spread of digital devices and their popularity among students lead to the need to develop the educator’s own DC.
A prerequisite for surveying educators was their familiarization with educational trends.
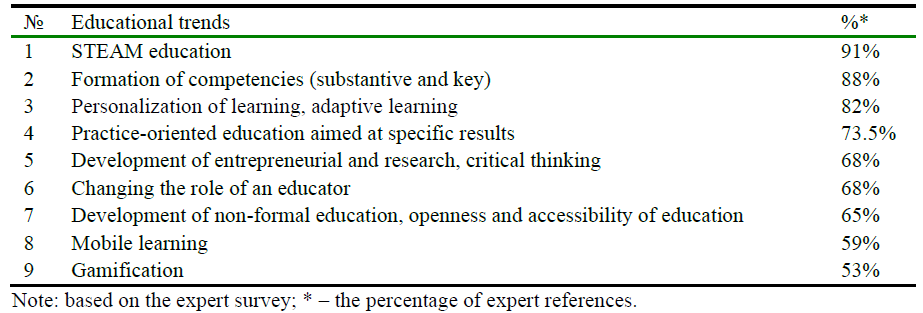
Using the online expert survey, nine trends were identified: STEAM education (Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, Mathematics); formation of competencies (substantive and key); personalization of learning, adaptive learning; practice-oriented education aimed at specific results; development of entrepreneurial, research, and critical thinking; gamification – learning through playing; development of non-formal education, openness and accessibility of education; mobile learning (use of mobile smart devices for training); changing role of the educator (Table 2).
Table 2. Educational trends.
The results of assessing the relevance of educational trends (1 – the least relevant, 9 – the most relevant) are presented in Table 3.
Table 3. Educational trends assessment results.
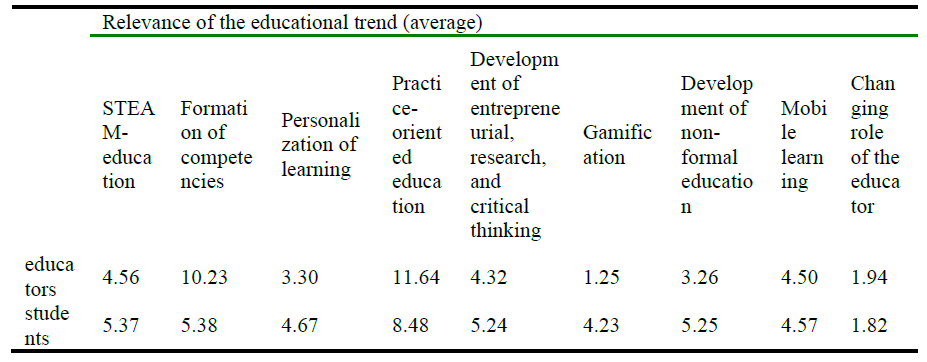
The results demonstrate a gap in interest, understanding, and considering certain trends by educators and students in their professional activities. Thus, the positions of STEAM-education, mobile learning, and gamification are of more interest to students. For educators, the most relevant trends are the formation of competencies, practice-oriented training, and development of entrepreneurial, research, and critical thinking.
This means that for the development of DC of educators, it is expedient to include in the professional development programs topics that will provide educational trends and methods of their implementation in the educational process. These trends will be a priority for educators and students.
According to the highlighted educational trends, innovative pedagogical technologies and methods were identified based on the expert survey, the use of which will make it possible to follow modern requirements for the digital transformation of education (Table 4).
Table 4. Innovative pedagogical technologies and methods.
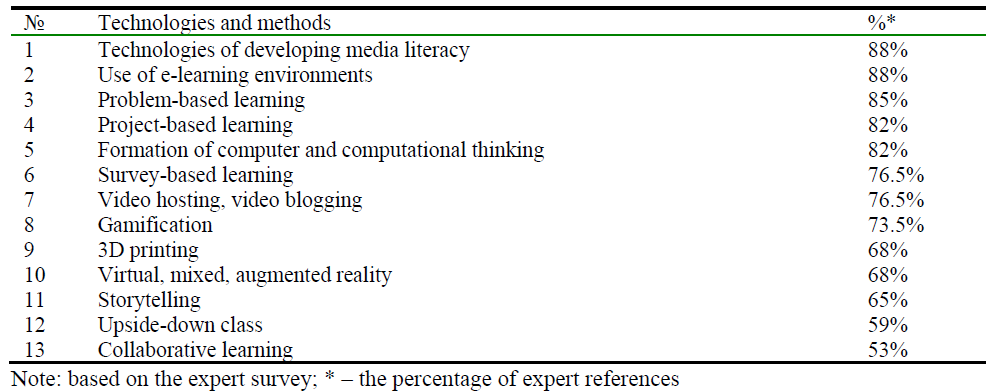
The respondents were asked to score on a 10-point scale (1 –unimportant, 10 – important), the necessity to implement and use innovative pedagogical technologies and methods in universities.
It appeared that for educators, the most relevant technologies and methods were: competence formation (media literacy), practice-oriented learning, and development of entrepreneurial, research, and critical thinking. In particular, the research demonstrated a significant gap between the interest of students and educators in the following innovative pedagogical technologies: collaborative learning, upside-down class, storytelling, and virtual, mixed, and augmented reality.
The research results allow to formulate recommendations to the system of improvement of professional skills of educators: first of all, it is necessary to consider features of the organization of practice-oriented training which lies at the heart of STEAM-education, with use of elements of gamification, design technique, and problem training at the courses.
For the implementation of the specified innovative pedagogical technologies and methods in the educational process, it is expedient to train educators to develop skills of using digital tools. For this purpose, the questionnaire contained questions related to the assessment of the importance of digital tools for use in professional activities.
The analysis of the research results showed that both educators and students were interested in mastering digital tools and using them effectively in the educational process. The digital tools were grouped for their intended purpose. The respondents were to give each tool one of the following levels of relevance: 1 – low; 2 – medium; 3 – high. The survey results are presented in the percentage ratio (Table 5).
Table 5. Level of interest in digital tools
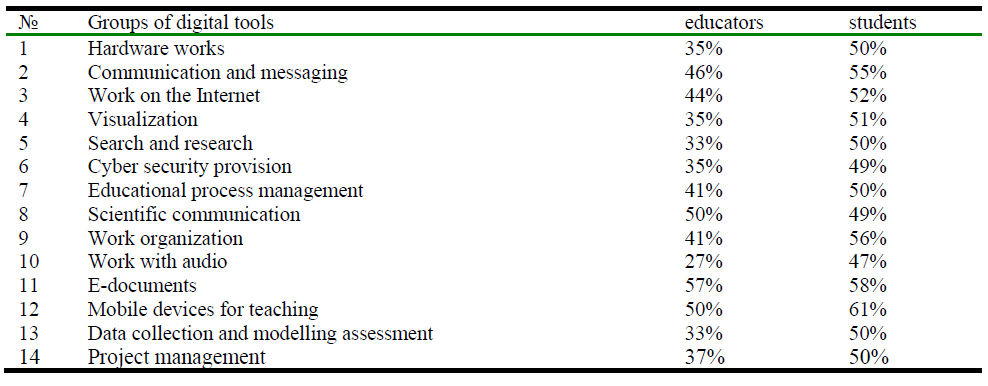
The high level of interest for both groups is shown in Table 5. The results show that students were more interested in using digital tools than educators. It is obvious that students need to use the presented resources in the educational process. In particular, the most relevant for them is the use of mobile devices for obtaining digital content, communication, discussion, and assessment. Educators, in turn, were more interested in mastering the tools for working with electronic documents, which indicates their readiness for the transition to electronic document management and, possibly, for the creation or modernization of electronic content. The low percentage of educators' interest in digital tools for search and research, organization of work, and work with audio also attracts attention.
Thus, the system of professional development of educators should include the study of electronic documents, tools for scientific communication, communication and messaging, learning management, and work organization, as well as focus on demonstrating the capabilities of mobile devices in the educational process.
Discussion
Based on the conducted research, it is possible to design the following model of professional development of educators in the direction of the digital transformation of the educational process (Table 6).
Table 6. Professional development model for DC development.
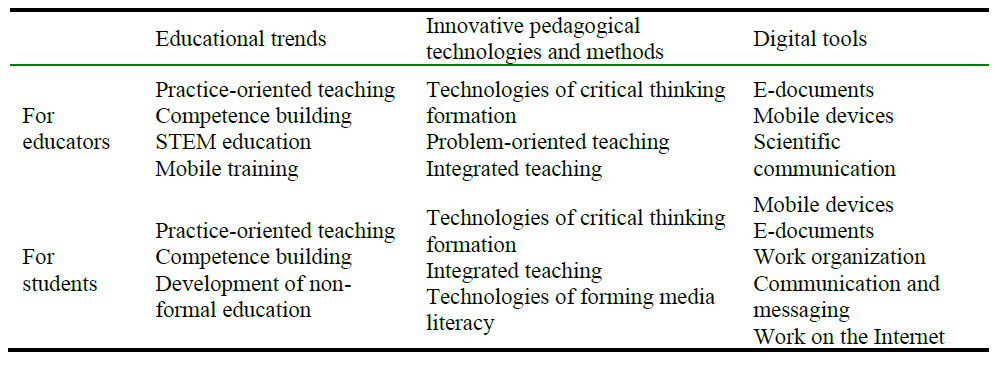
In general, the system of professional development of educators should be based on the use of information technologies and innovative methods and approaches. The use of technology by educators in the educational process allows them to involve the student in this process and provide the necessary skills to create new knowledge using technologies.
The results of the study can serve as a guide for the preparation of professional development programs for university professors.
Besides, the experts saw the following ways to improve DC:
1. Promotion and popularization of educational trends and innovative pedagogical technologies and methods as effective components of the modern educational process by demonstrating examples and results of their practical application;
2. Involvement of students in creating and performing tasks using digital tools;
3. Introduction of a system of seminars and workshops on the use of digital tools for grouped tasks;
4. University leaders may provide a system of incentives for educators who enhance their DC and implement innovative teaching technologies and methods that encourage students to use digital tools effectively in the educational process.
According to the experts, university management can create an enabling environment for the acquisition of skills in the use of digital tools, in particular for the Internet, e-documents, visualization, organizing and conducting research, use of mobile devices for learning, communication, and messaging, scientific communication, and cooperation in the educational process.
Based on the expert survey, an indicative list of training courses for educators is proposed (Table 7), based on which the ICT skills development module can be introduced and educators can be involved in the training according to their level of DC.
Table 7. Indicative list of workshops and training sessions that will contribute to the DC of educators.

Conclusions
The digitalization of all sectors of the economy and the introduction of digital technologies into all spheres of life offer unrivalled opportunities for economic development and, as a result, improvement in the quality of life.
DC is essential for the development of higher education, as digital technologies provide new opportunities to improve the quality of teaching, learning, scientific research, and organizational management. Investing in the digital skills of students and staff brings individual and organizational benefits, such as providing quality education in flexible and innovative forms that meet the expectations and needs of students, improving employment opportunities through awareness of aspects of the digital economy, and building organizational capacity to maximize the return on investment in learning technology.
To increase DC of university professors, it is necessary to transform approaches to the organization of the educational process in such a way that the educator has the opportunity to develop those skills that are, on the one hand, relevant for their professional development and, on the other hand, demanded by students.
The results of the study confirmed the hypothesis that it is possible to design a model of professional development of a university's scientific and pedagogical staff based on a study of educators' awareness of the use of ICT in professional pedagogical activities and their conscious need to improve DC.

